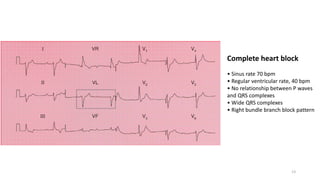
This document contains an ECG report that summarizes various cardiac conditions including:
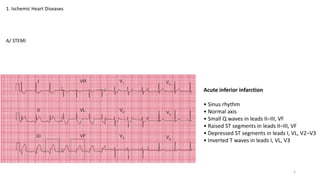
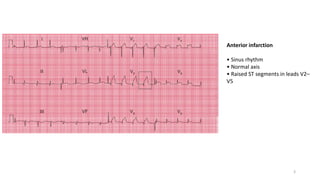
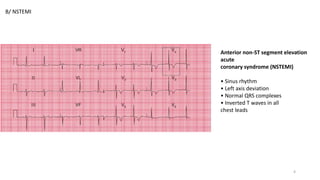
1) Ischemic heart diseases such as ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI).
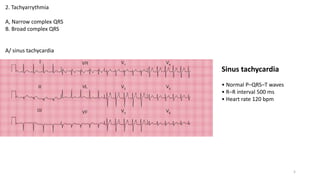
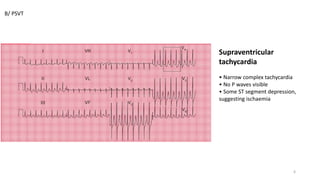
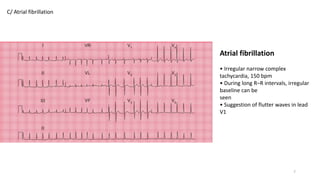
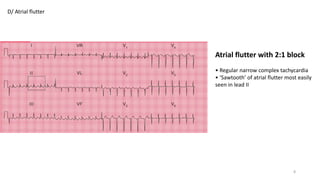
2) Tachyarrhythmias such as sinus tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter.
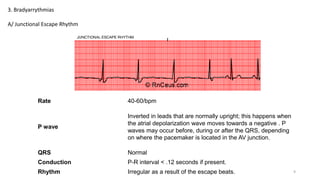
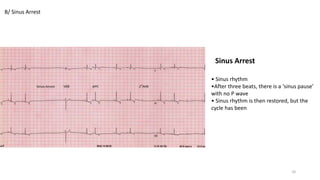
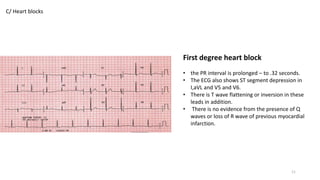
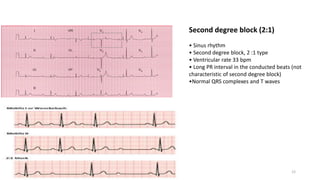
3) Bradyarrhythmias including junctional escape rhythm and sinus arrest.
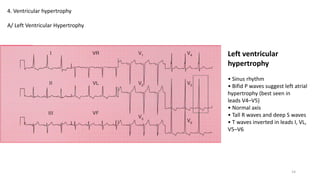
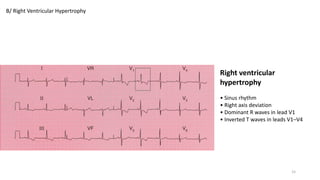
4) Ventricular hypertrophy of the left and right ventricles.
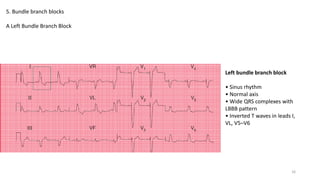
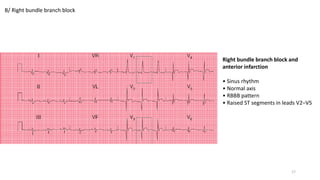
5) Bundle branch blocks including left and right bundle branch blocks.
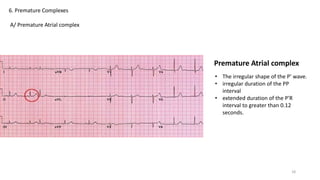
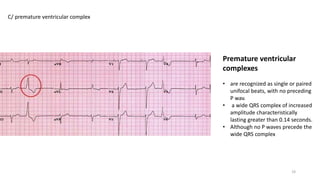
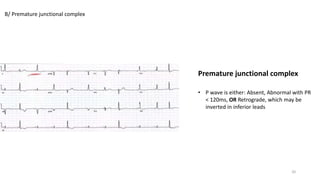
6) Premature complexes including premature atrial, junctional, and