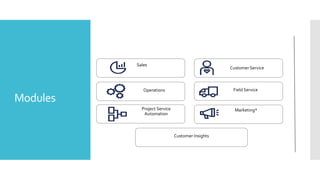
This document provides an overview of courses and topics related to Microsoft Dynamics 365. It discusses courses for introduction, functional areas like customer service and sales management, and customization. It also summarizes basics of CRM including entities, activities, and searching. Sections cover specifics of customer service, marketing including campaigns, and sales management features like opportunities and orders. Deployment models of on-premise versus online are compared.