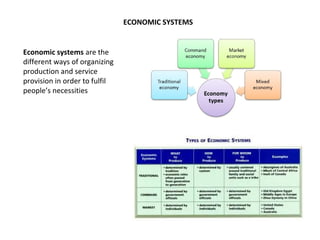
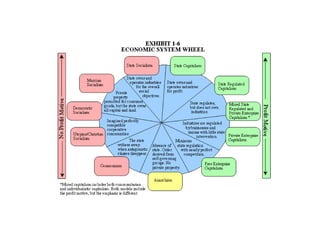
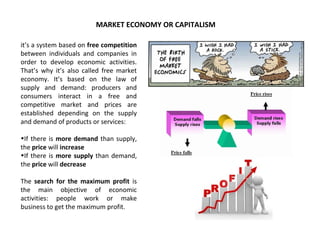
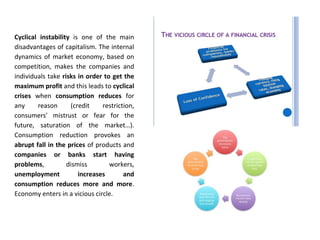
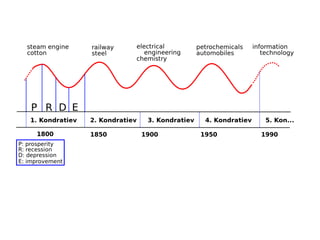
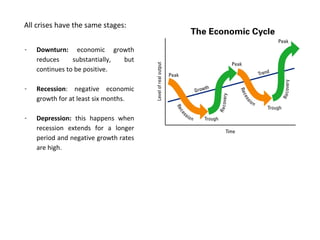
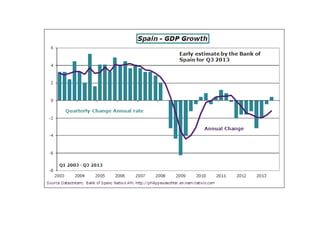
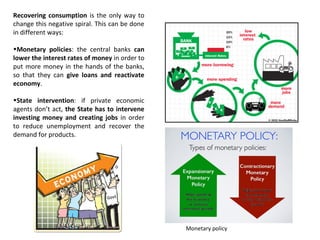
This document discusses different economic systems and economic crises. It describes subsistence economies, market economies, centrally planned economies, and alternative economic models. It notes that market economies are prone to cyclical instability which can lead to downturns, recessions, and depressions during economic crises. Recovering consumption through monetary policy and state intervention is needed to change the negative spiral of an economic crisis.