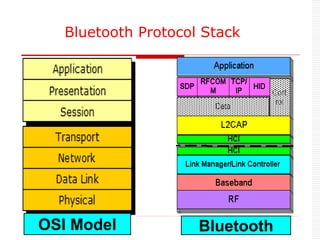
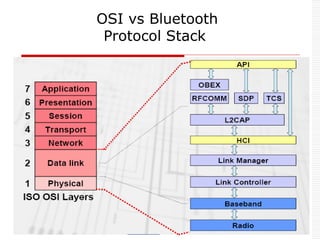
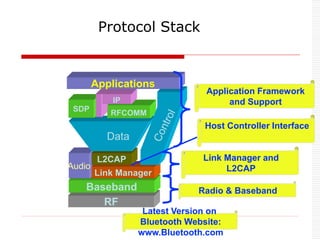
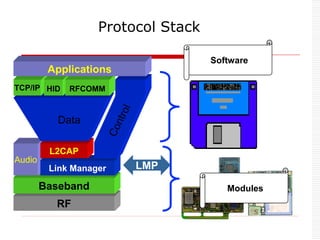
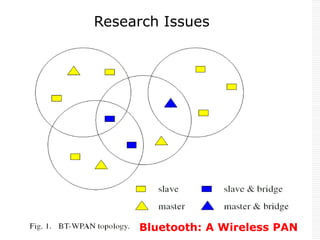
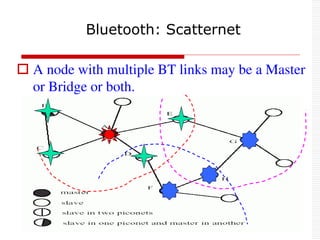
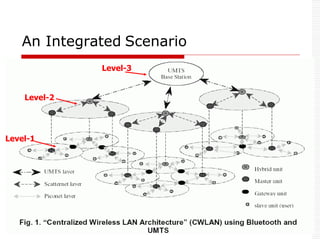
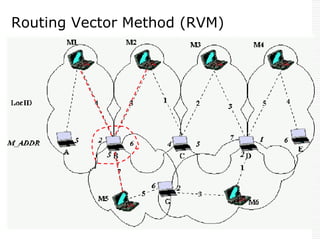
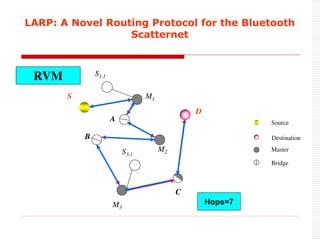
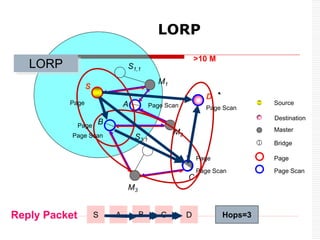
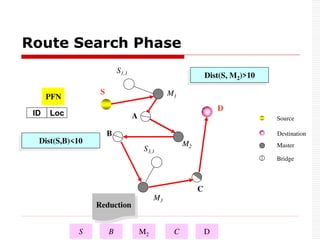
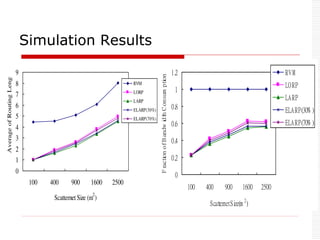
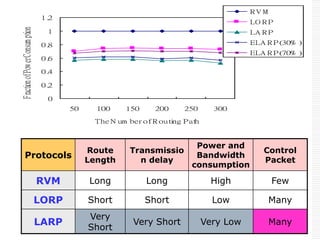
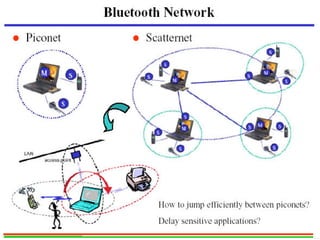
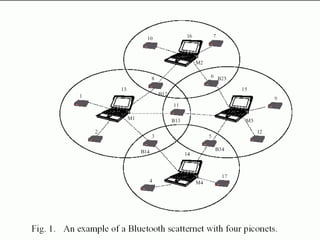
This document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology and discusses routing protocols for Bluetooth scatternets. It describes the history and applications of Bluetooth, its technical specifications including frequency hopping and the Bluetooth protocol stack. Several routing protocols for Bluetooth scatternets are presented, including RVM, LORP and LARP (the authors' proposed Location Aware Routing Protocol). LARP aims to improve upon other protocols by finding shorter routing paths to reduce transmission delays, bandwidth consumption and power usage. Simulation results show LARP performs better across these metrics compared to RVM and LORP as scatternet size increases.









