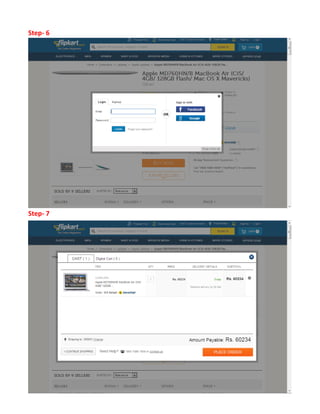
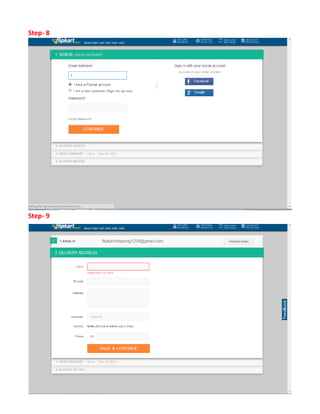
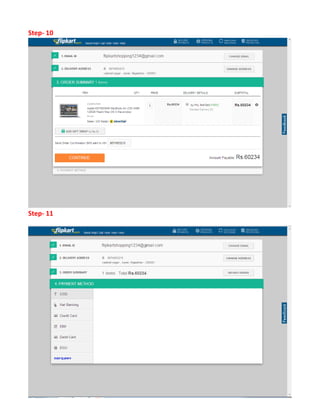
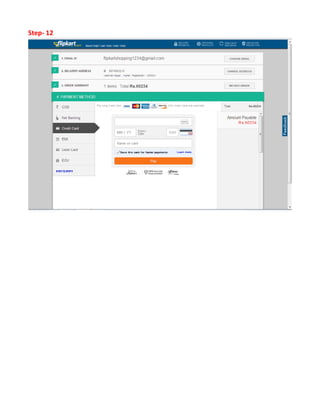
This document provides an overview of electronic commerce and discusses various aspects of its technological framework. It describes 6 layers that make up the architecture for electronic commerce applications: 1) application services, 2) brokerage and data management, 3) interfaces and support, 4) secure messaging, 5) middleware services, and 6) network infrastructure. Each layer provides distinct functions to enable integration, data sharing, and transactions across organizations. The document also discusses specific technologies and standards that comprise the different layers, such as EDI, HTML, and encryption, which work together to facilitate electronic commerce.