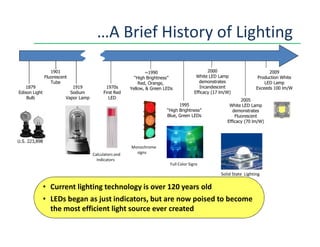
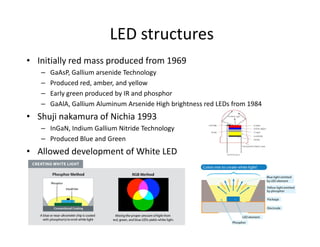
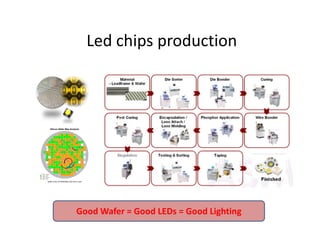
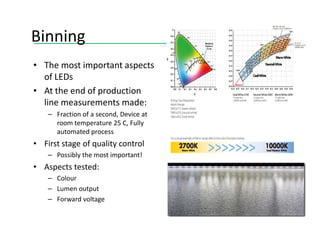
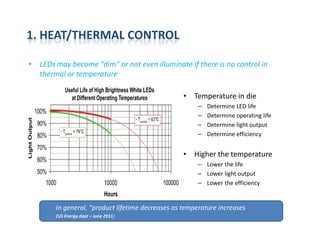
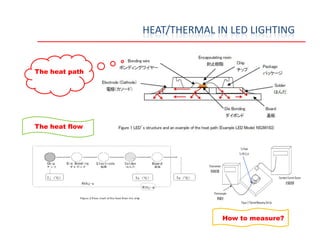
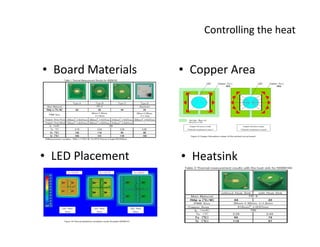
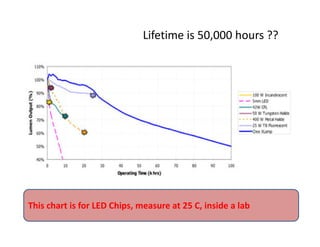
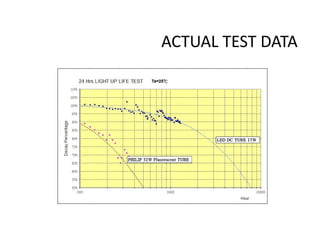
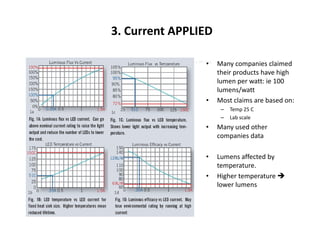
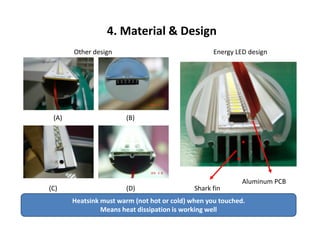
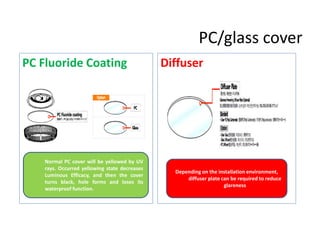
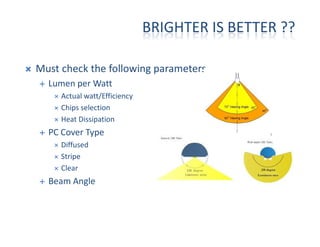
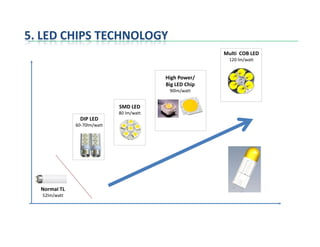
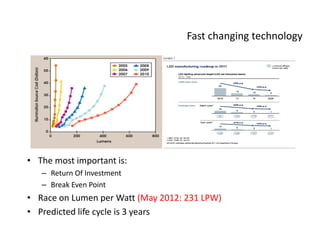
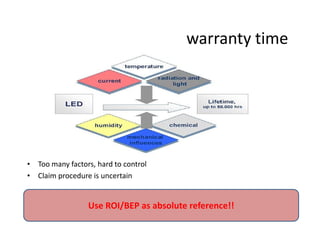
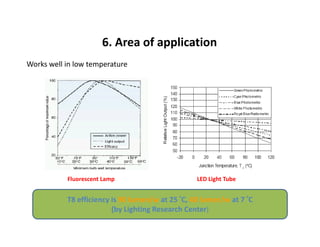
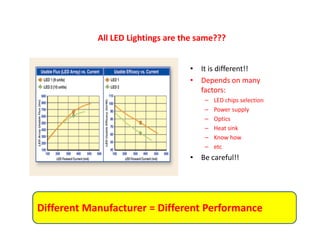
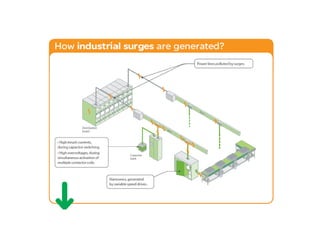
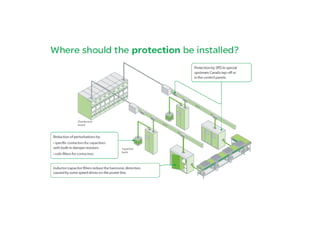
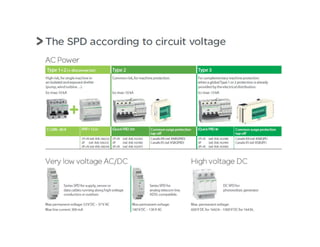
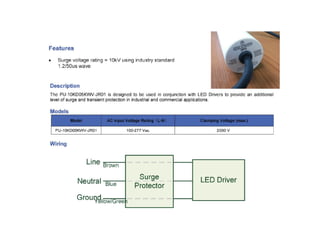
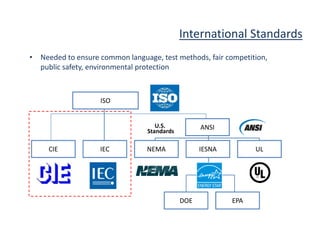
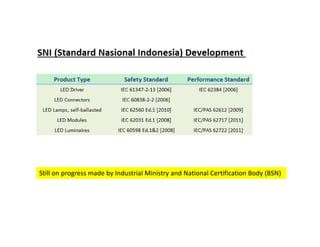
This document provides an overview of LED lighting technology and considerations for LED lighting implementation. It discusses the history of lighting technology leading up to LEDs. It then covers key advantages of LED lights like energy efficiency, longevity, and environmental friendliness. Some challenges of LED technology like heat dissipation, driver lifespan, and rapidly changing performance are also addressed. Recommendations are provided on when LED lighting is appropriate and factors to consider like lumens per watt, heat dissipation design, and chip technology. Standards and certifications for LED products are also briefly discussed.