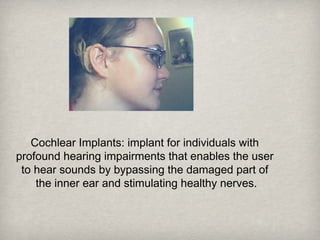
This document discusses assistive technology and examples that can help students with various disabilities. It defines assistive technology as equipment or software that helps people perform tasks that may otherwise be difficult. Laws like the ADA and IDEA require accommodating students with disabilities. Examples provided for hearing, visual, learning, and physical disabilities include hearing aids, screen readers, word processors, and switches operated by mouth/head. The assistive technologies aim to provide access to education for students with diverse needs.