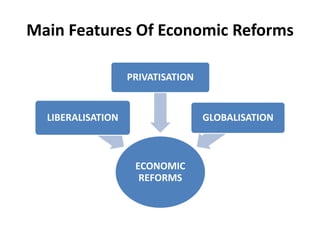
The document discusses the economic reforms in India that began in 1991 in response to an economic crisis. It provides context around the need for reforms, including increased fiscal deficits, adverse balance of payments, and falling foreign exchange reserves. Early crisis management measures focused on fiscal correction, industrial decontrol, and balance of payments stabilization. The major features of the economic reforms were liberalization, privatization, and globalization. Liberalization involved reducing government controls over industries and the economy to allow market forces to guide growth more effectively.