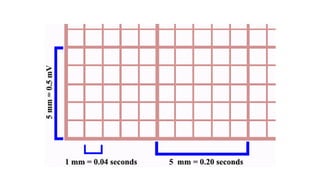
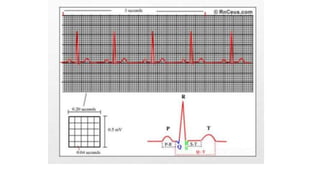
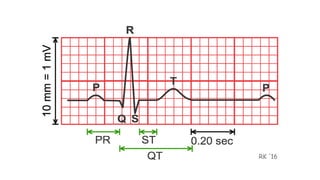
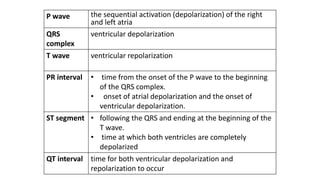
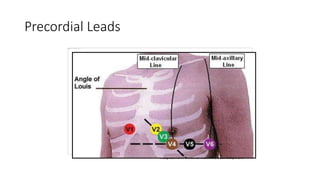
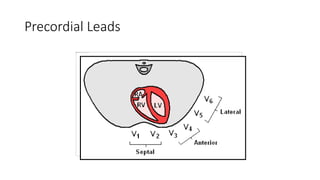
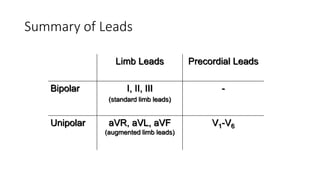
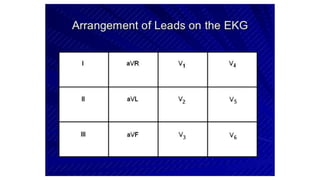
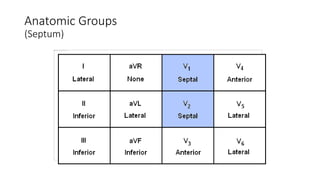
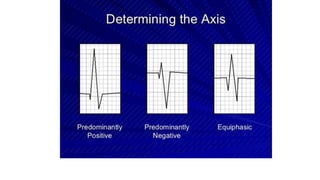
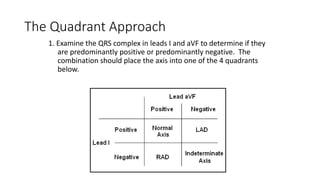
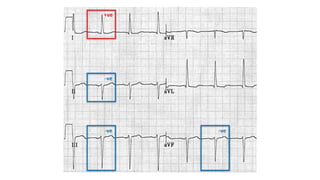
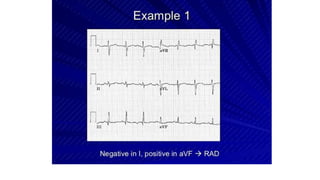
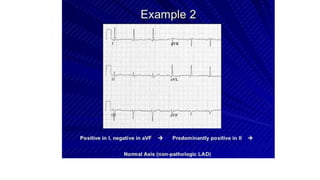
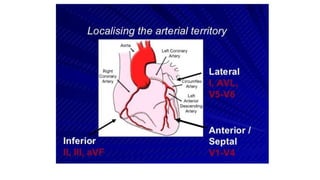
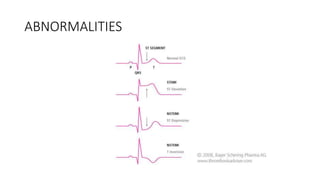
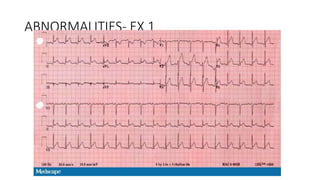
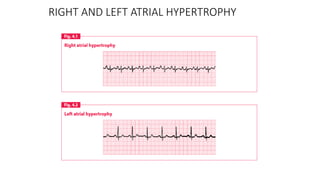
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart on paper. It is recorded at a rate of 25mm/s, with each large square measuring 0.2 seconds and containing 5 small squares of 0.04 seconds each. The P wave represents atrial depolarization, the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, and the T wave represents ventricular repolarization. Various intervals between the P, QRS, and T waves provide information about electrical conduction through the heart. Abnormalities in the ECG patterns can provide clues about conditions affecting different areas of the heart muscle.