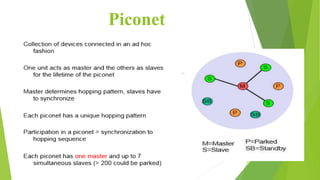
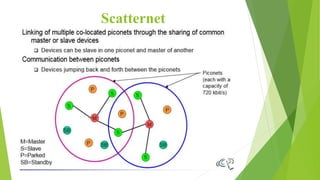
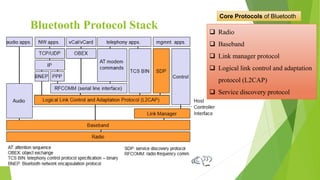
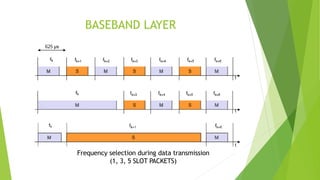
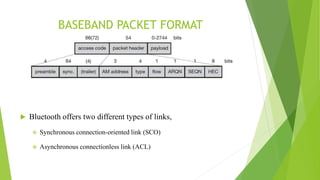
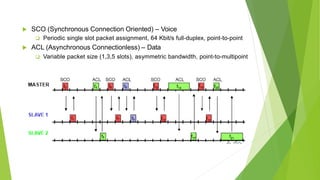
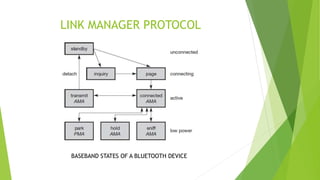
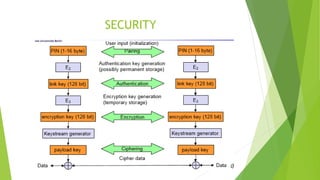
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances using radio transmissions in the 2.4 GHz band. It allows for ad-hoc connections between devices within 10 meters using frequency hopping spread spectrum and time-division duplexing. Bluetooth devices can connect in a piconet topology managed by a master device or scatternet topology connecting multiple piconets. The Bluetooth protocol stack includes layers for radio, baseband, link management, logical link control and adaptation, and various service protocols.