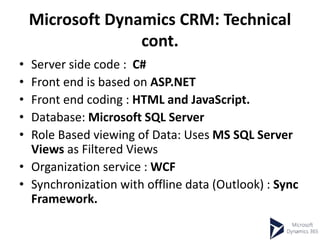
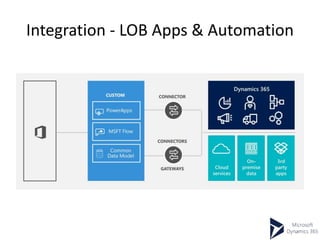
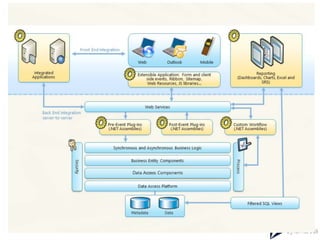
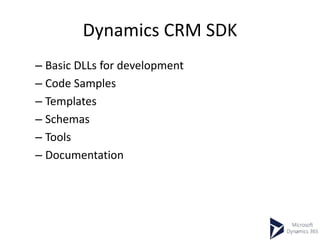
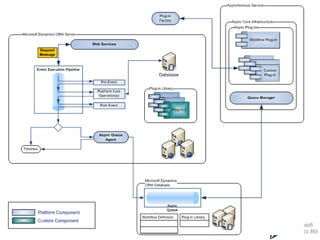
This document provides an overview of Microsoft Dynamics 365 and CRM. It describes Dynamics 365 as a business process management and ERP software with integrated applications. It outlines the main modules of an ERP system like supply chain management, accounting, HR, and project planning. The document compares ERP and CRM software, noting that ERP focuses on back-office functions while CRM focuses on front-office functions like marketing and sales. It also provides examples of ERP and CRM software vendors and availability models.