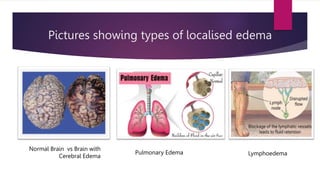
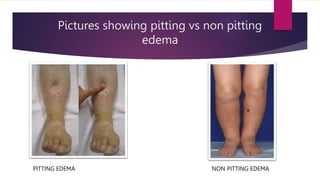
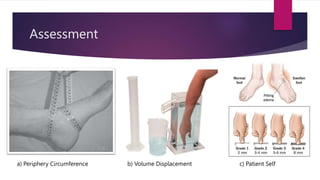
Edema is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the intercellular spaces or cavities of the body. It can be generalized, affecting multiple organs, or localized to a specific area. Common types of localized edema include cerebral, pulmonary, and lymphedema. Edema is caused by factors that increase capillary pressure or reduce plasma oncotic pressure. It is assessed by measuring circumference, volume displacement, or patient report. Treatment involves diuretics, compression garments, elevation, exercise and manual lymphatic drainage to improve circulation and remove excess fluid from tissues.