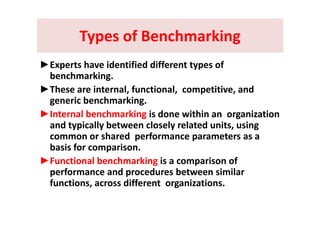
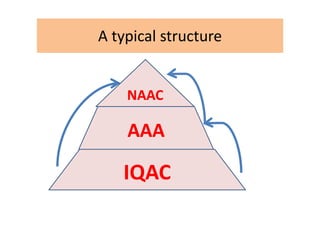
The document outlines the Framework for Academic and Administrative Audit (AAA) in higher education institutions, emphasizing its importance for quality enhancement and sustainability. It details the objectives, methodologies, and expected outcomes of conducting AAA, alongside the role of the Internal Quality Assurance Cell (IQAC) established by NAAC. The AAA process is aimed at continuous improvement by evaluating strengths and weaknesses, promoting accountability, and integrating best practices in educational institutions.