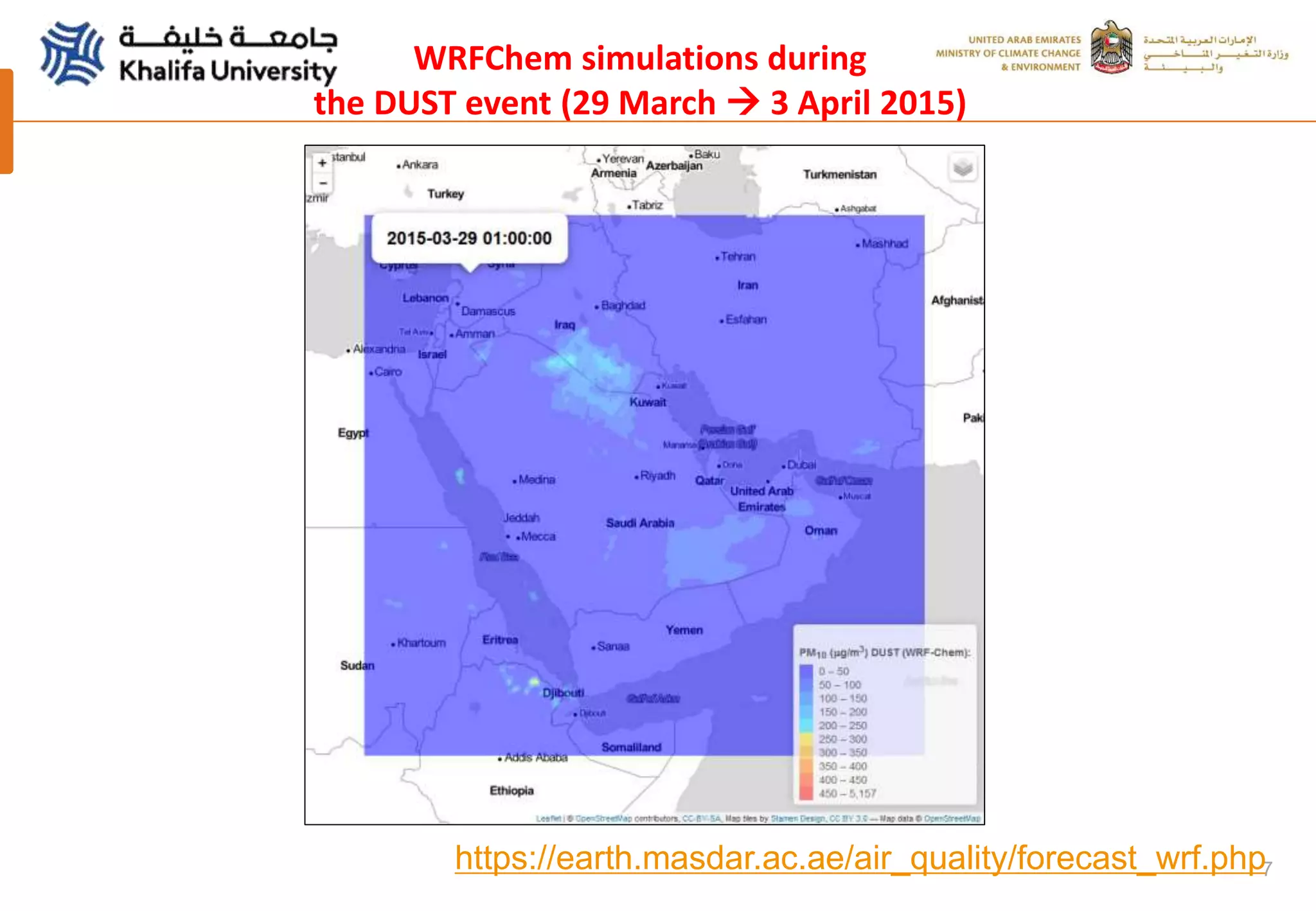
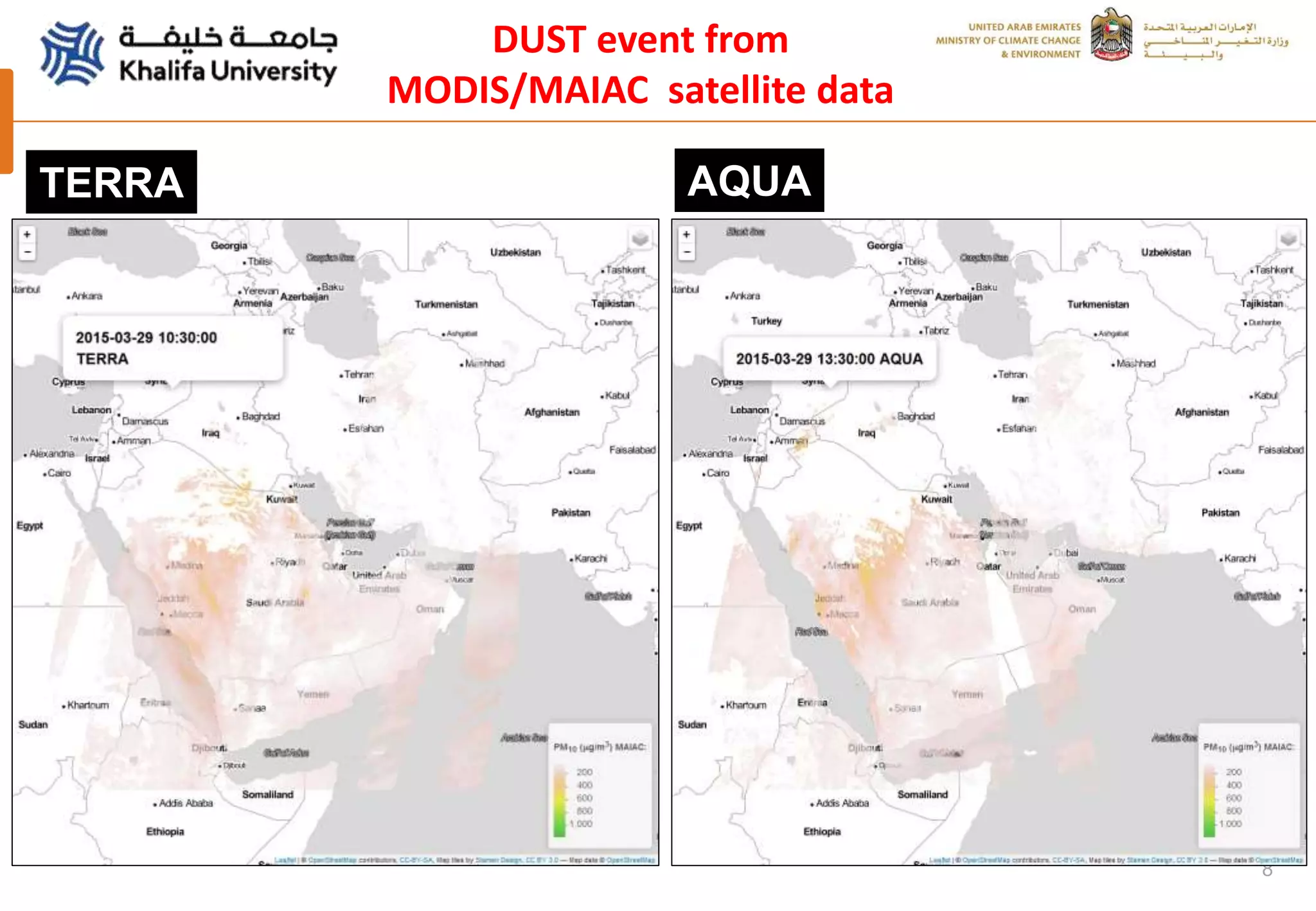
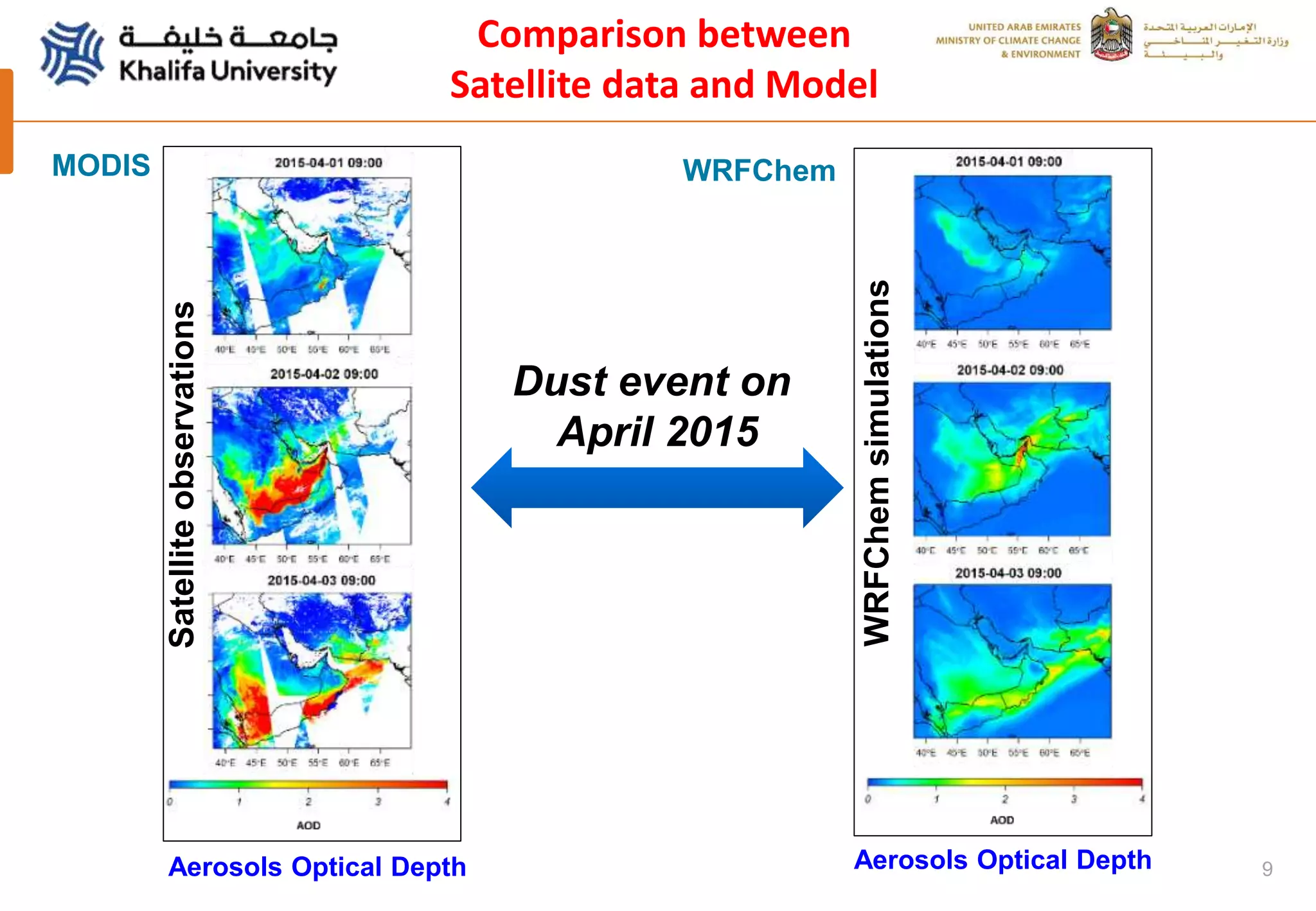
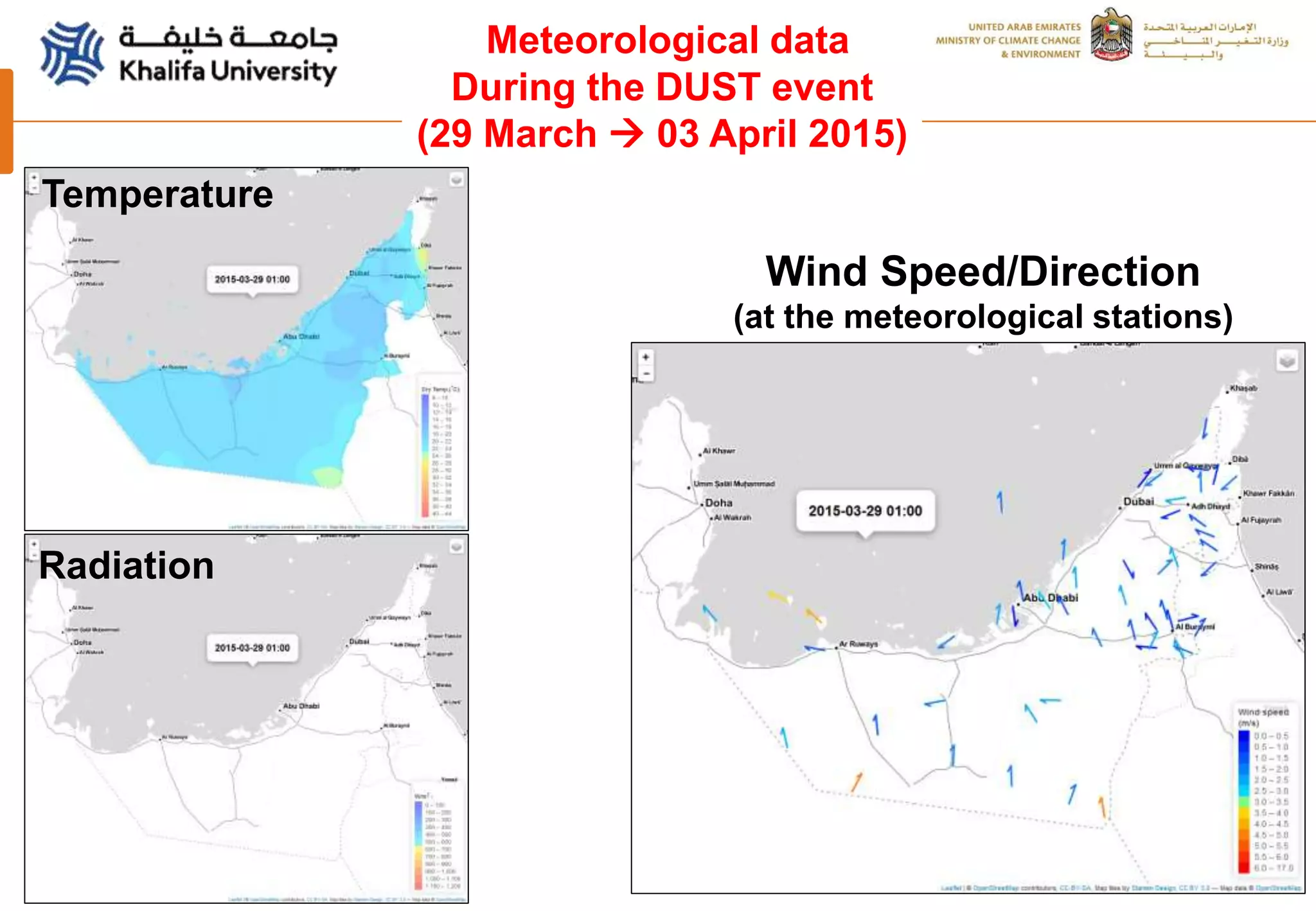
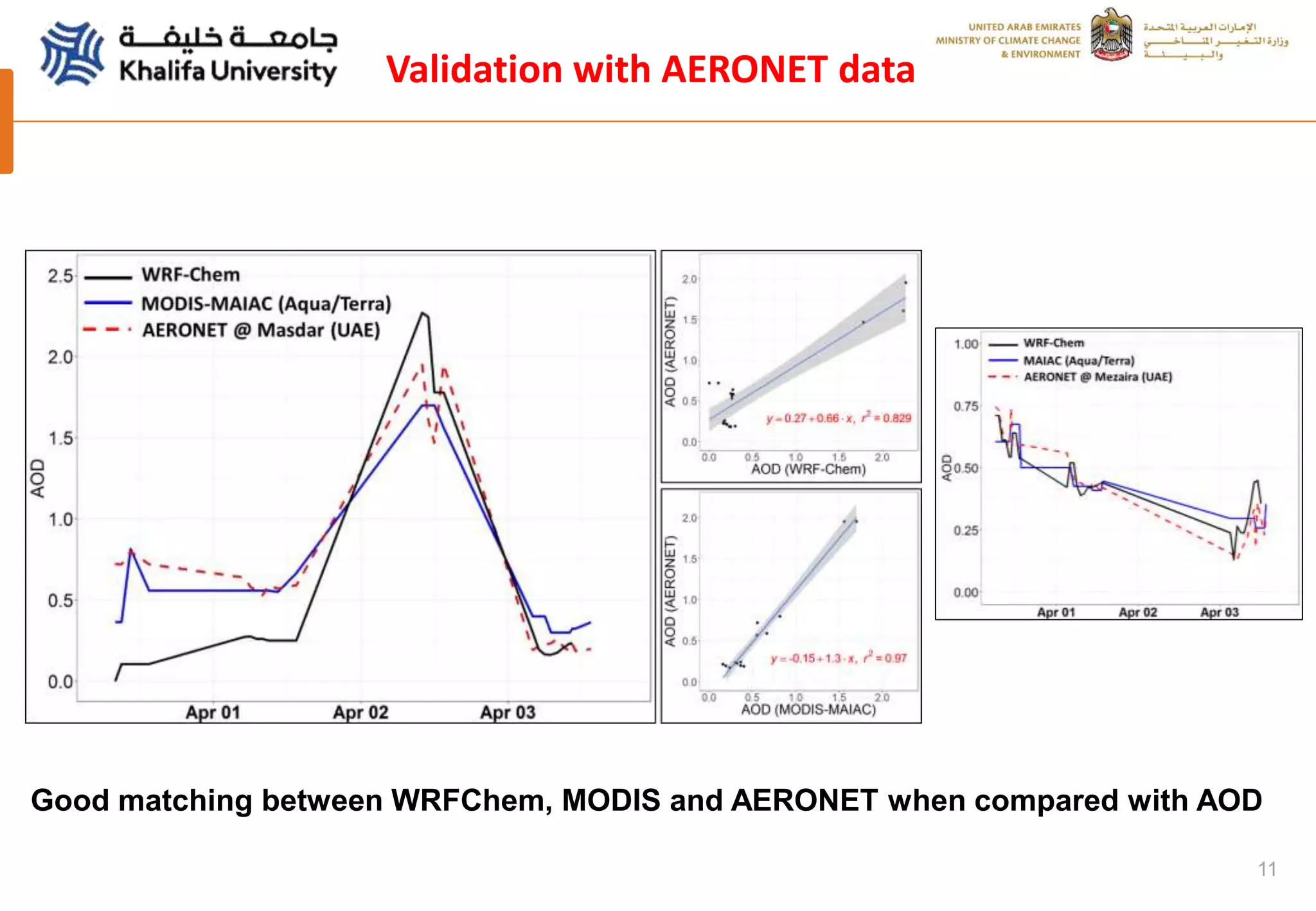
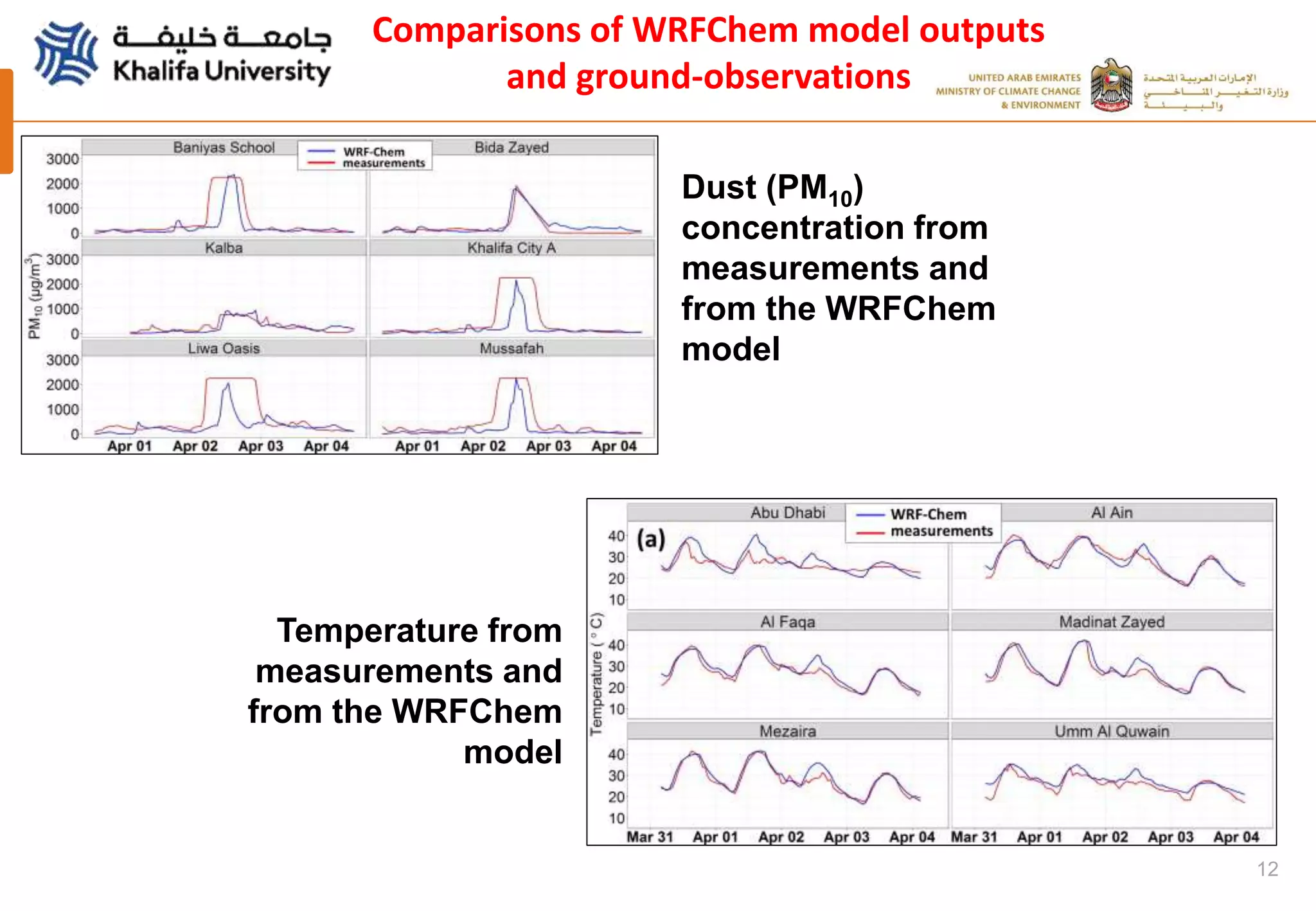
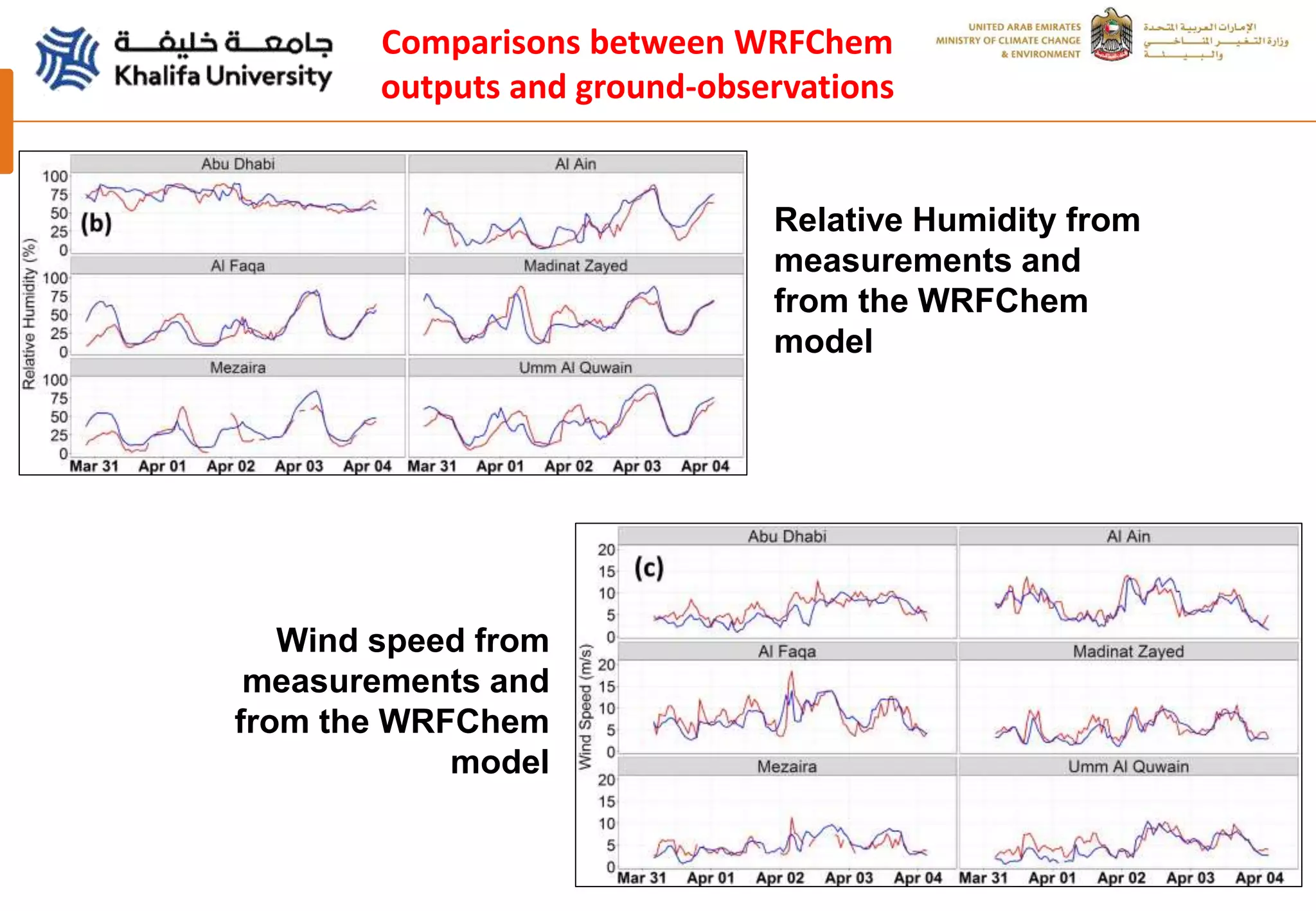
