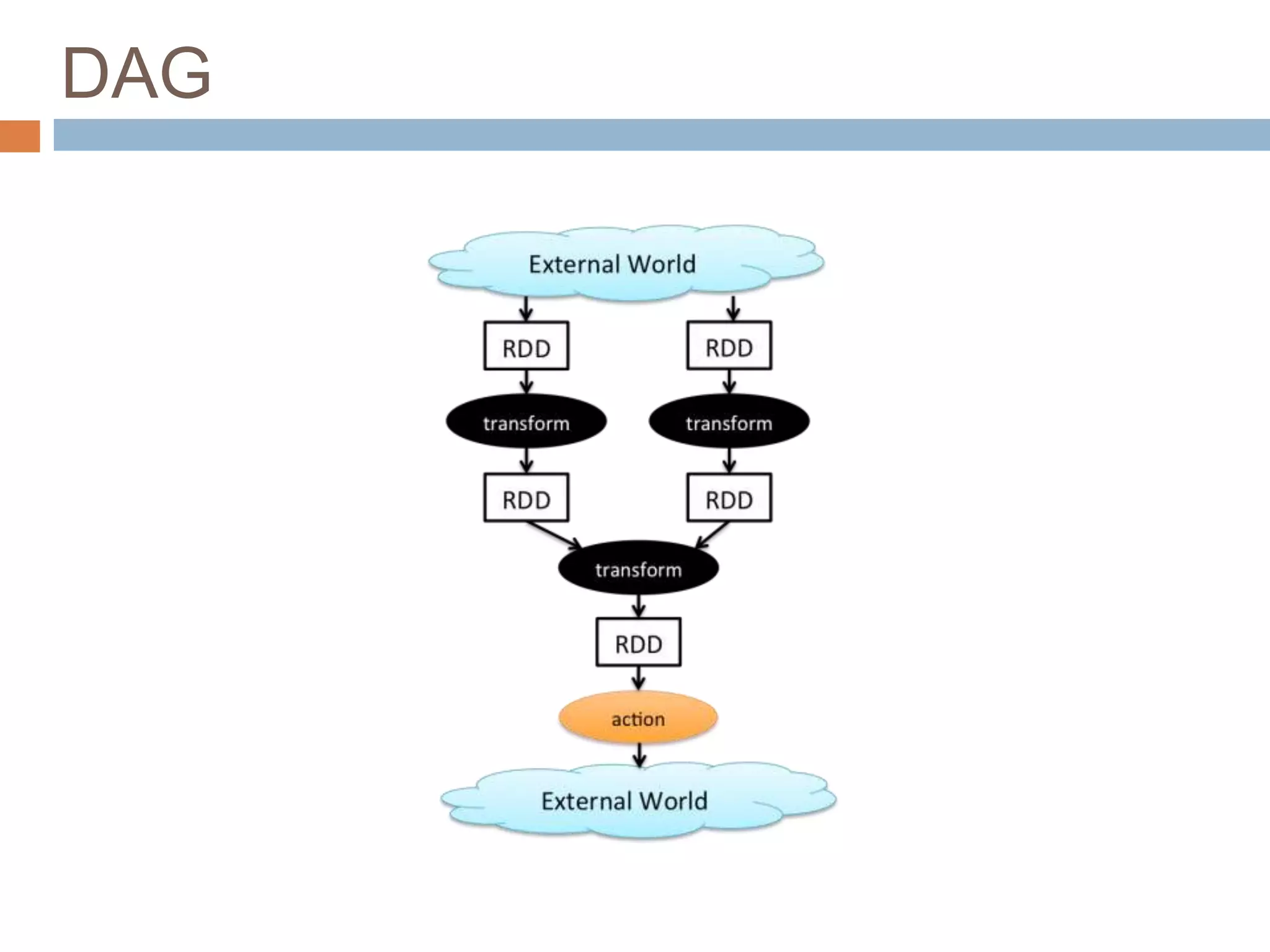
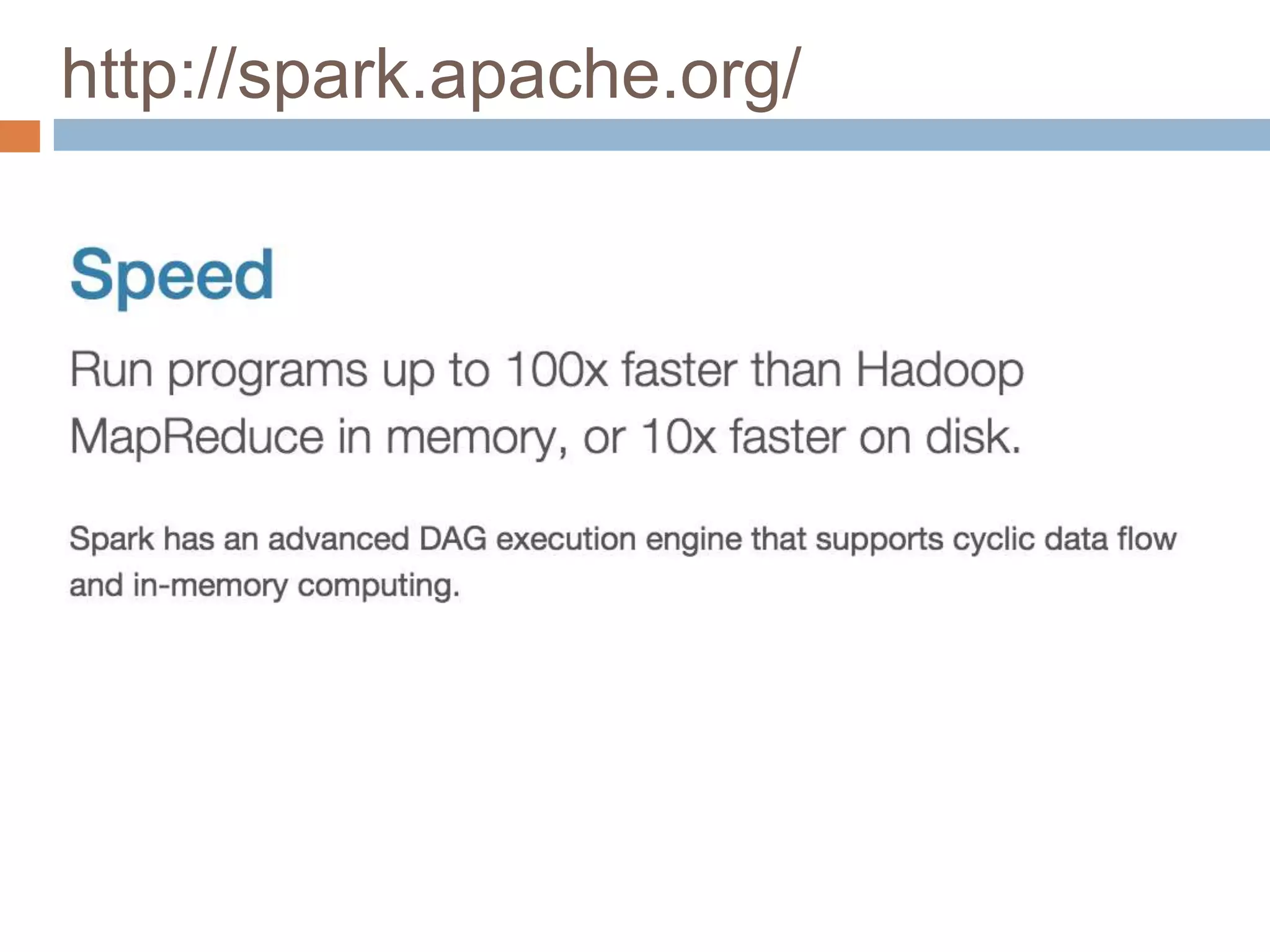
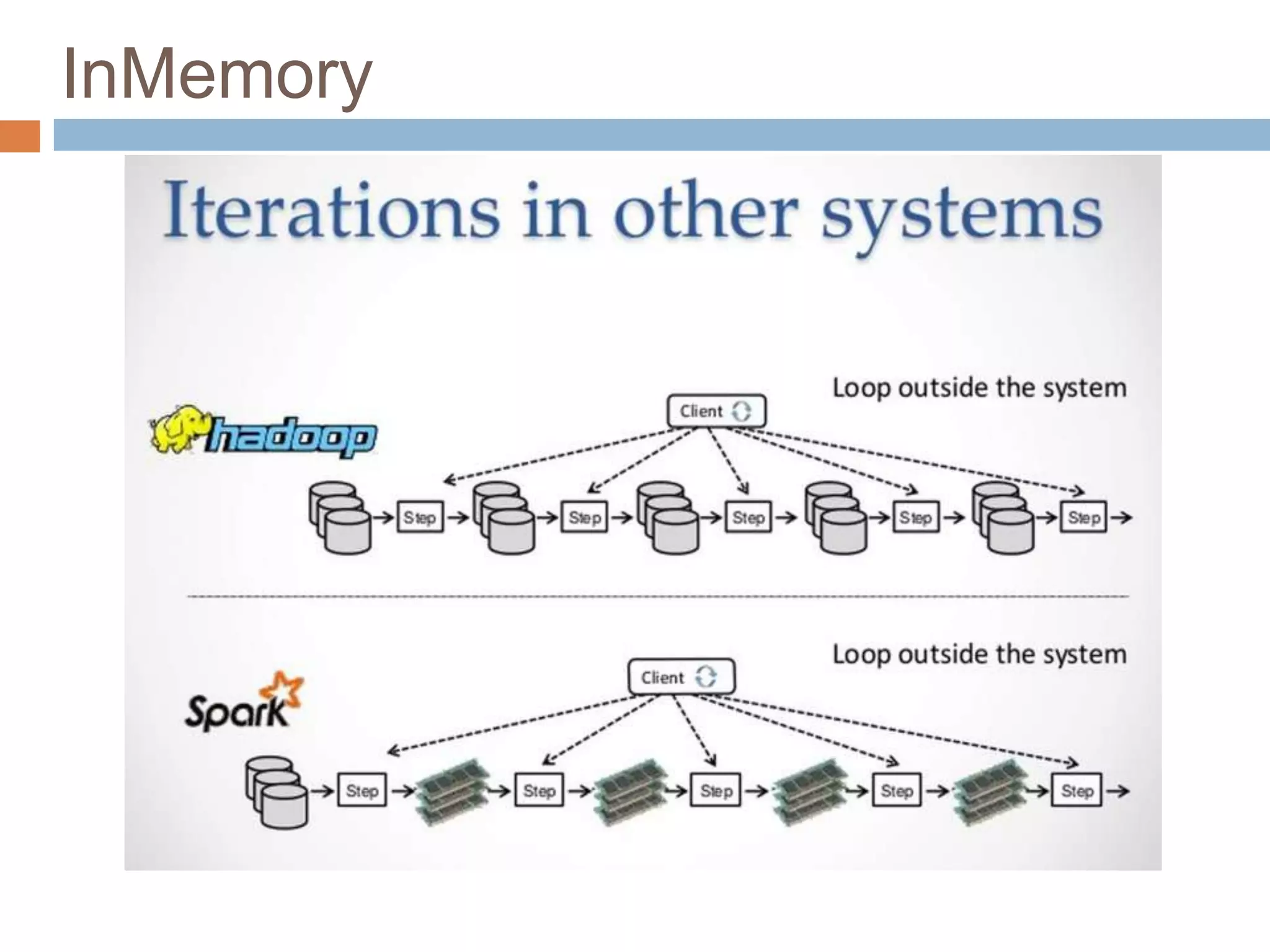
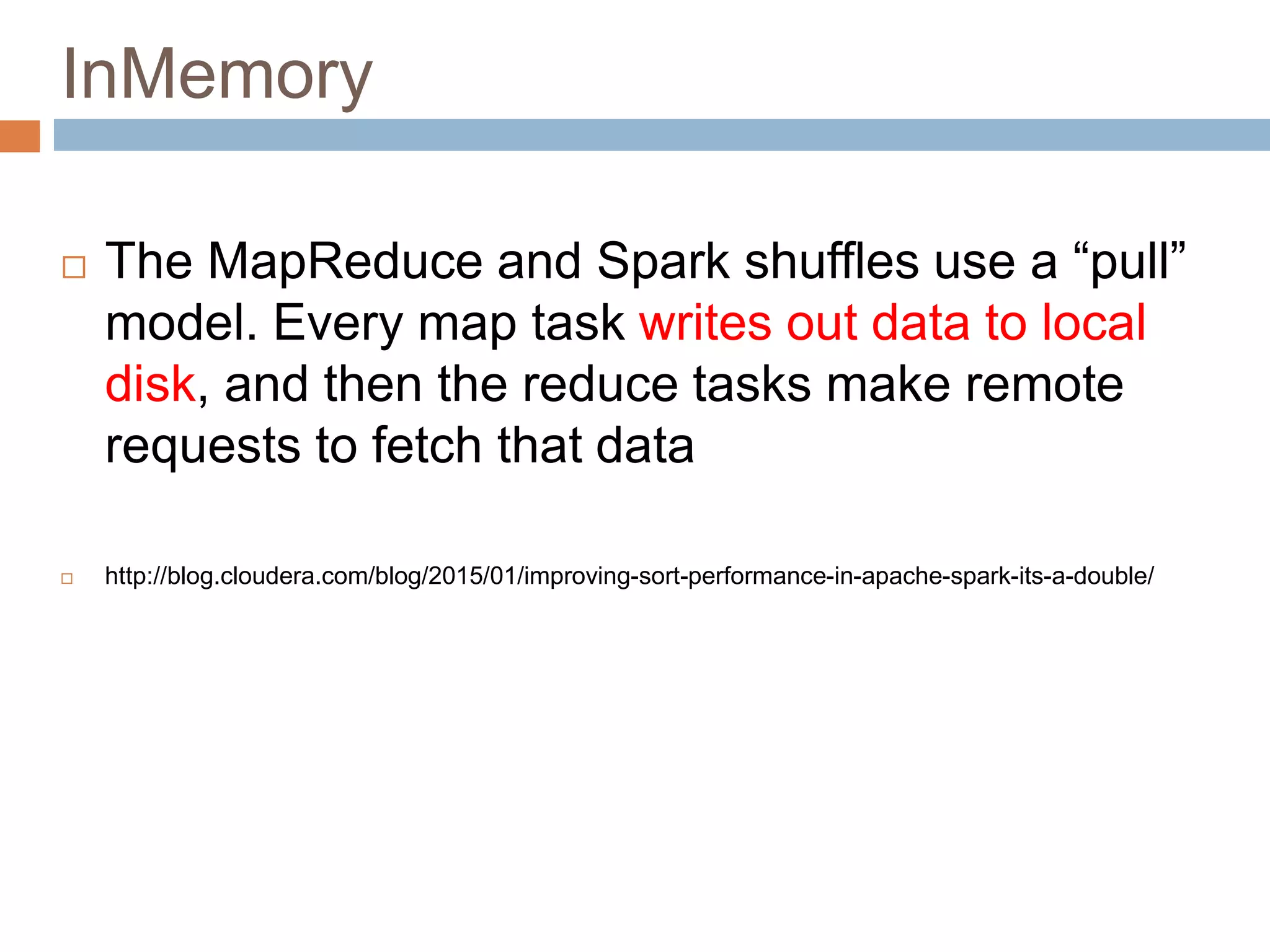