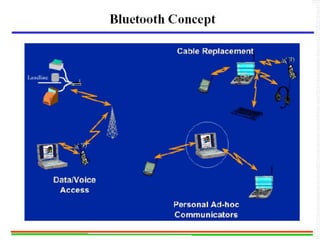
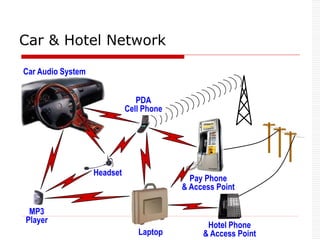
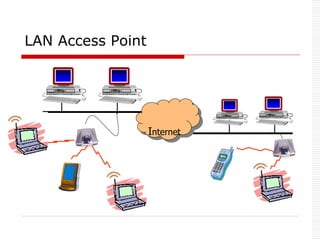
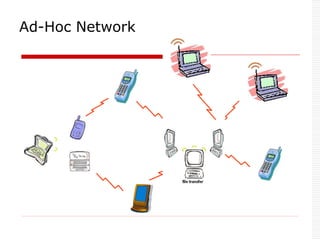





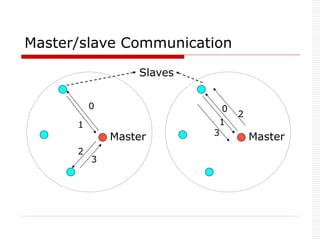
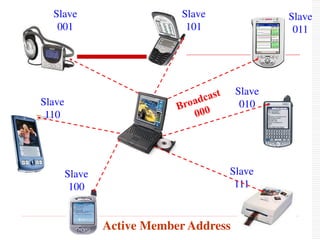
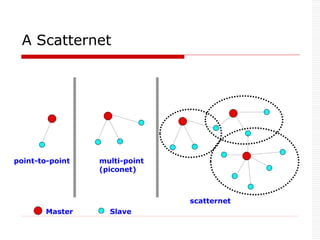
![ Two parts: Piconet & Scatternet
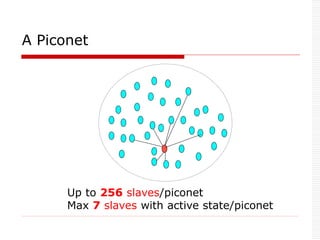
Piconet: 1 Master can connect to 7 active
slaves simultaneously.
7 active slaves
256 parked slaves [power saving mode].
Master controls the slaves in the piconet.
Bluetooth Network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-240124183531-b313000a/85/Bluetooth-Technology-Introduction-to-Bluetooth-Technical-Specifications-Bluetooth-Protocol-Stack-27-320.jpg)


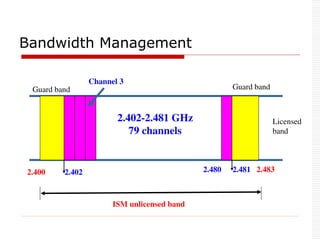
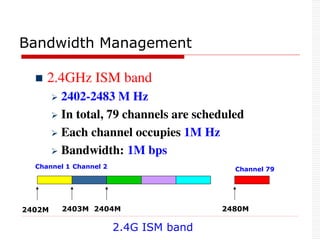
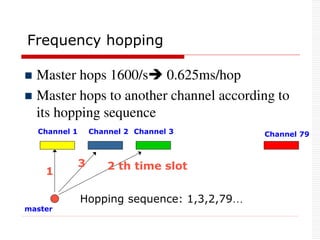
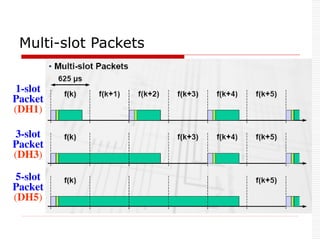
![Technical Specifications
Data rate: 1Mhz
Symbol rate: 1M bps
Data rate: 721Kbps excluding header [Data]
Uses Time Division Duplex (TDD) technique.
Time is divided into 625ms(1 time slot)
Master sends packet to its slaves in the Even time
slot
Slave sends packet to its Master in ODD time slot
Uses 3 Power classes.
Communication Range: 10 m, can be extended to 100 m.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-240124183531-b313000a/85/Bluetooth-Technology-Introduction-to-Bluetooth-Technical-Specifications-Bluetooth-Protocol-Stack-35-320.jpg)