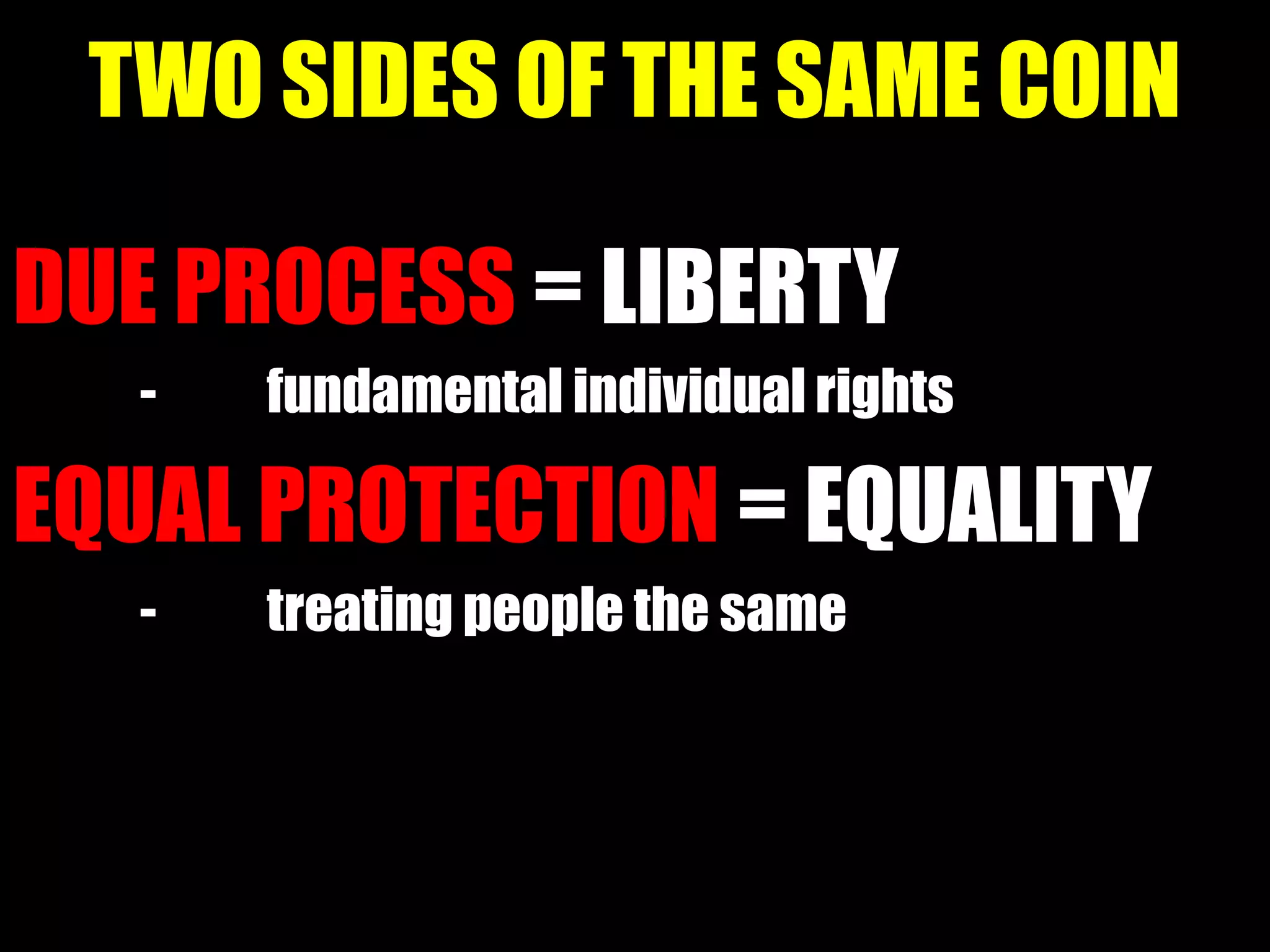
This course aims to help students understand key concepts related to human rights such as historical influences, major international declarations, and individual rights guaranteed by constitutions. Specifically, students will learn about the definition of terms like due process, equal protection, and freedom of expression as outlined in the Philippine Constitution's Bill of Rights. They will also gain an appreciation of the importance of protecting individual rights and applying principles of legal documents.