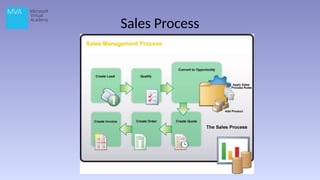
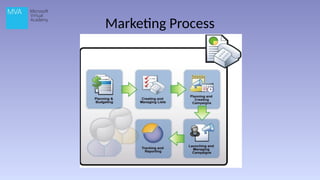
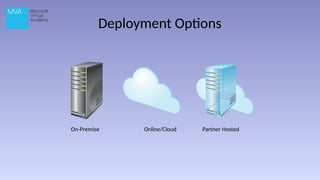
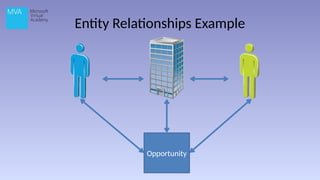
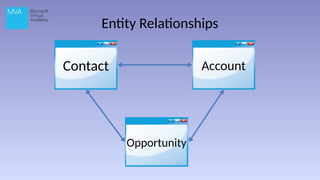
The document provides an overview of Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2013, outlining its functionality, deployment options, and navigation features. It details the CRM's capabilities in sales, marketing, and customer care, highlighting specific functionalities like lead management, case recording, and marketing campaigns. Additionally, it discusses various deployment options, including on-premise and cloud solutions.