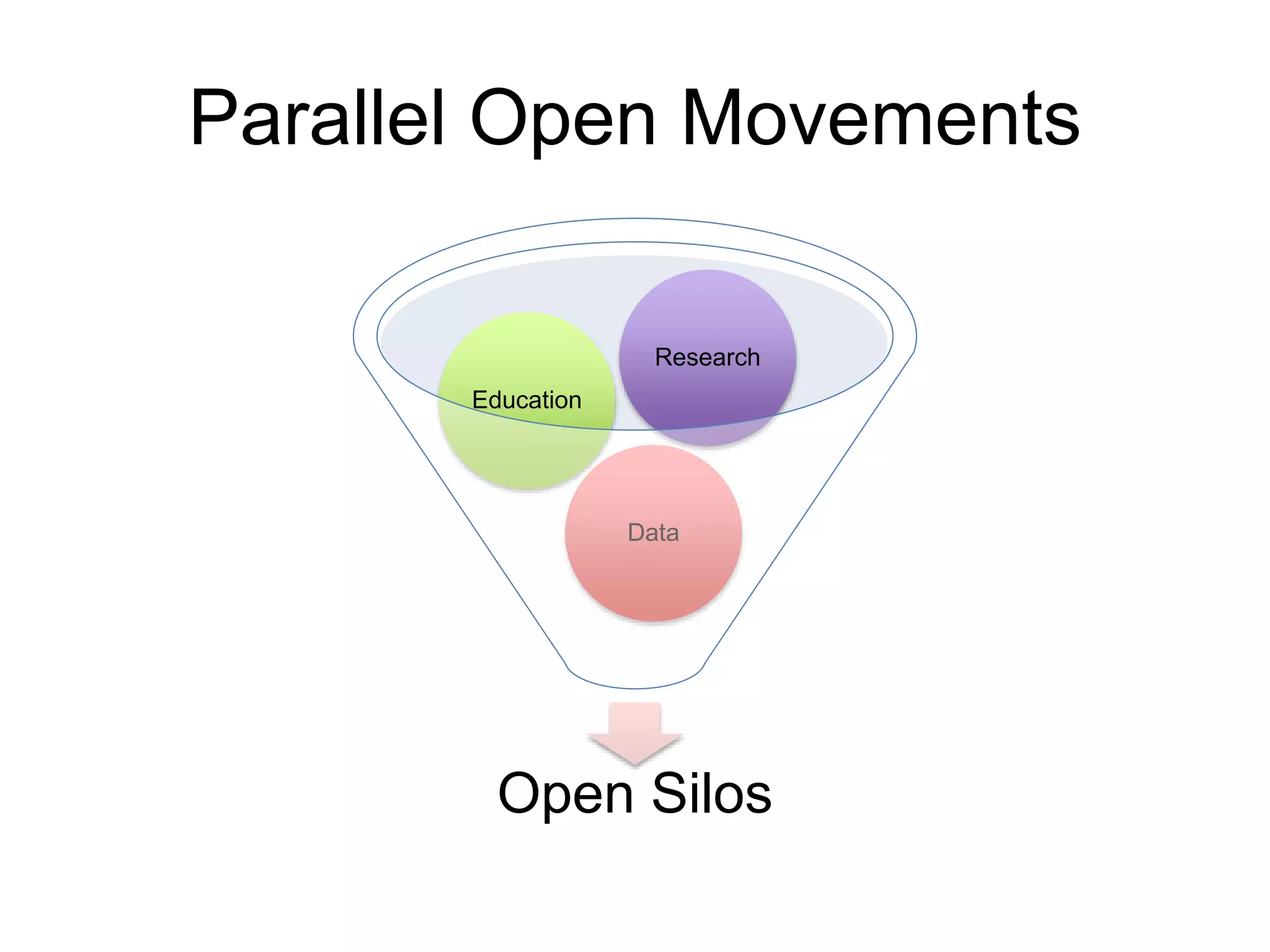
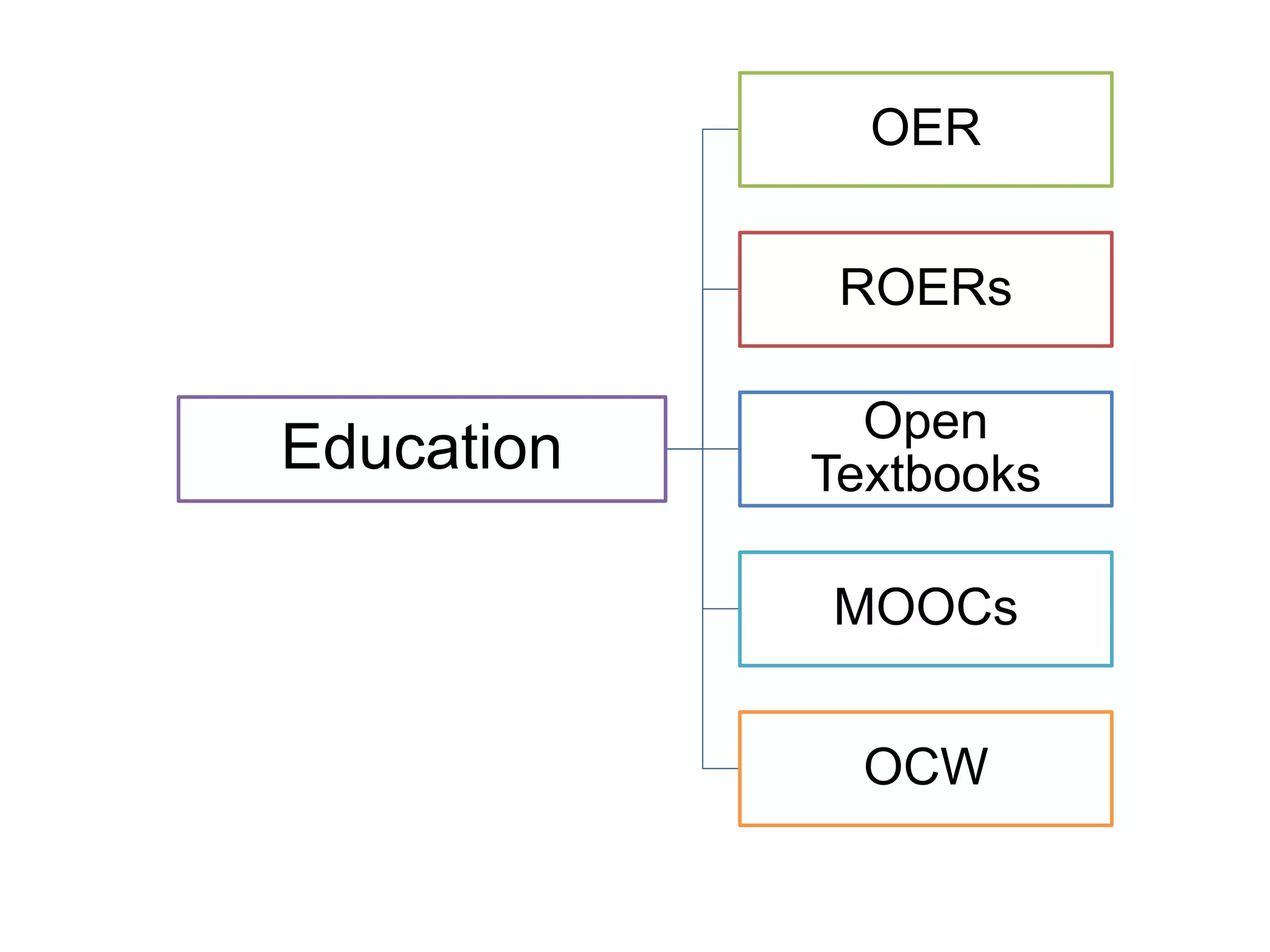
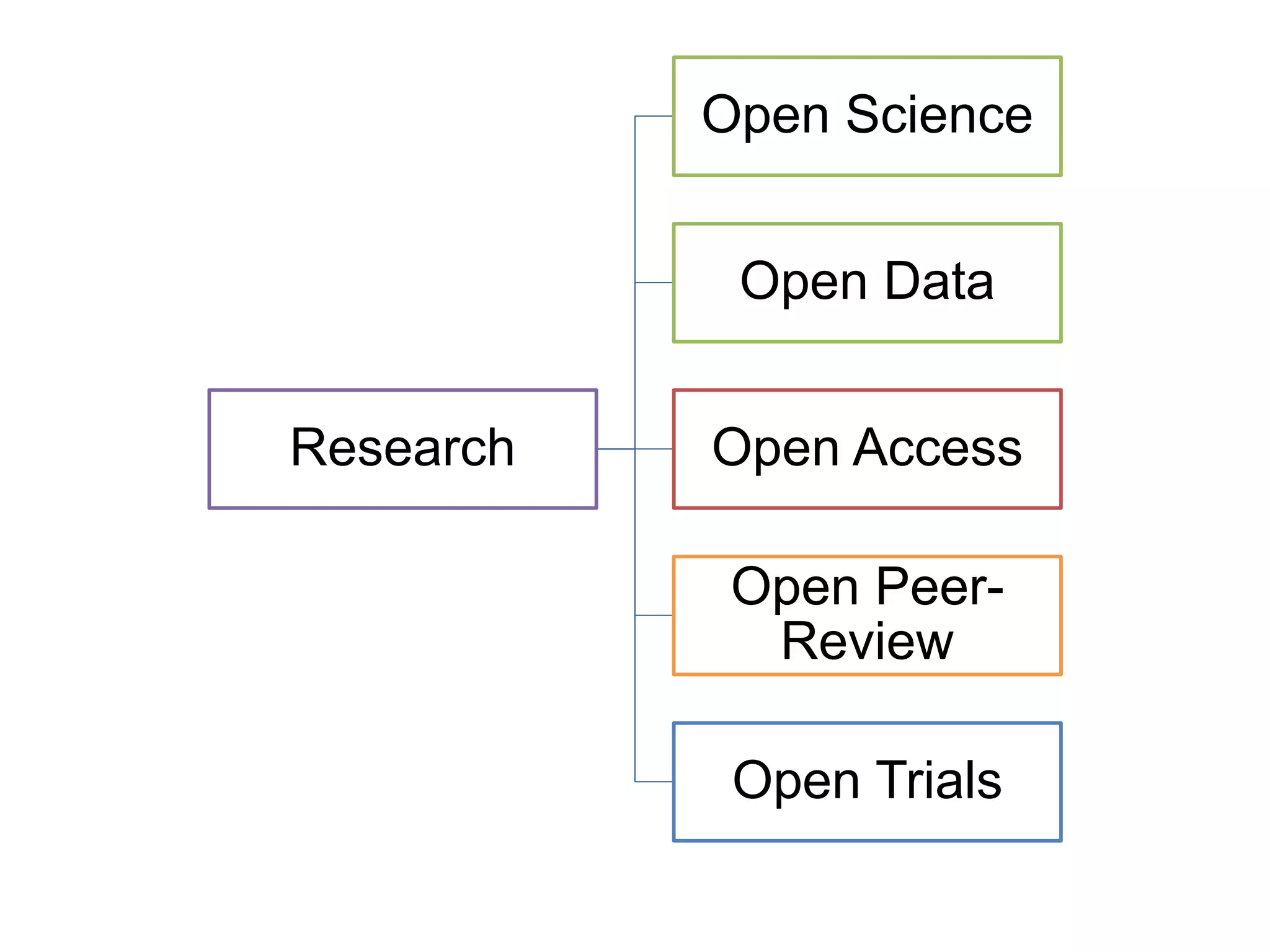
