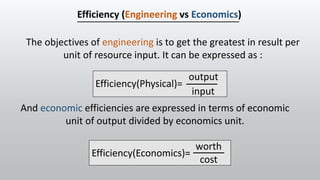
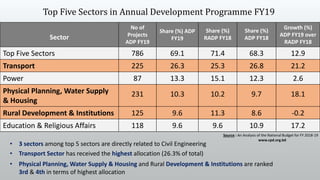
Economics relates the limited resources available to the infinite demand for those resources. It quantifies the costs and benefits of engineering projects to determine if they are economically feasible. Engineering economics evaluates projects based on minimizing costs and maximizing benefits. It considers the worth of a project relative to its costs. Projects that are technically feasible but not economically viable are discarded. Civil engineering requires an understanding of economics to design structures people demand that can be effectively built and maintained within budget constraints. This ensures resources are used efficiently with minimal waste.