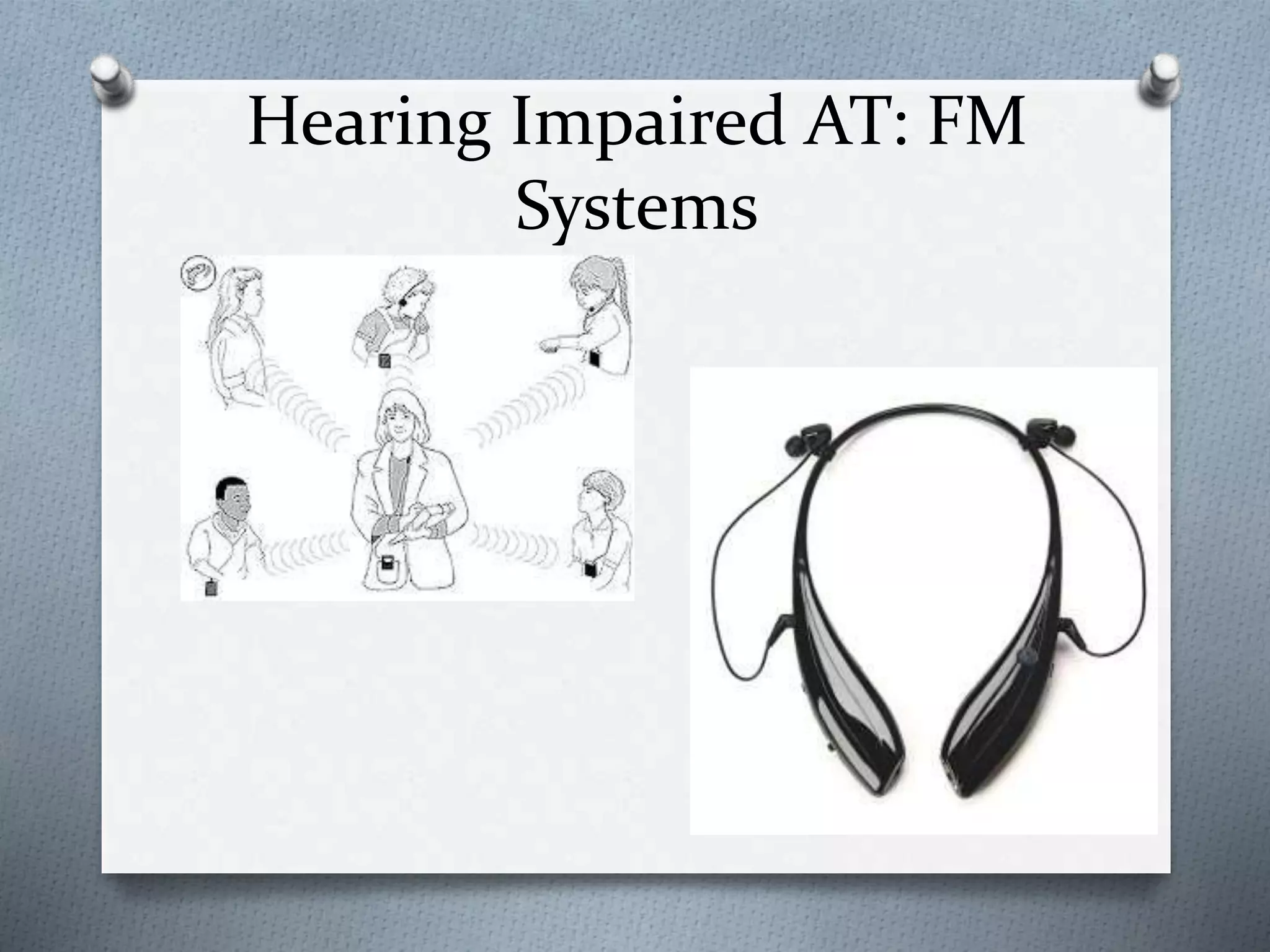
This document discusses various assistive technologies that can help students with disabilities access education. It defines assistive technology as any device or method that allows equal access and opportunities for students with physical or mental disabilities. Examples of assistive technologies described include FM systems to help hearing-impaired students, text-to-speech systems for visual impairments, electronic math worksheets for learning disabilities, and oversized trackball mice for physical disabilities. The document also discusses laws like IDEA that require schools to evaluate and provide assistive technologies if needed.