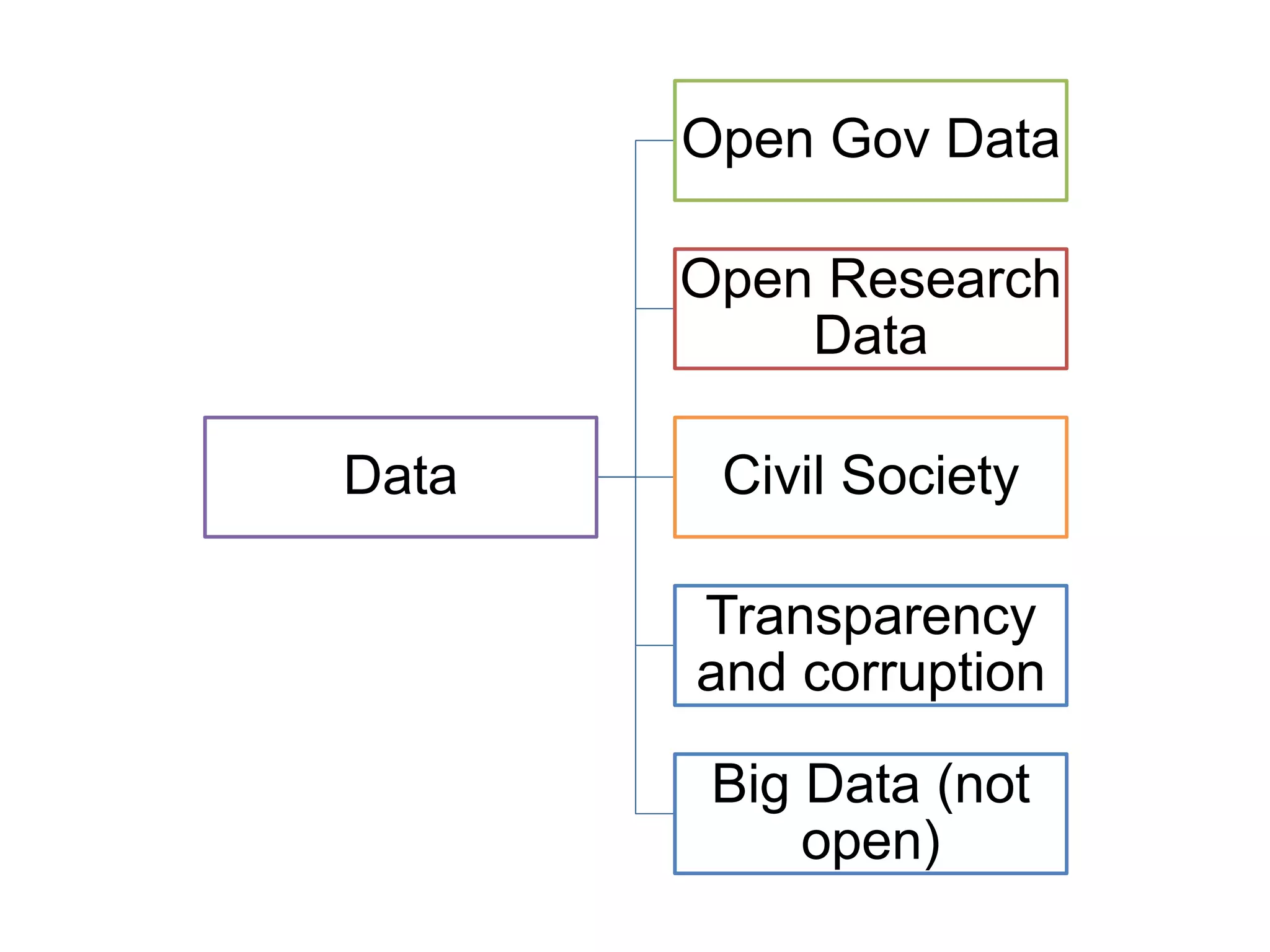
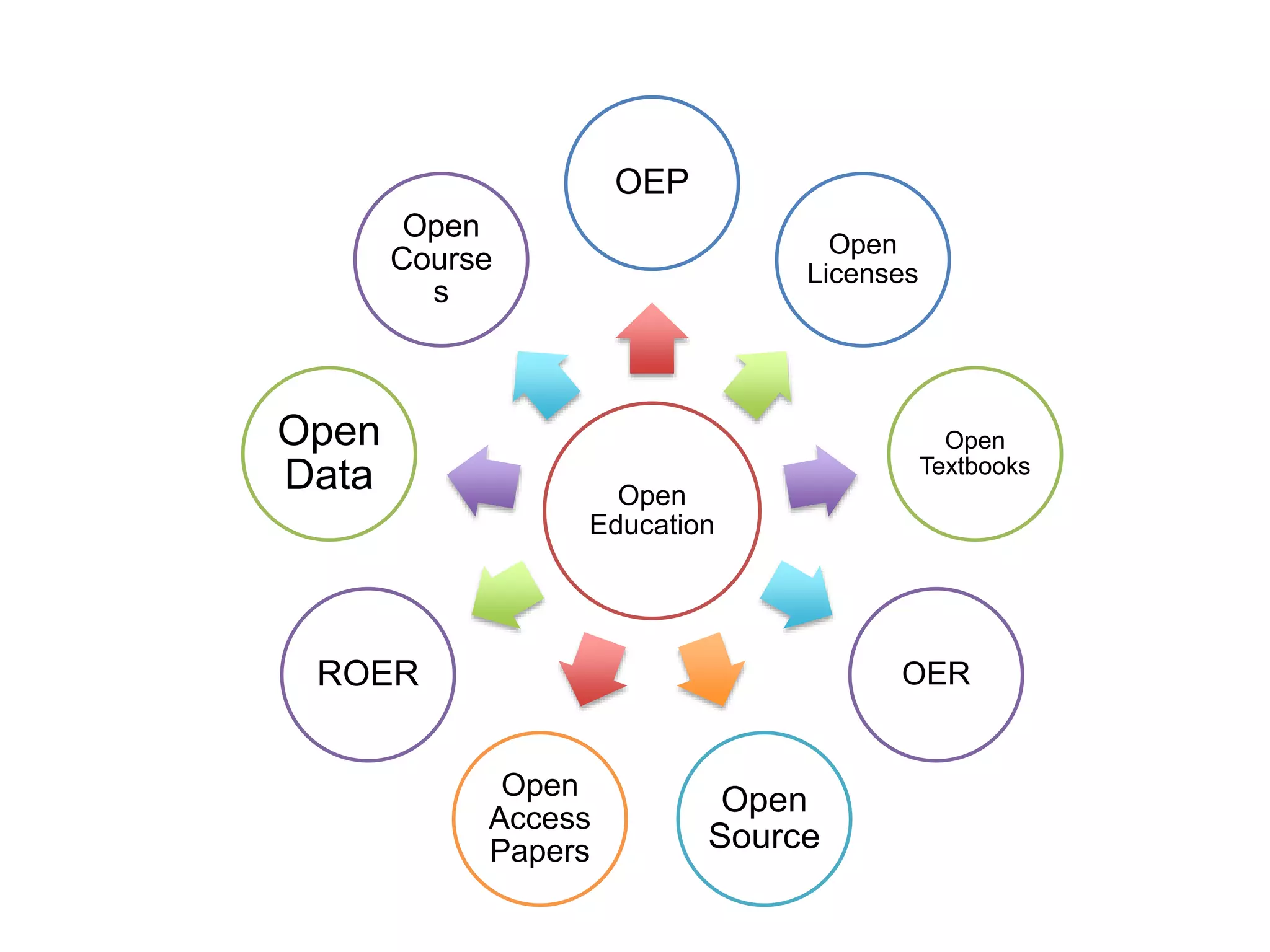
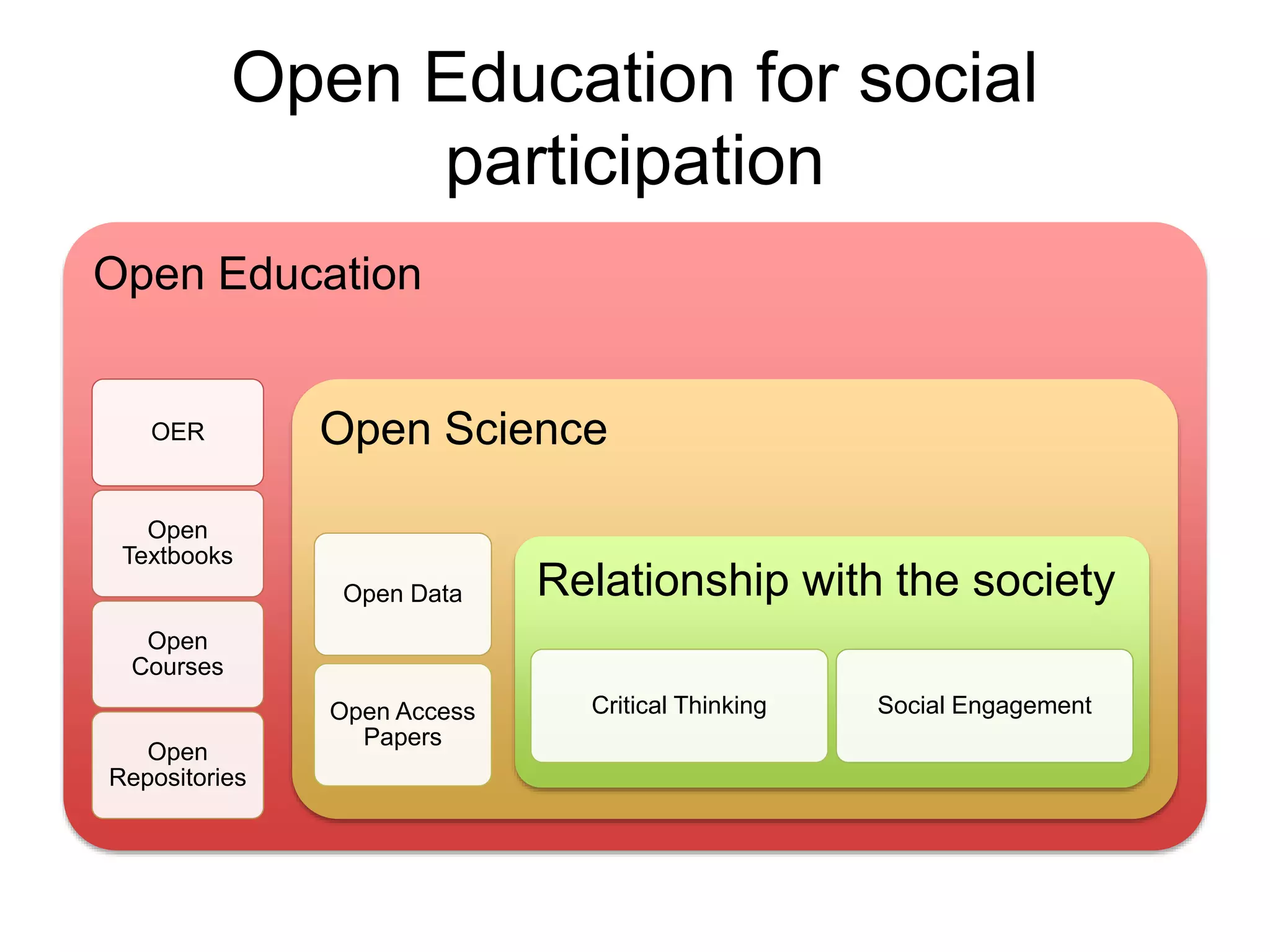
