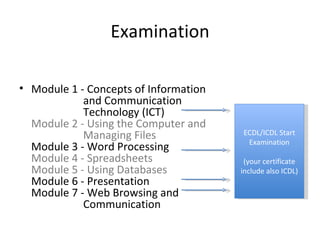
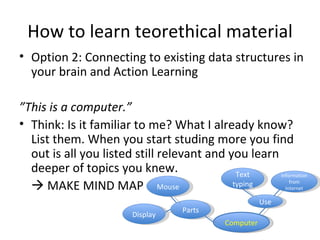
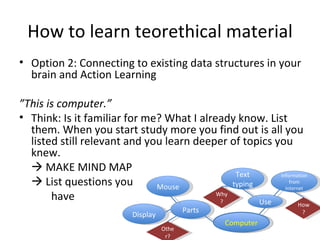
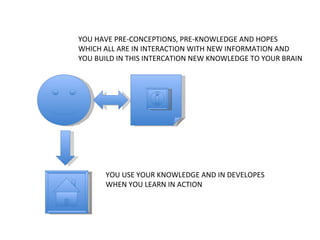
The document discusses the ECDL/ICDL certification program, which tests proficiency in common computer applications. It provides benefits of obtaining the ECDL/ICDL certification such as learning important job skills and accessing online services. The certification consists of 7 modules that cover topics like word processing, spreadsheets, databases, and web browsing. Effective learning methods are described, including making mind maps to connect new concepts to prior knowledge and discussing questions to reinforce understanding.













![Contact persons IT-specialist Åke Jonsson (Sweden) [email_address] Pedagogist Päivi Nuora (Finland, living in Kenya) [email_address] 0714844497 Local contact person Anne Kagiri (Kenya) [email_address] 0721356200](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecdlmkfctipsforlearning-100409063844-phpapp01/85/Ecdl-Mkfc-Tips-For-Learning-19-320.jpg)

