This document proposes using interactive video learning to improve education access in rural areas of India. The key points are:
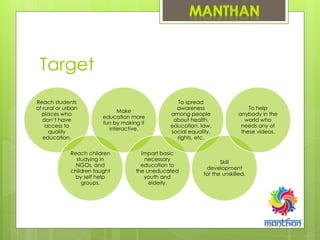
1. It aims to create educational videos that can be distributed on CDs and accessed online to improve reach in rural schools that lack qualified teachers.
2. The videos would provide primary to secondary level education, job skills training, and raise awareness on health, rights, and social issues.
3. It outlines a structure to develop the videos through expert teachers and content creators, and distribute them to schools, NGOs, and online.
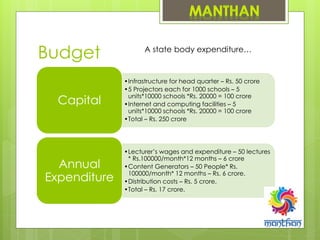
4. An initial budget of 250 crore rupees is estimated to set up the infrastructure and equip 10,000 schools per state with project