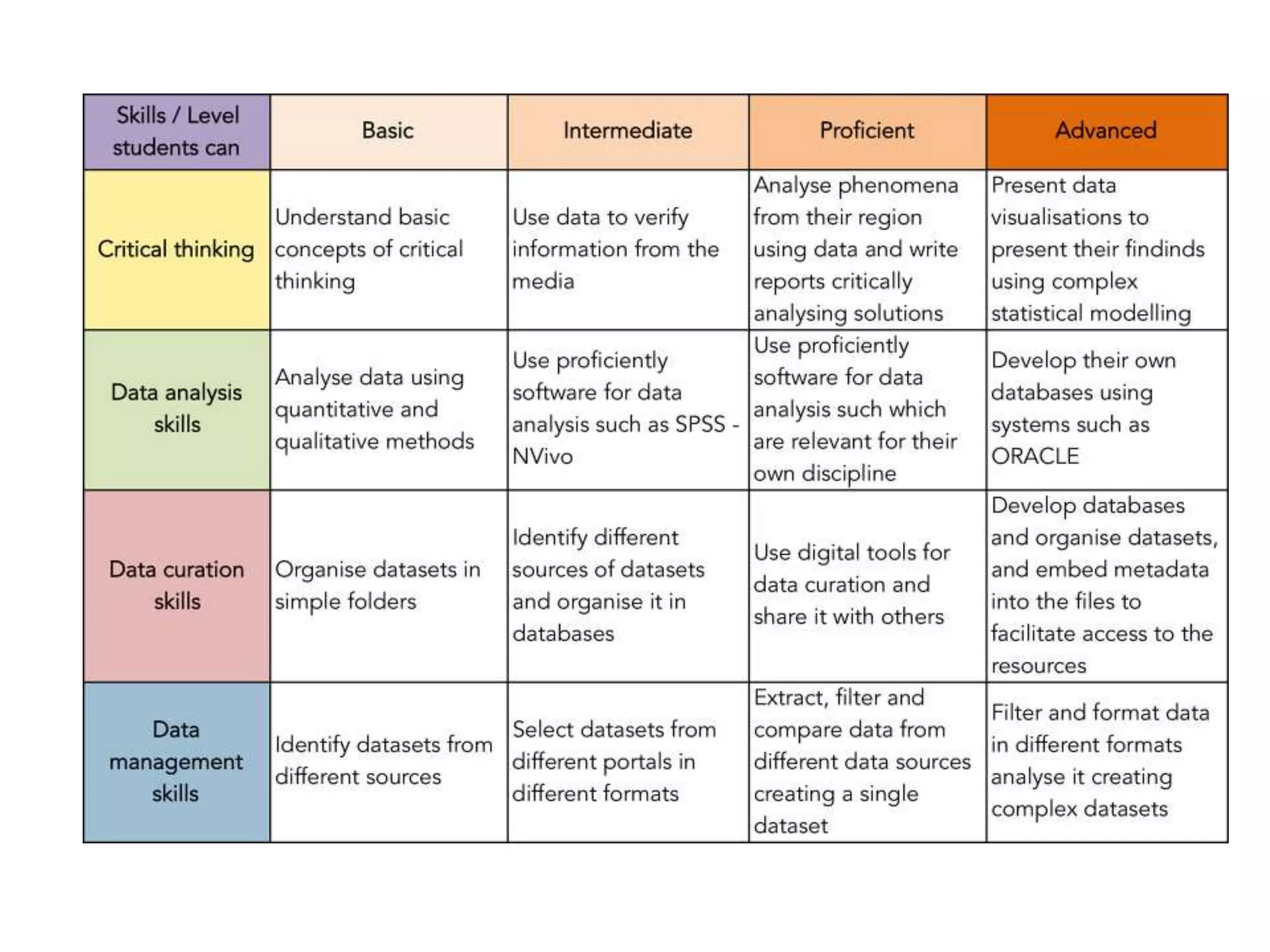
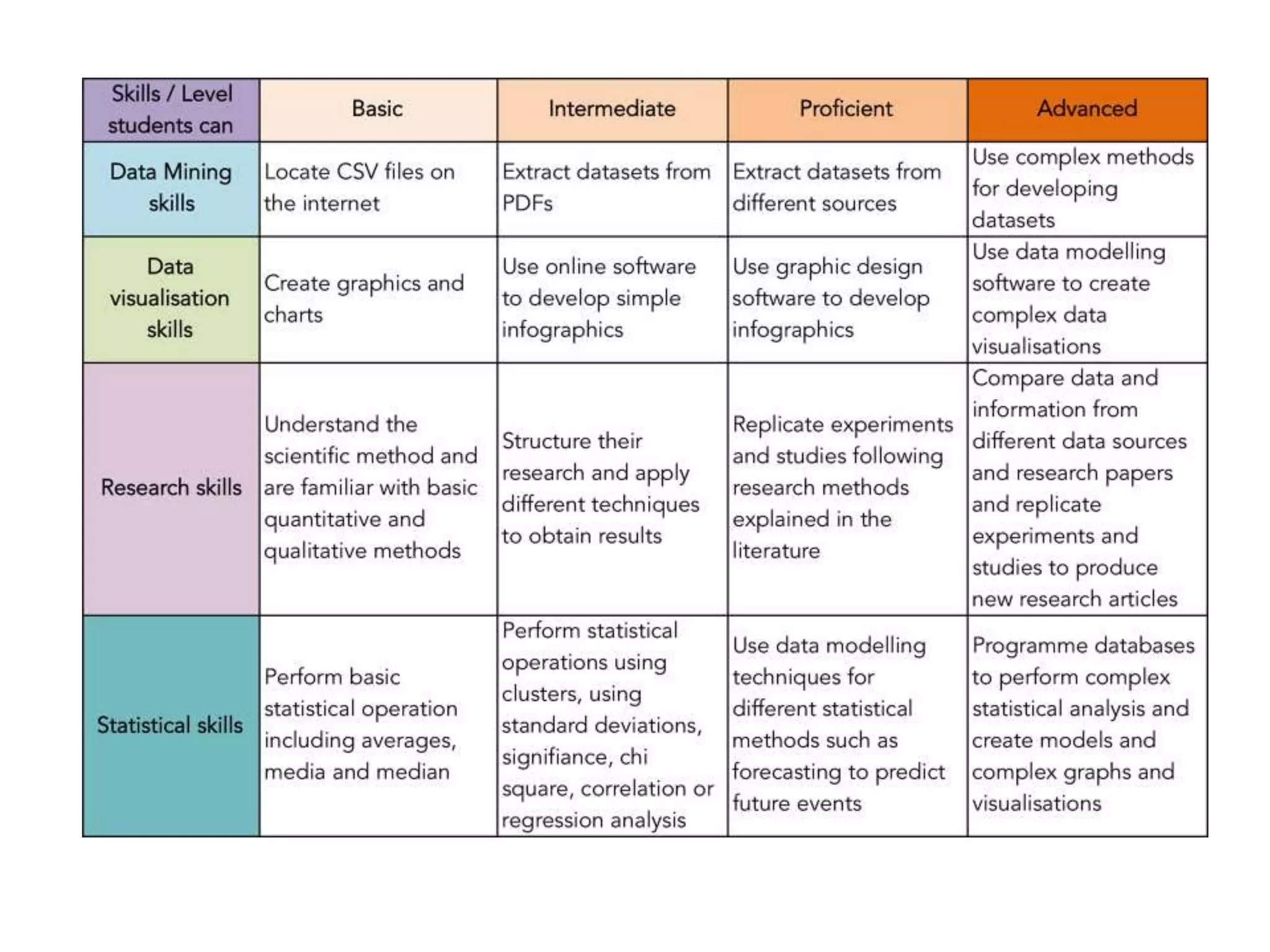
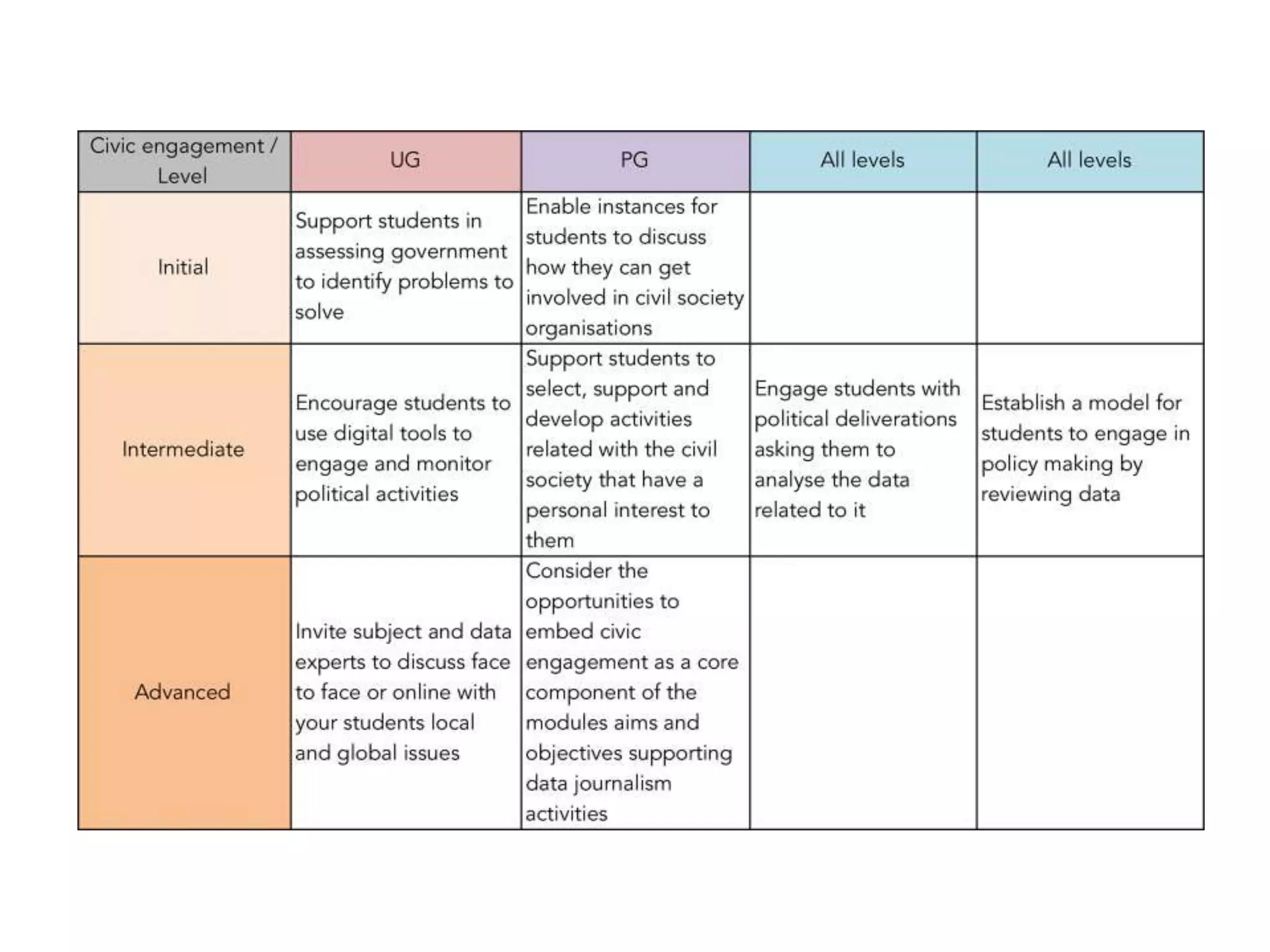
