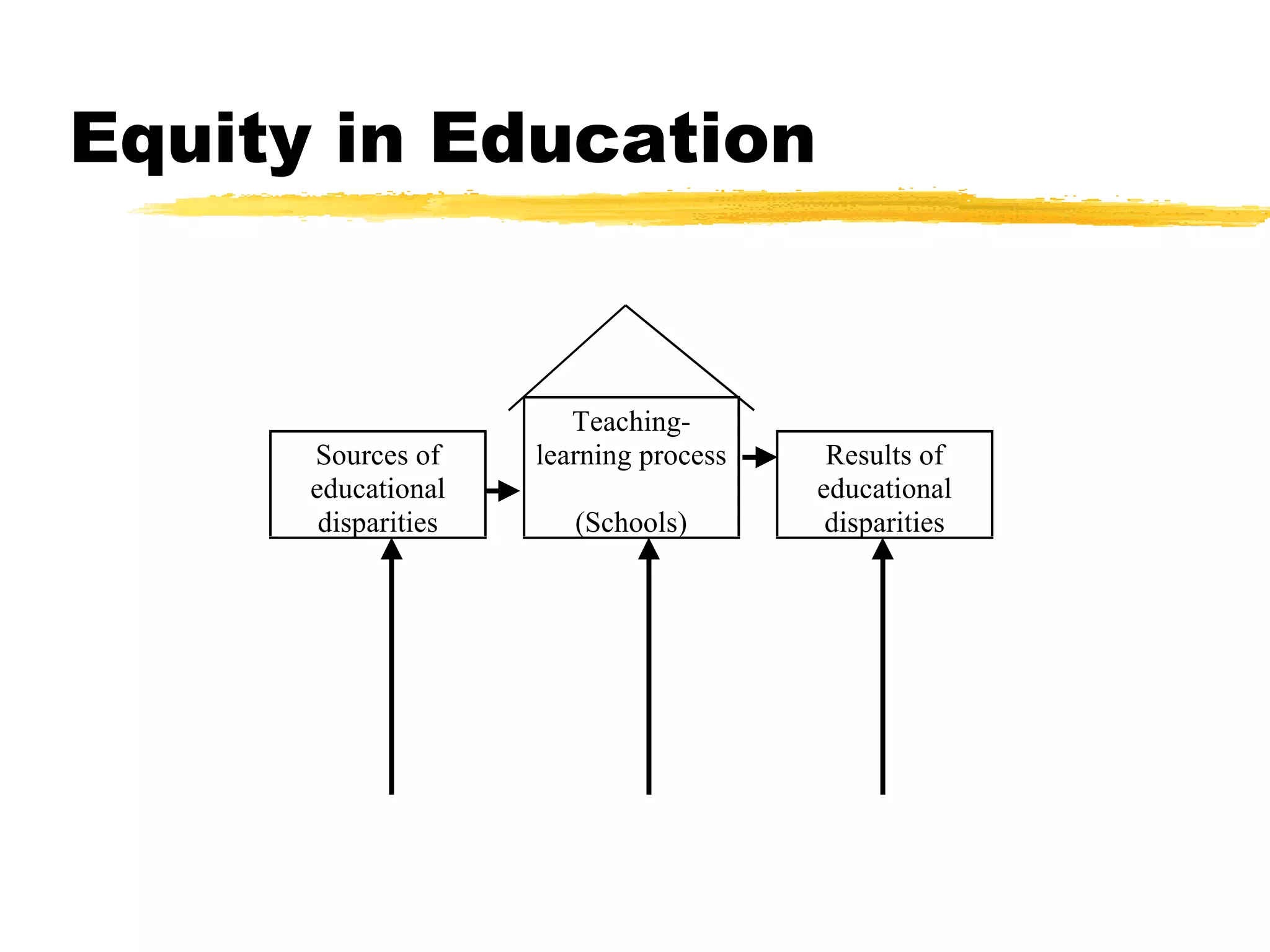
The document discusses equity in education and outlines key points regarding policy implications. It identifies different perspectives on educational policies and reasons for promoting equity, such as strengthening social cohesion and reducing costs. It then discusses dimensions of educational disadvantage, signs of selectivity in education systems, and ways policy can promote equitable, quality education for all students. The document proposes "transition compatible" policy tools to monitor achievement, target resources, and support schools serving disadvantaged students.