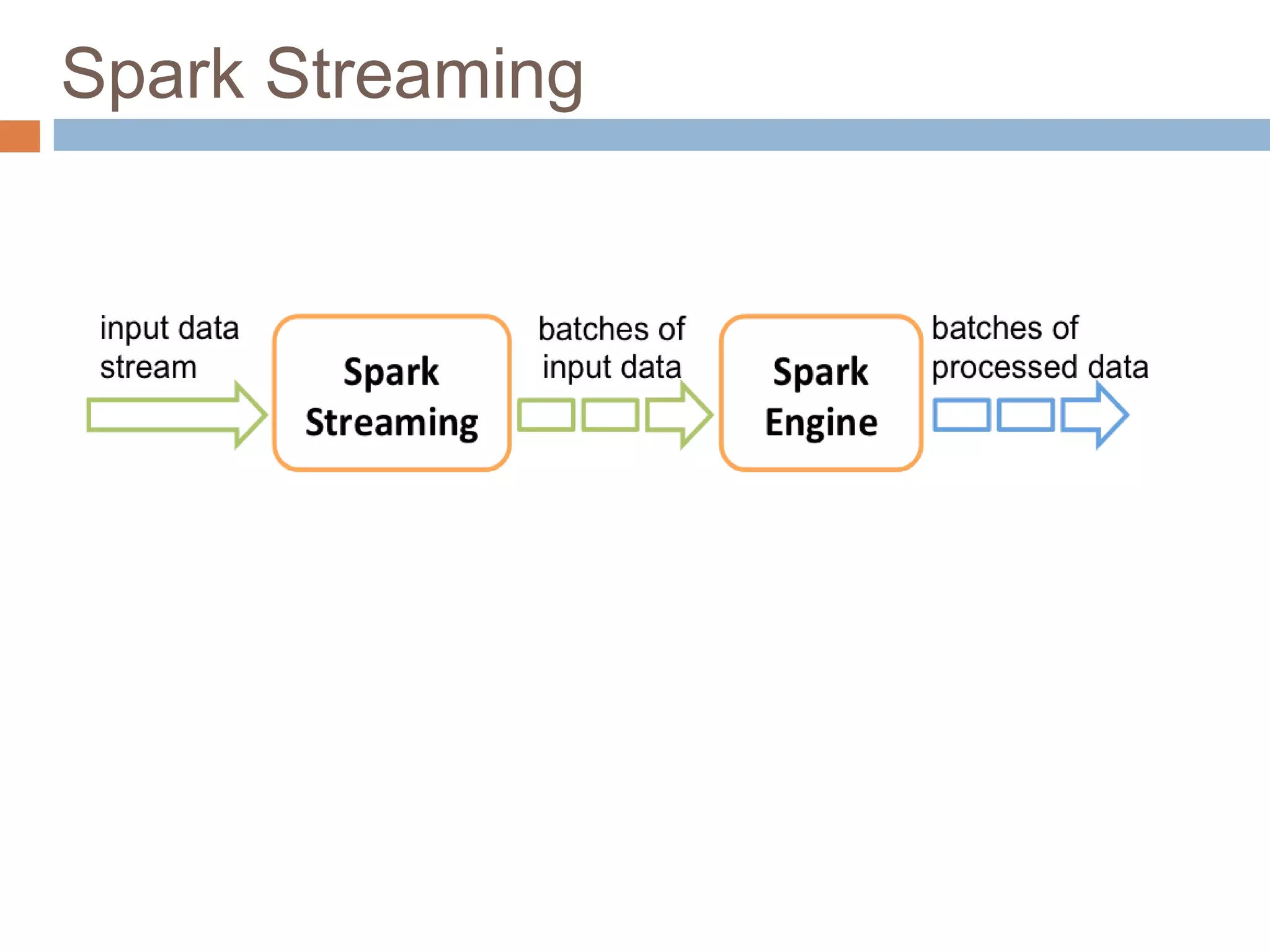
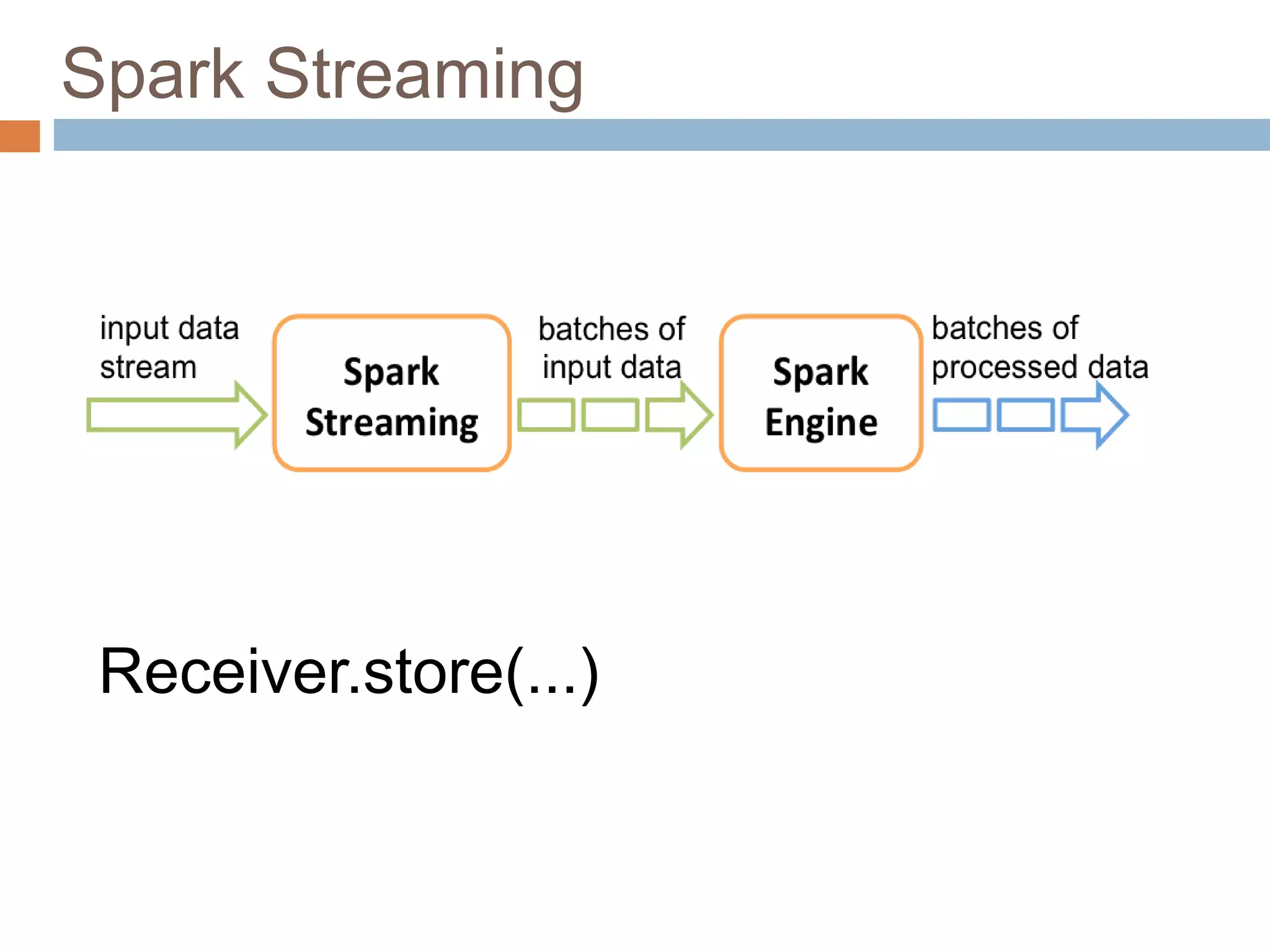
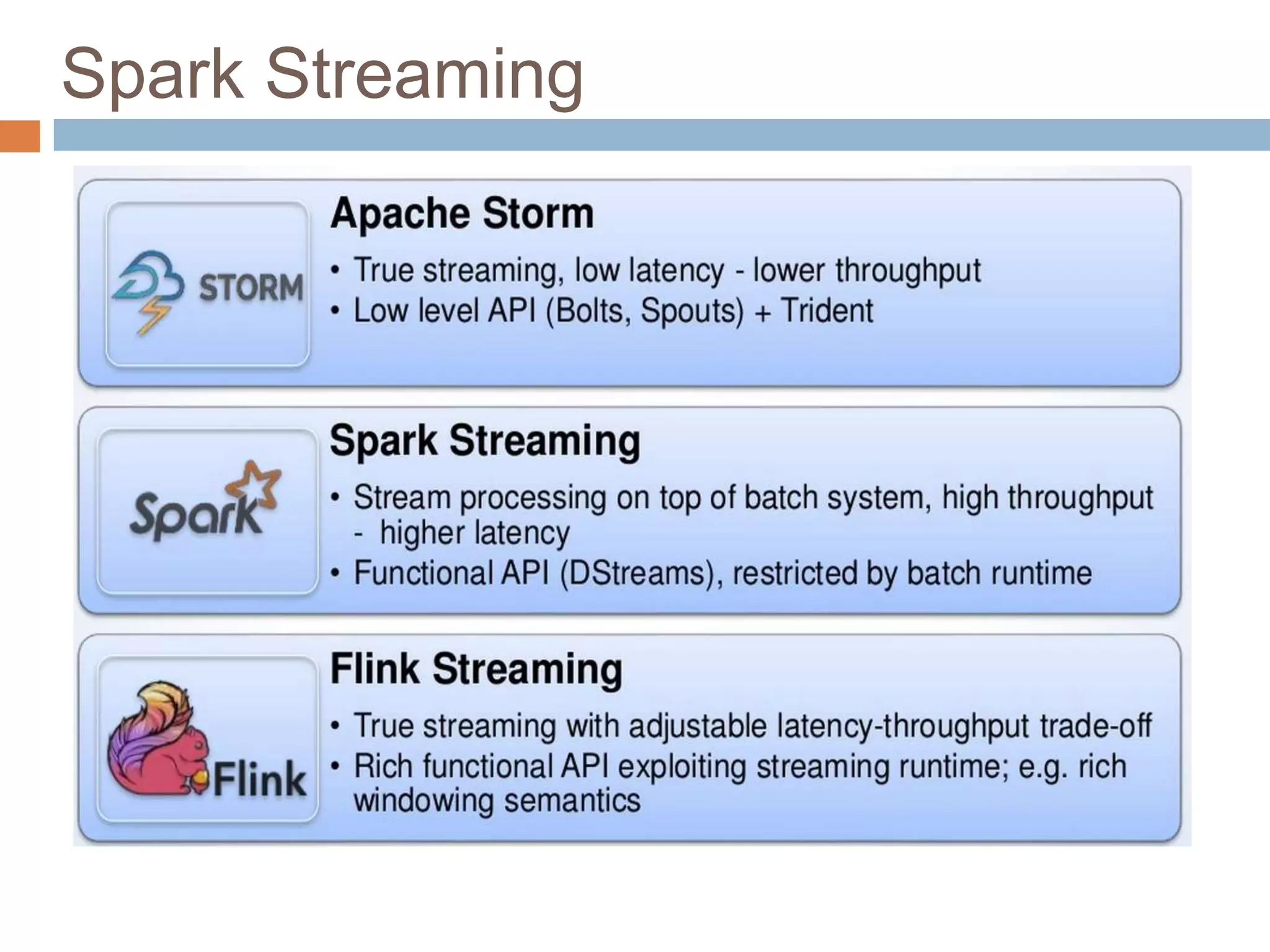
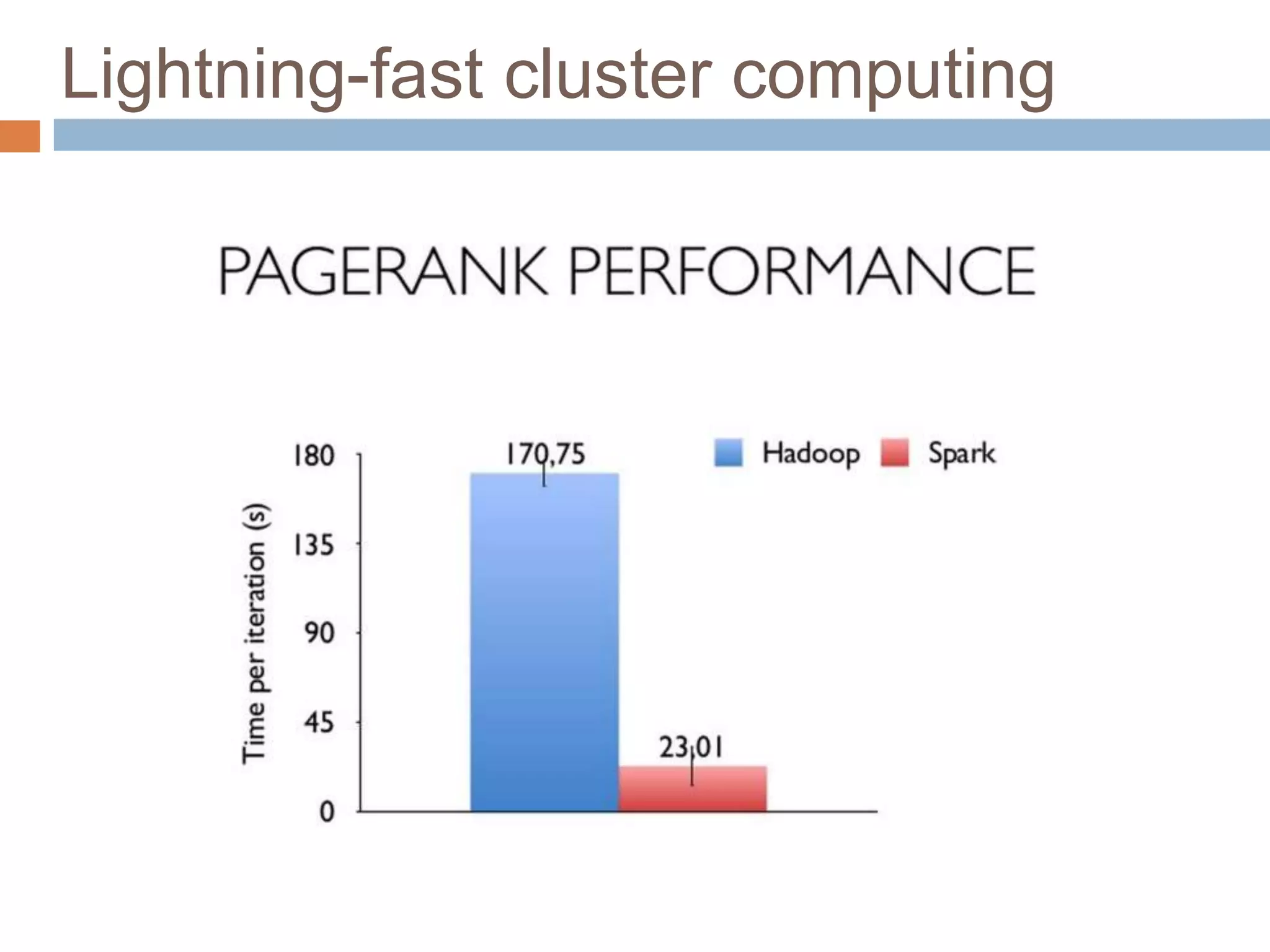
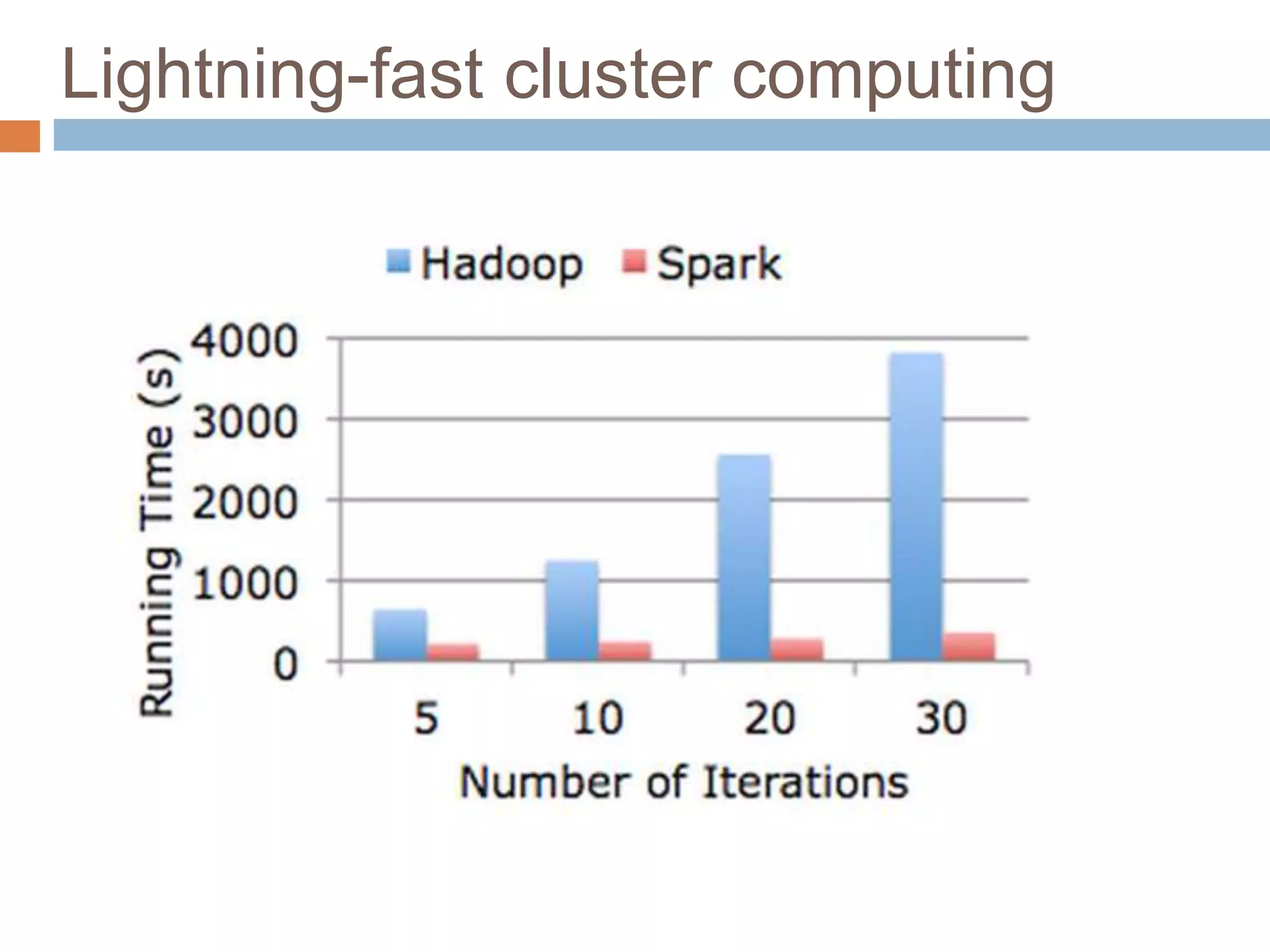