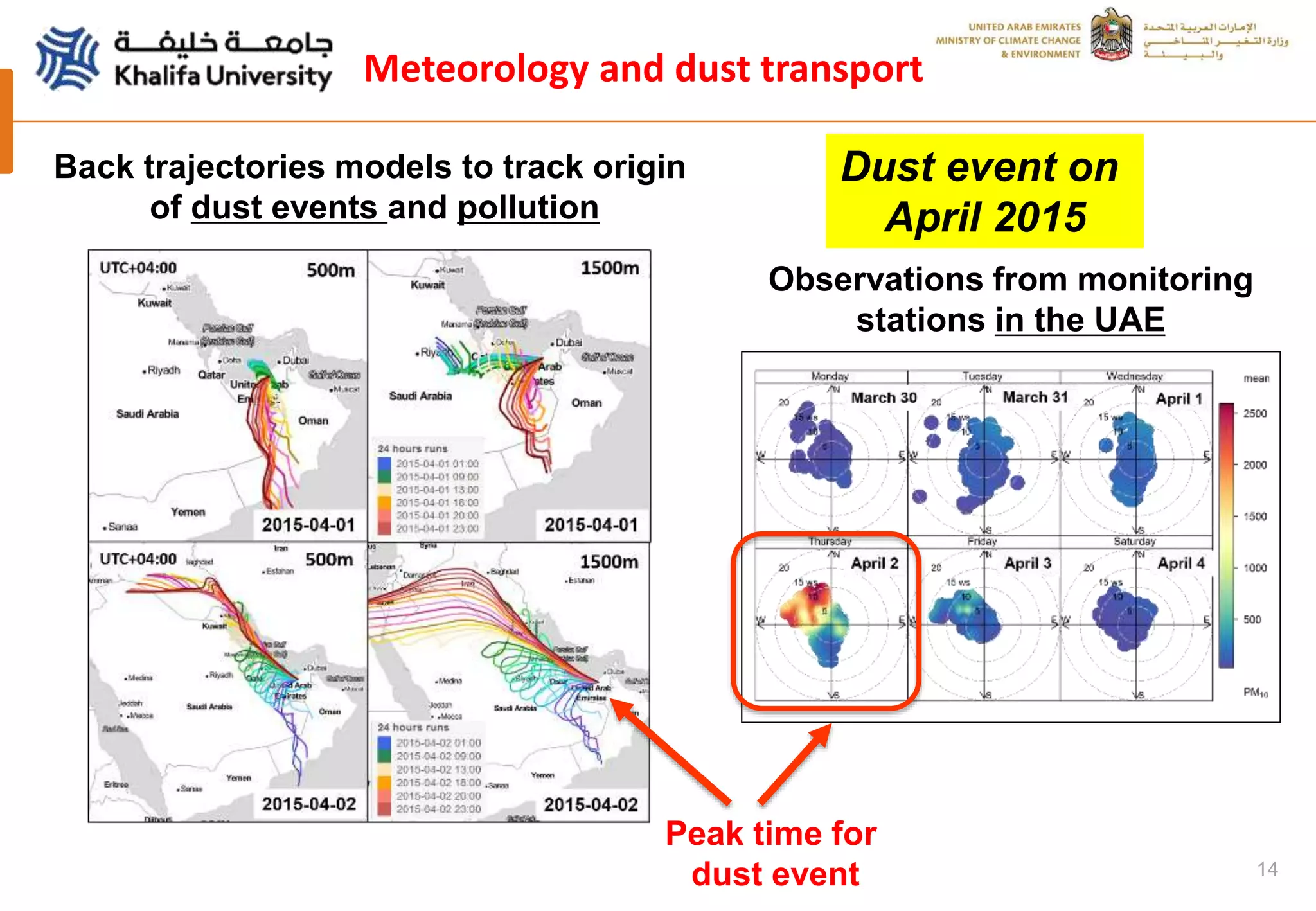
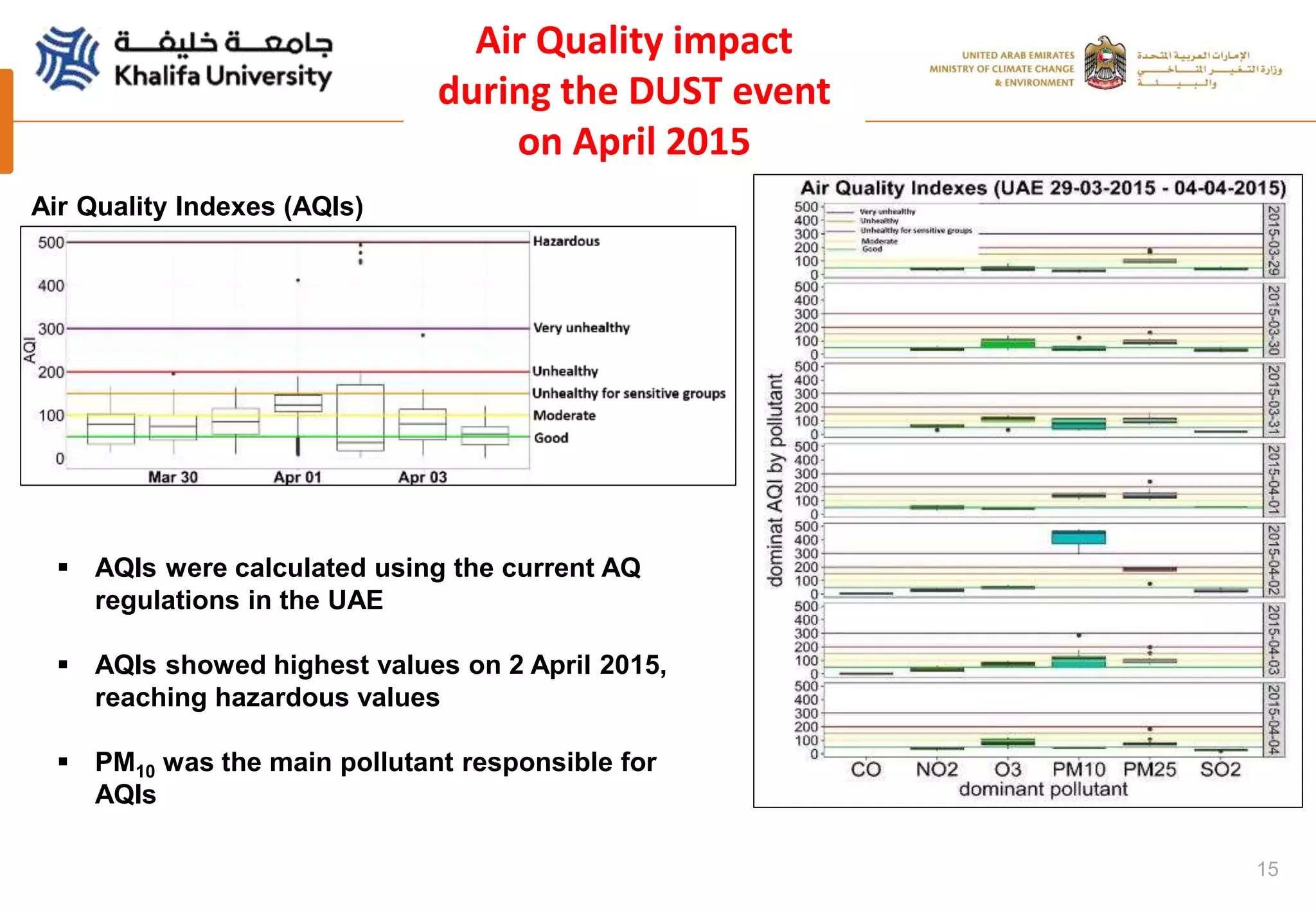
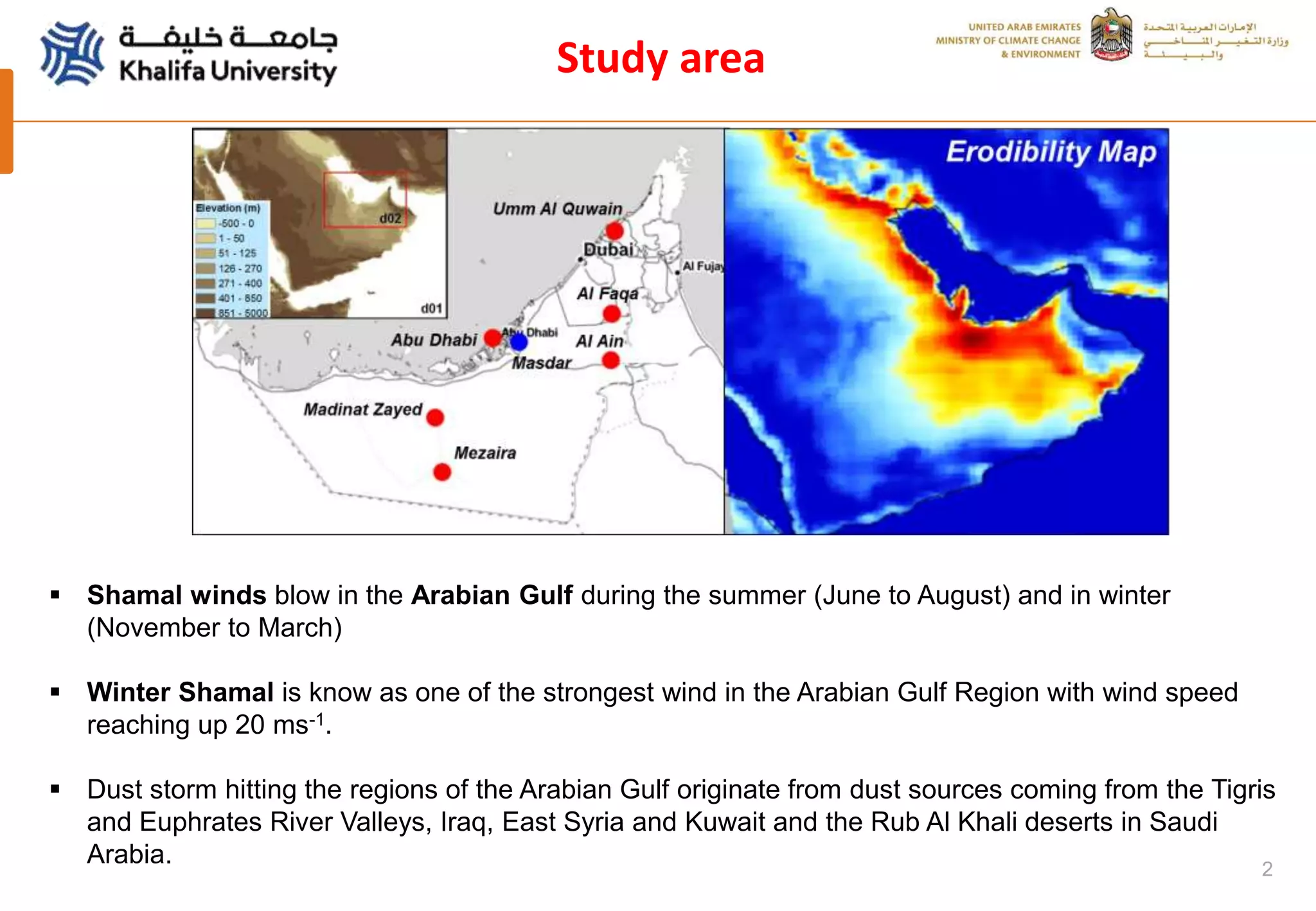
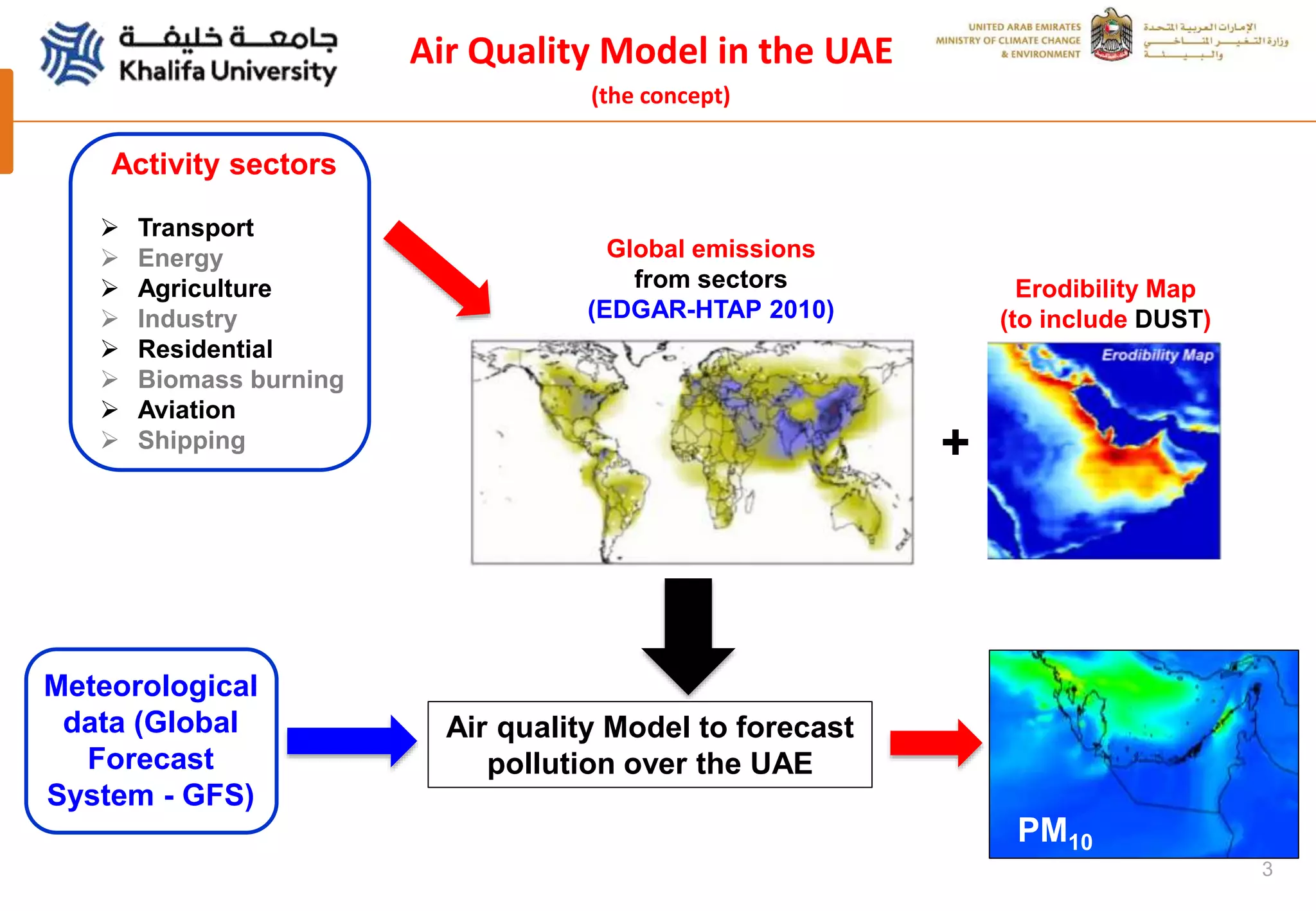
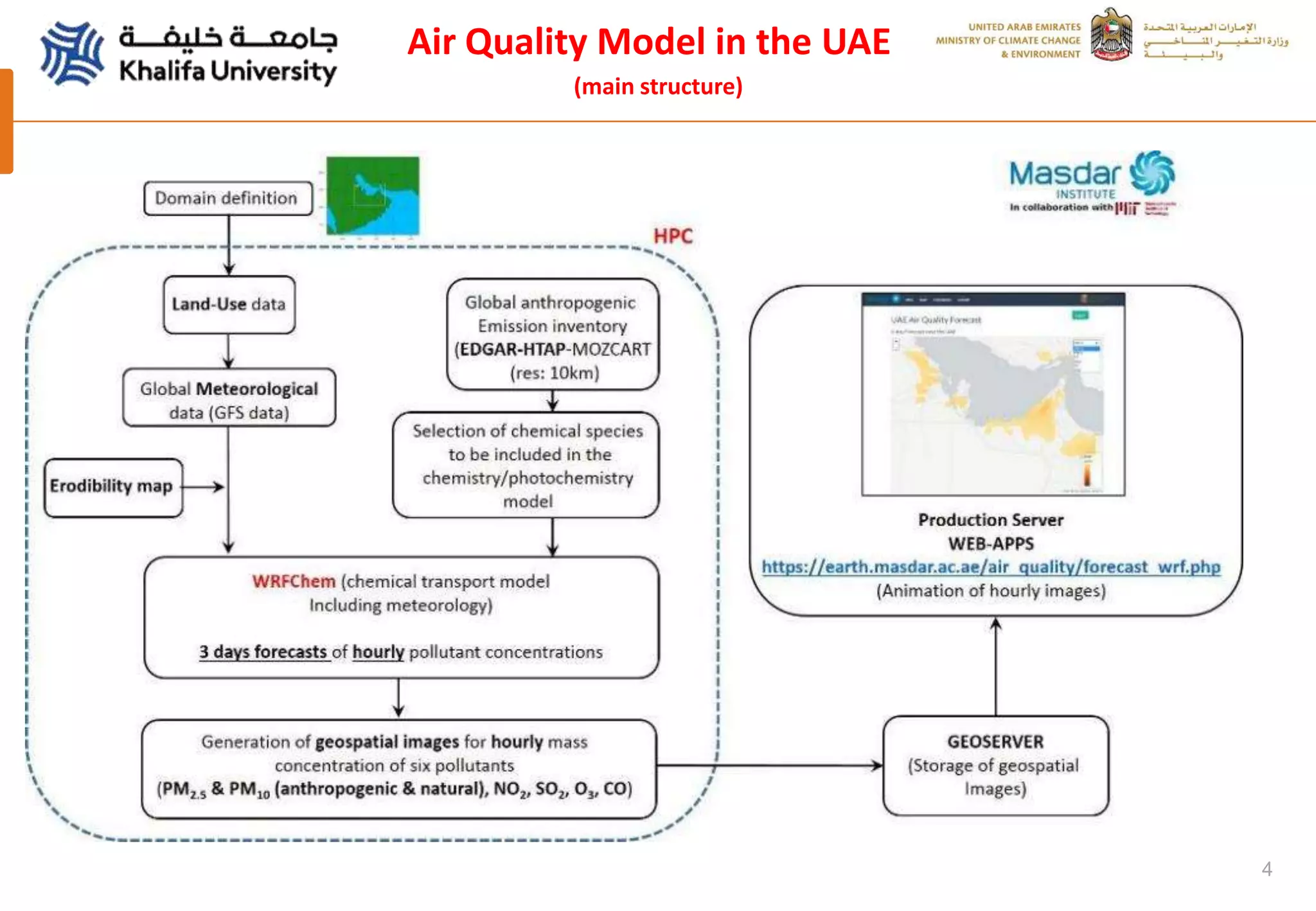
This document summarizes a study analyzing a severe dust storm in the Arabian