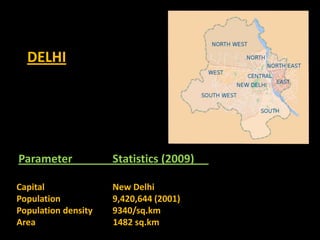
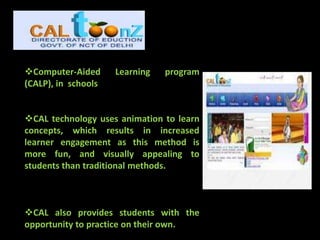
This document summarizes initiatives taken by the Department of Education in Delhi, India to incorporate information and communication technologies (ICT) into primary education through partnerships with NGOs and corporations. Key projects discussed include establishing computer kiosks in slum areas, using buses as mobile classrooms in remote areas, and Hole-in-the-Wall stations that provided freely accessible computers for children. The initiatives aimed to increase access to education, disseminate information more quickly, and reduce dropout rates, with reported success in mainstreaming hundreds of children. Limitations encountered included lack of quality teachers and content as well as infrastructure challenges.