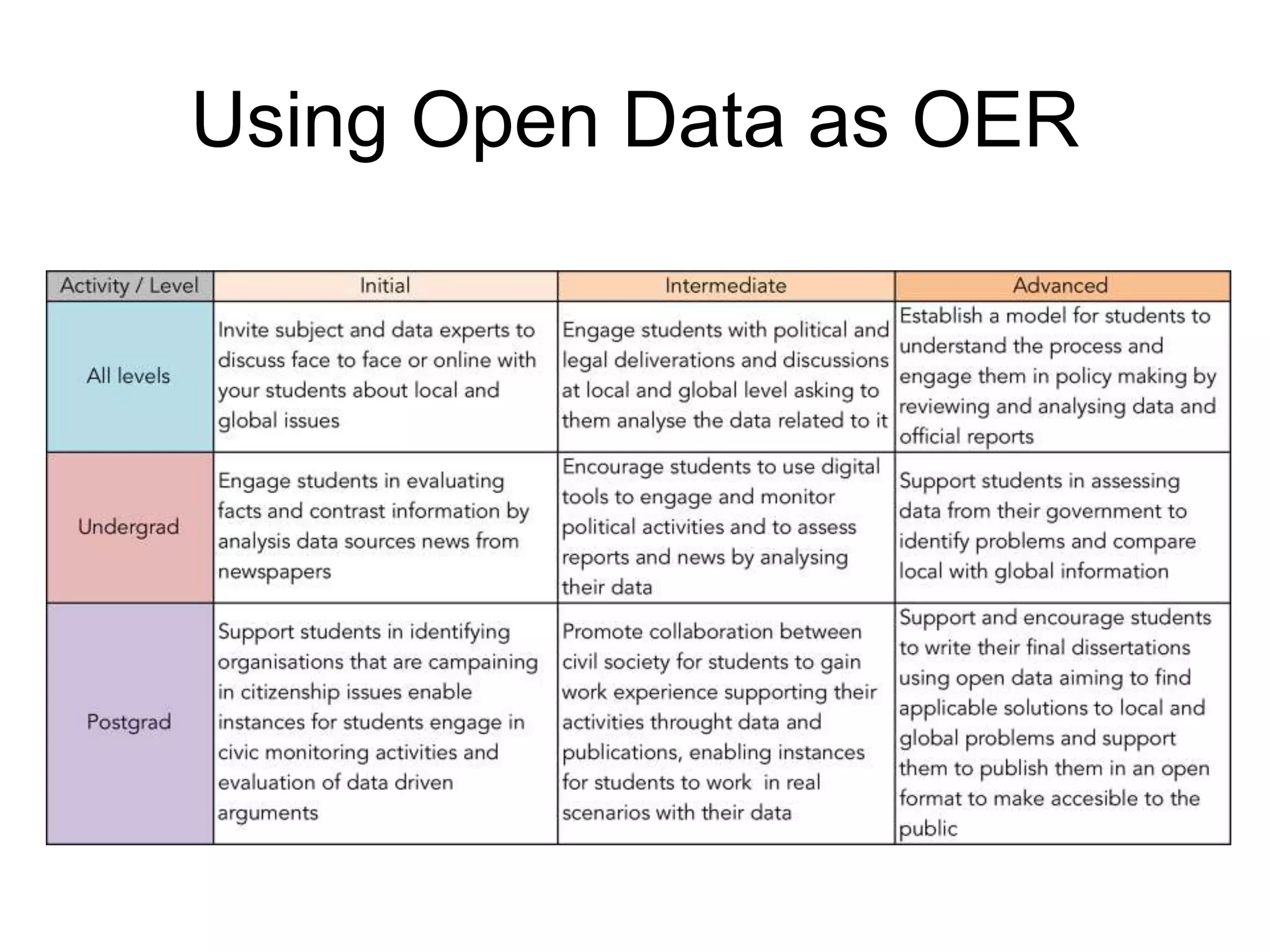
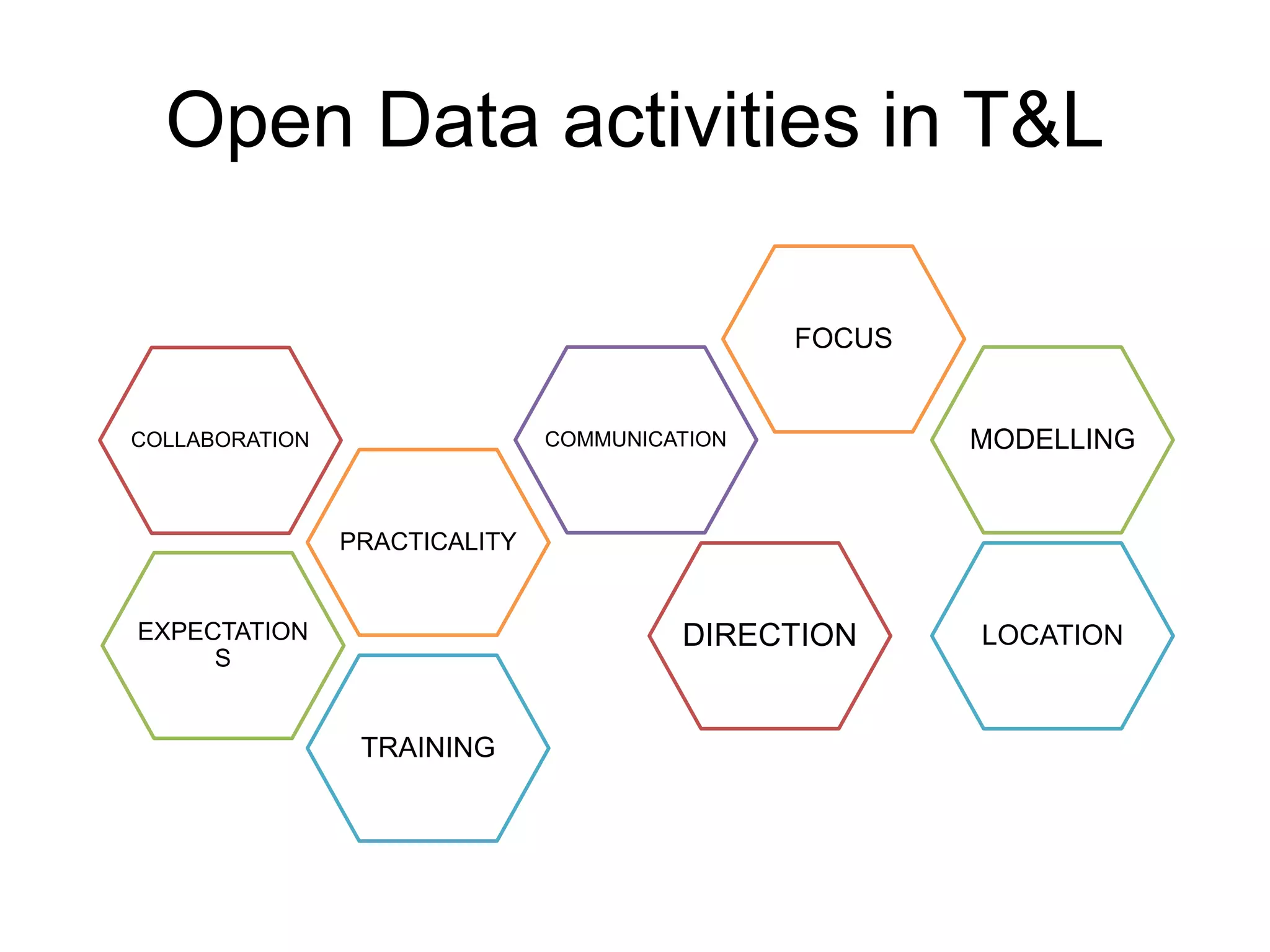
The document discusses the integration of open data as open educational resources (OER) to enhance social participation and develop transversal skills in students. It emphasizes the importance of critical analysis of data and collaboration to foster engagement within society, while outlining key elements for embedding open data in teaching and learning activities. Additionally, it provides resources and guidelines for educators to implement open data effectively in educational contexts.