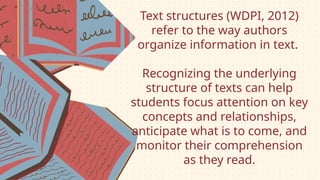
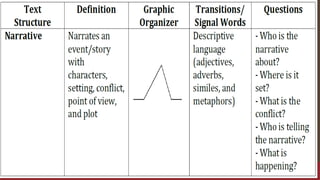
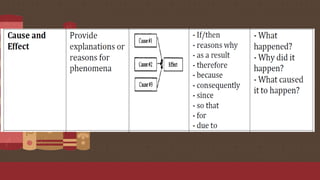
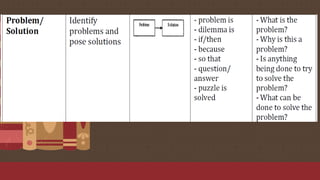
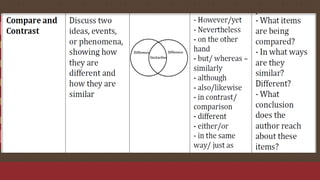
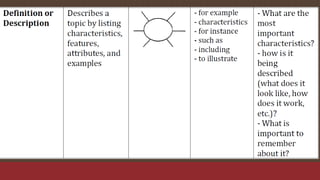
The document discusses the importance of text structures in reading comprehension, emphasizing how recognizing these structures allows readers to focus on key concepts and enhance their understanding. It highlights close reading as a vital skill for uncovering deeper meanings and author intentions. Additionally, it outlines various types of text structures and their significance in organizing and summarizing information.