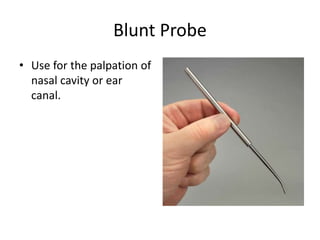
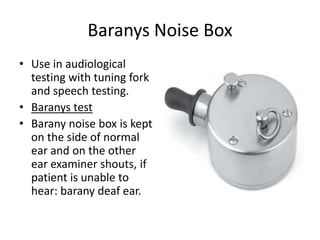
This document describes various instruments and procedures used in ENT examinations in an outpatient department. It discusses bull's eye lamps, head mirrors, tongue depressors, nasal speculums, laryngeal mirrors, otoscope, tuning forks, probes, forceps, eustachian tube catheters and other tools. It provides details on how each instrument is used and procedures for examining the ears, nose, mouth and throat.