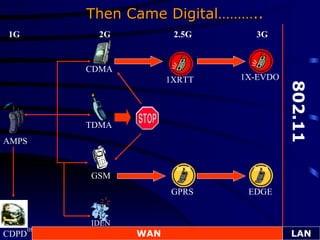
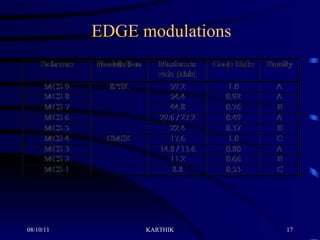
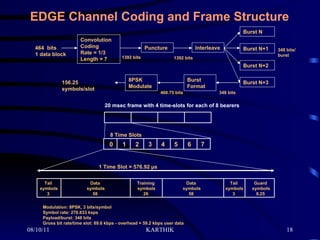
The document discusses the evolution of mobile technology from 1st generation to 3rd generation networks. It specifically focuses on EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) technology, which allows 2G GSM networks to transmit data at up to 384 kilobits per second, providing a higher speed alternative to GPRS for packet-based data services. EDGE builds on existing GSM infrastructure and provides a smooth transition path to 3G networks for mobile operators. It also enables new multimedia and data applications to be introduced on existing GSM networks.