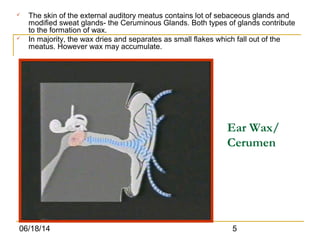
This document discusses conductive hearing loss caused by earwax impaction. It describes how earwax is normally produced in the ear canal and may accumulate if not removed. Common symptoms of earwax impaction include deafness, pain, tinnitus, and vertigo. Examination reveals black, brown, or dry wax in the ear canal obstructing the eardrum. Treatment involves removing the wax either through wet or dry methods. The wet method soaks the wax to soften it for removal by syringing warm water into the ear canal. The dry method uses tools like a wax hook or suction to extract hard wax. Proper removal of earwax helps restore hearing and prevent further blockage.