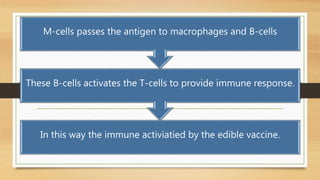
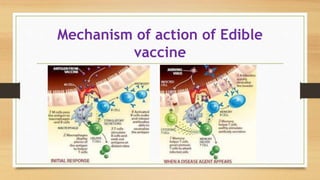
This document discusses edible vaccines, which are vaccines produced in transgenic plants or animals that are meant to be orally administered. It defines edible vaccines and notes their advantages over traditional vaccines like lower cost, easier storage and distribution, and needle-free administration. The document outlines the mechanism by which edible vaccines activate both mucosal and systemic immunity when consumed. It identifies the first researcher to demonstrate an edible vaccine and provides examples of clinical trials of edible vaccines for diseases like ETEC, norovirus, cholera, measles, and hepatitis B that have shown promise in animal and some human studies. Both advantages like lower cost of production and distribution in developing countries as well as disadvantages related to quality control and dosage