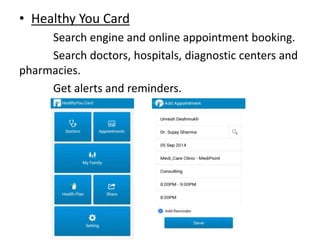
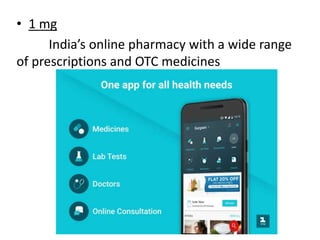
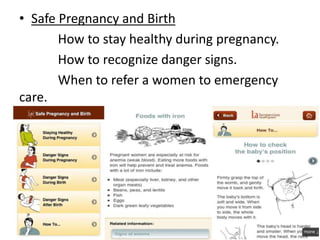
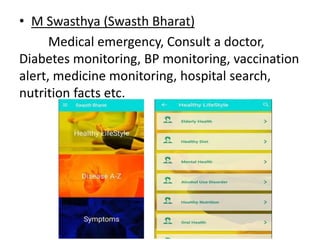
The document provides a comprehensive overview of eMedicine, detailing its history, significance for patients and doctors, and its implementation across various health initiatives in India. It highlights the evolution of digital health practices such as e-health and m-health, and their roles in enhancing patient empowerment and delivering healthcare information. Additionally, the document outlines various systems and apps developed to improve medical care and patient management, illustrating the shift towards data-driven healthcare.