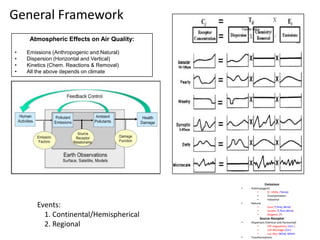
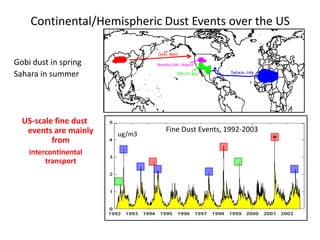
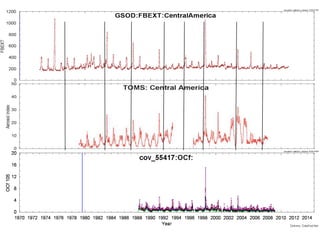
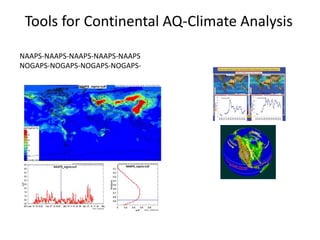
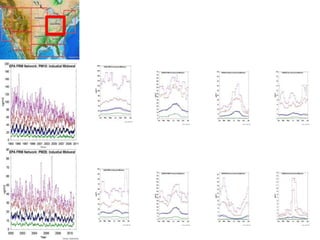
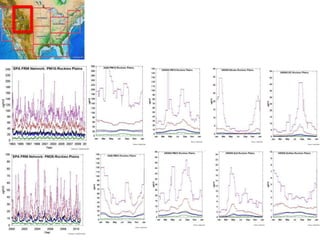
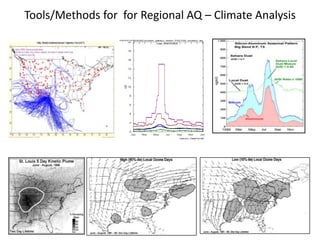
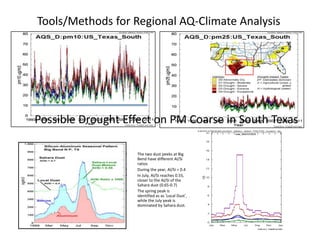
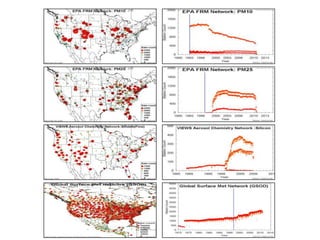
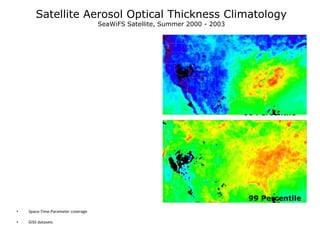
This proposal outlines a study on the influence of weather and climate events on air quality issues like dust, smoke, and sulfate events. The study would examine these events at both the continental/hemispherical scale and regional scale. At the continental scale, the analysis would demonstrate the role of global climate and emissions and identify tipping points for air quality regulations. At the regional scale, the study would analyze the effects of regional emissions, climate, and precipitation on air quality. The proposal describes tools and methods for conducting continental and regional air quality-climate analysis, including models, datasets, and satellite data. The goals are to support air quality management and identify implications for policy.