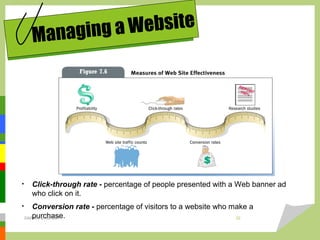
This document discusses e-business and how organizations can use the internet for business purposes. It defines e-business as conducting business via the internet, and lists some common forms like e-tailing, B2B transactions, EDI, and using communication tools. The document outlines the capabilities of e-business like global reach, personalization, and cost savings. It also discusses challenges like privacy, fraud, and website usability issues. Finally, it covers topics like using websites for marketing, communications functions, measuring website effectiveness, and the global scope of e-business.