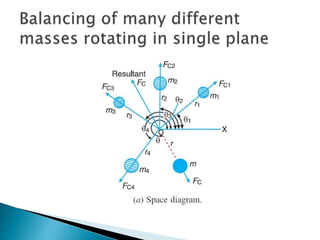
Balancing is a technique used to eliminate unwanted forces and moments in rotating or reciprocating masses. If dynamic forces are not balanced, they can cause excessive vibration, noise, and wear on machines. There are different types of balancing, including balancing of rotating masses using a second counteracting mass, and balancing of reciprocating masses in engines by satisfying conditions where the sum of primary and secondary forces and couples are zero. Proper balancing is important for reducing vibration and increasing the life of machine components like crankshafts and pumps.