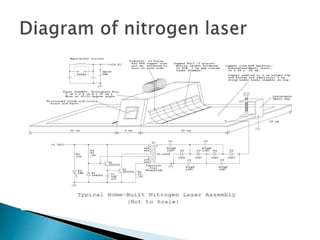
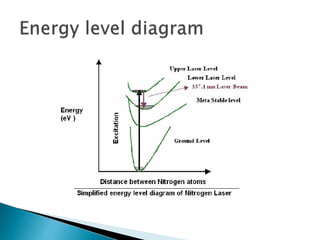
A nitrogen laser operates by using molecular nitrogen as its gain medium, emitting ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 337.1 nm. When an electric spark excites nitrogen atoms, stimulated emission produces a laser beam. Nitrogen lasers have a short pulse width and high intensity, drawing high power through electrical discharge. They can be used for applications like laser-induced fluorescence, photochemistry, spectroscopy, and pumping dye lasers.