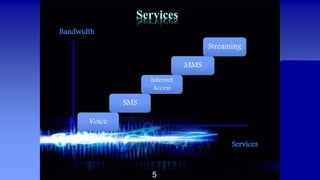
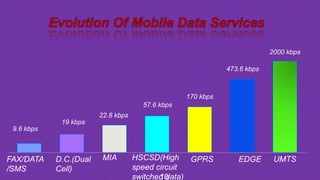
EDGE is an upgrade to GPRS that allows higher data transmission rates for 2G and 2.5G cellular networks. It introduces a new modulation technique called 8-PSK that encodes 3 bits per symbol instead of 1, tripling the data capacity within existing GSM spectrum and infrastructure. No changes are required to core networks, only software upgrades to base stations. This allows peak data rates of 474 kbps, much faster than GPRS's 115-160 kbps. EDGE provides benefits to users like higher speeds for data and multimedia, as well as benefits to operators through improved spectral efficiency and low upgrade costs since it reuses existing network components.