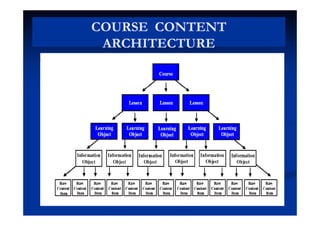
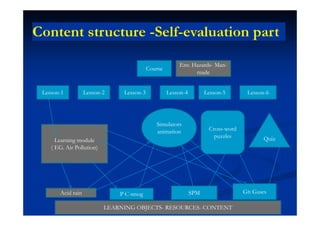
The document outlines the principles and practices of e-content development, focusing on learning management systems (LMS) and asynchronous e-learning. It covers the objectives, features, and steps involved in creating e-learning materials, including the design of learning objects and the integration of assessments. Key components include content creation, delivery methods, and the management of user data and course administration.