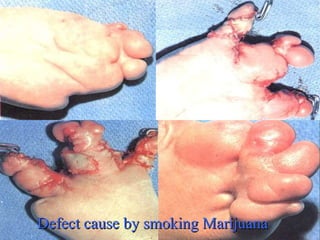
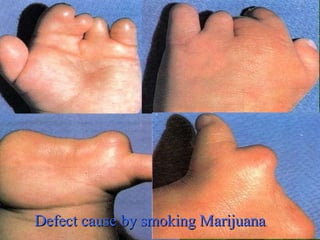
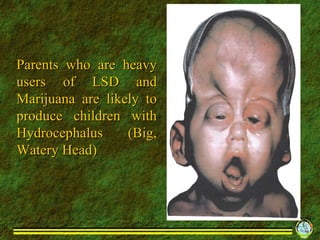
The document discusses various topics related to drug use including:
1. It profiles the typical drug user as being male, aged 15-29, and using shabu which was typically introduced by friends between ages 15-19.
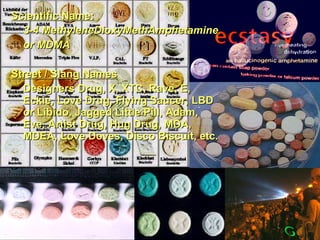
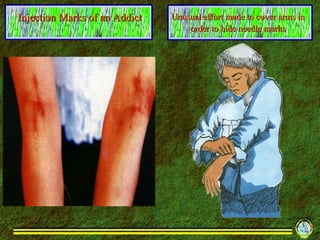
2. It describes different forms drugs can take and methods of ingestion including orally, through inhalation, and injection.
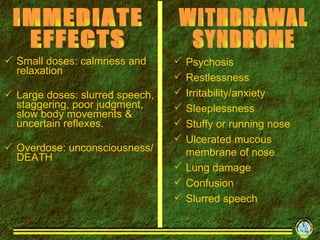
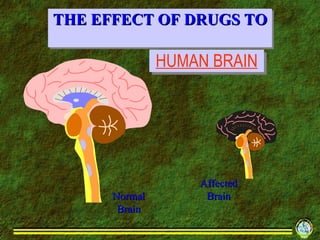
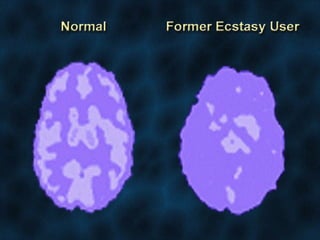
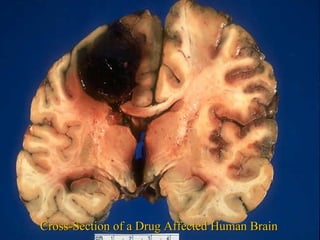
3. It outlines various short-term and long-term effects of different drug types like stimulants, depressants, hallucinogens and others.
4. It also discusses signs of drug use like changes in behavior, mood, and appearance as well as common reasons for drug abuse like family and peer problems.