Peninsula using an air quality model (WRF-Chem), satellite imagery, and ground observations. The study area experiences strong seasonal winds that carry dust from sources in Iraq and Saudi Arabia. The WRF-Chem model was used to simulate meteorology and dust transport during a 2015 dust event, and validated using satellite data, ground measurements, and AERONET data. Model results matched observations and showed dust concentrations and air quality indexes reaching hazardous levels during the event, with PM10 being the main pollutant degrading air quality.

![5
SEVIRI satellite data processing
[1] Martínez, M. A.; Ruiz, J.; Cuevas, E. Use of SEVIRI images and derived
products in a WMO Sand and dust Storm Warning System. IOP Conf. Ser.
Earth Environ. Sci. 2009, 7, 012004, doi:10.1088/1755-1307/7/1/012004
[2] Ashpole Ian; Washington Richard An automated dust detection using
SEVIRI: A multiyear climatology of summertime dustiness in the central and
western Sahara. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2012, 117,
doi:10.1029/2011JD016845.
[3] Banks, J. R.; Brindley, H. E. Evaluation of MSG-SEVIRI mineral dust
retrieval products over North Africa and the Middle East. Remote Sens.
Environ. 2013, 128, 58–73, doi:10.1016/j.rse.2012.07.017
[4] MétéoFrance Algorithm theoretical basis document for cloud products
(CMa-PGE01 v3.2, CT-PGE02 v2.2 & CTTH-PGE03 v2.2). Technical Report
SAF/NWC/CDOP/MFL/ SCI/ATBD/01. Paris: MétéoFrance, 2011.
References
Used two methodologies to process
SEVIRI satellite data:
1) EUMETSAT algorithm
2) MeteoFrance algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dustpresentationkaragulian-190107212209/75/Dust-Detection-in-the-UAE-5-2048.jpg)