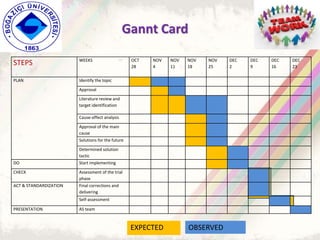
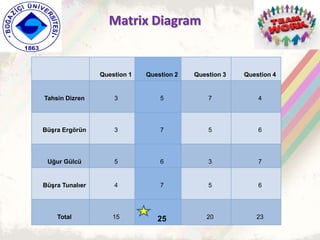
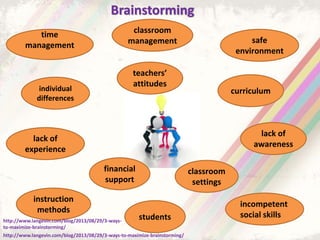
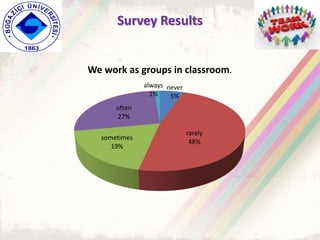
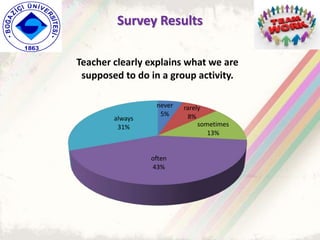
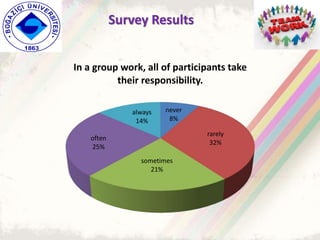
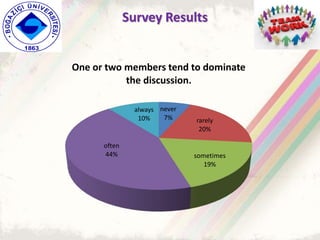
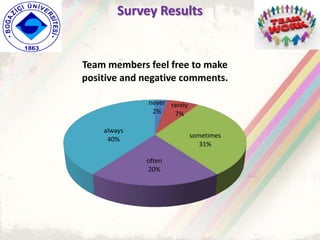
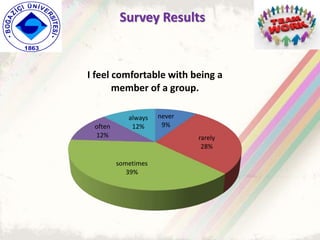
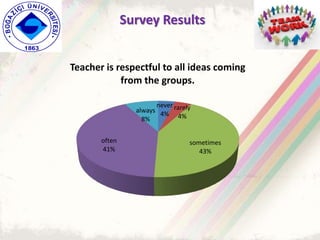
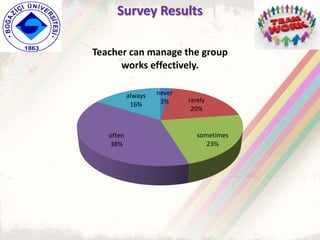
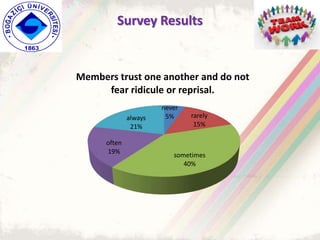
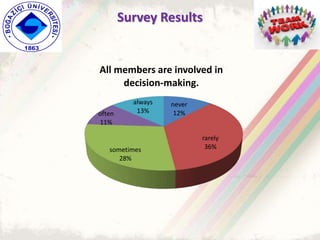
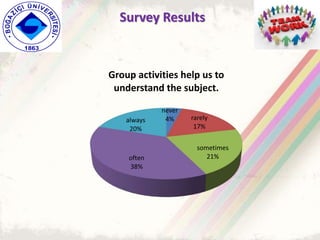
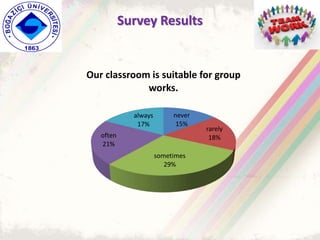
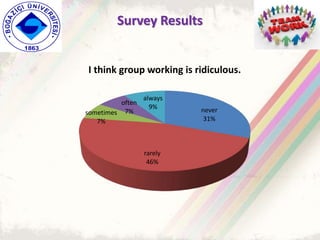
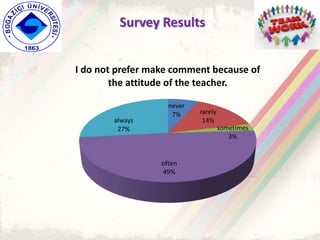
The document summarizes a group project on productive group work conducted by students in Dr. Hayal Köksal's classroom management class. The group reviewed literature on effective group work strategies and conducted a survey of students. The survey found that students sometimes participate in groups but roles and responsibilities are not always clear. Suggestions to improve group work included teacher training, extracurricular activities to build student social skills, and using inquiry-based methods instead of lectures. The group thanked Dr. Köksal for her guidance on the project.