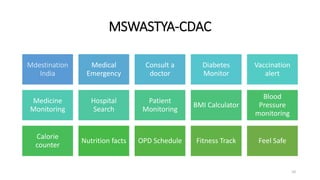
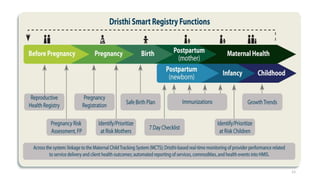
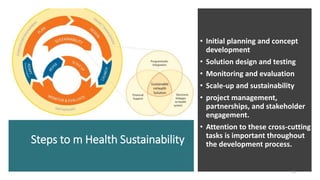
The document outlines the significance of mobile health (mHealth) as a subset of eHealth, leveraging mobile technologies to improve health outcomes. It discusses various mHealth applications in areas like maternal health, disease tracking, and health education, while highlighting benefits and limitations related to access and implementation. The importance of partnerships and sustainability in mHealth projects is also emphasized to enhance healthcare delivery.