The document provides an overview of Apache Spark, emphasizing its ability to run programs significantly faster than MapReduce, with speeds up to 100x in memory and 10x on disk. It highlights Spark's functionalities, including resilient distributed datasets (RDDs), Spark Streaming for real-time data processing, and related technologies such as Google Cloud Dataflow. Additionally, the document touches on performance optimization techniques and mentions various resources and APIs associated with Spark.
















![Memory
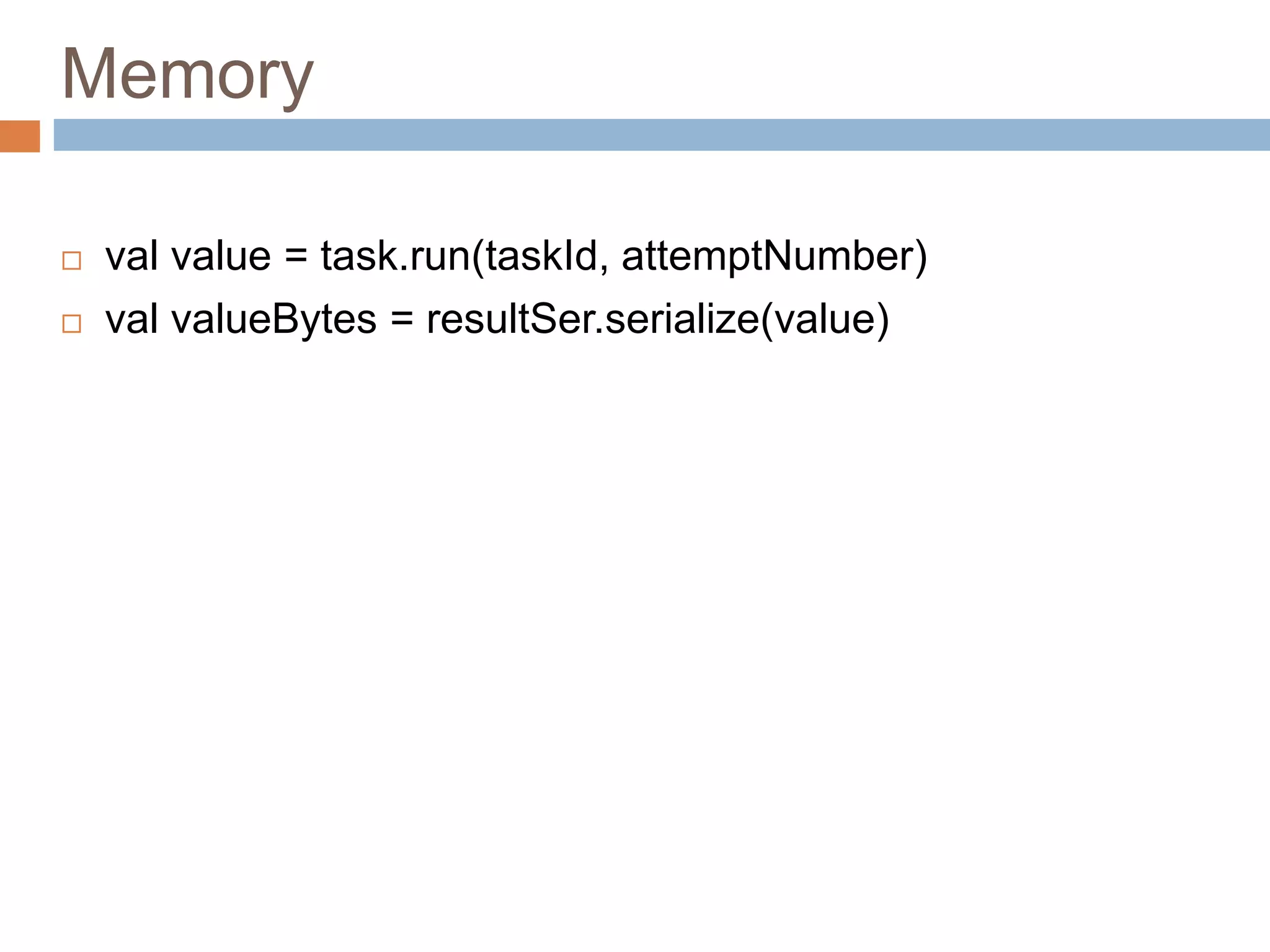
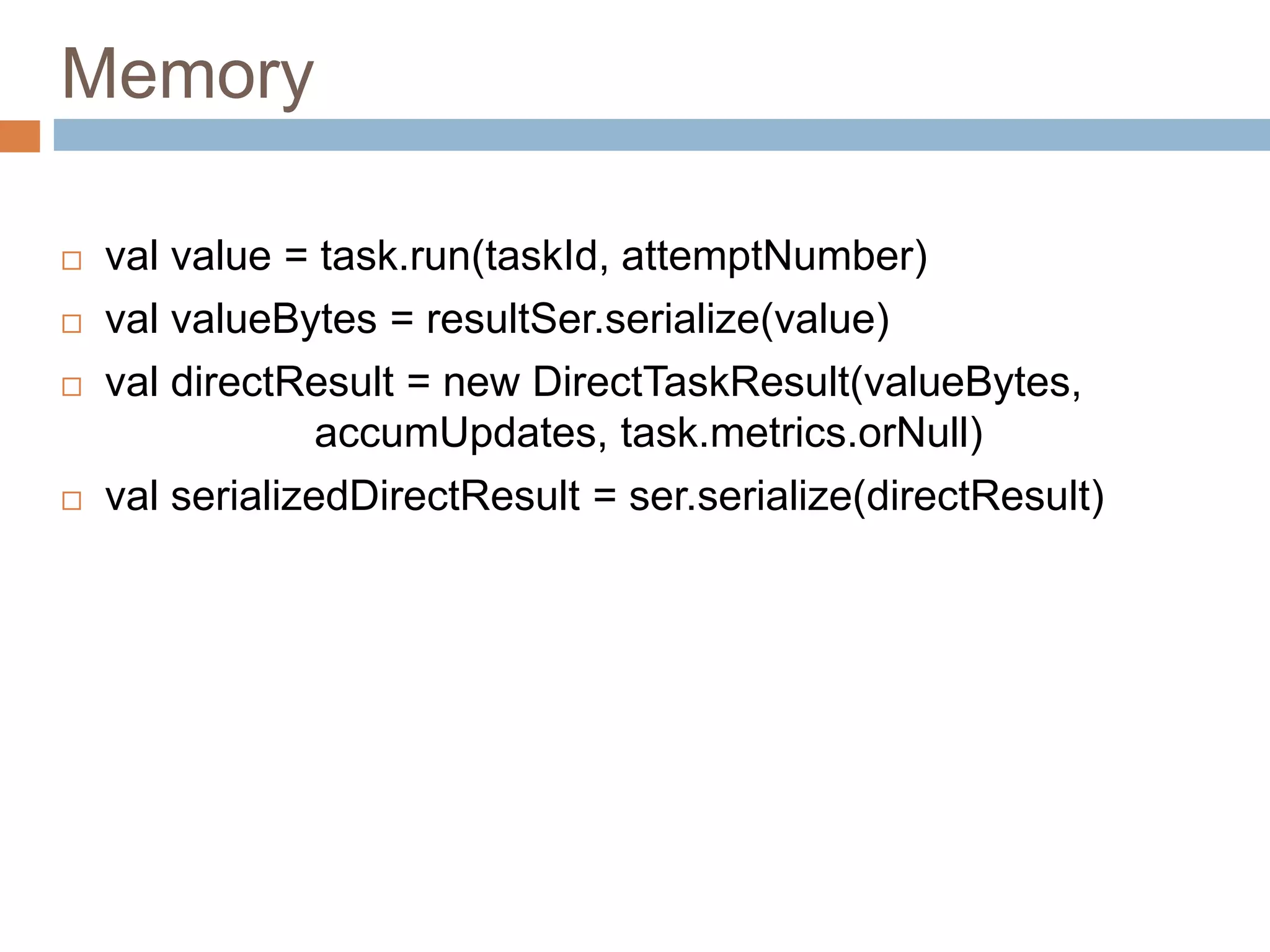
val value = task.run(taskId, attemptNumber)
val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value)
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes,
accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull)
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
Default JavaSerializer
public synchronized byte toByteArray()[] {
return Arrays.copyOf(buf, count);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-150326065657-conversion-gate01/75/Spark-42-2048.jpg)