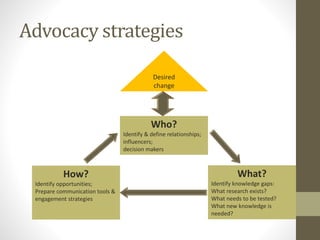
The document discusses educational equity and social justice, emphasizing the importance of special education for children with disabilities and exceptional abilities. It outlines the philosophical foundation, objectives, and ultimate goal of special education, stressing the need for integration and dignity for all learners. Additionally, it explores the role of education in promoting social justice and equity in society, and highlights advocacy strategies for influencing educational policies.














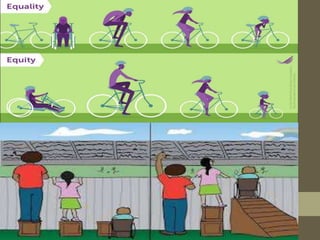



![Social justice education
The goal of social justice education is full and equal
participation of all groups in society that is mutually
shaped to meet their needs.
A prominent social justice education theorist,
Lee Ann Bell (1997) puts it:
“… [S]ocial justice education is both a process and a goal. Social
justice includes a vision of society in which the distribution of
resources is equitable and all members are physically and
psychologically safe and secure. We envision a society in which
individuals are both self-determining
(able to develop their full capacities) and interdependent (capable of
interacting democratically with others).”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/educationalequitysocialjustice-240706041859-32405e9d/85/EDUCATIONAL-EQUITY-SOCIAL-JUSTICE-pptx-19-320.jpg)