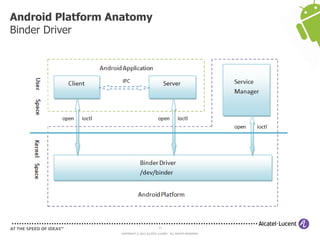
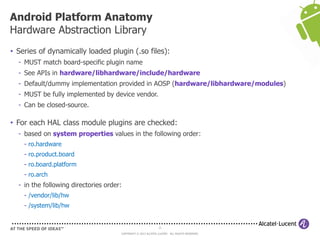
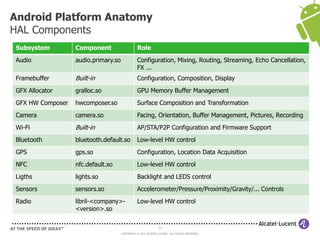
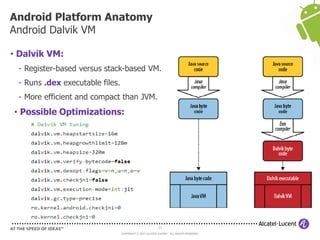
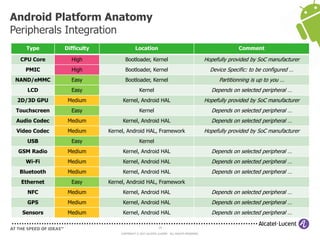
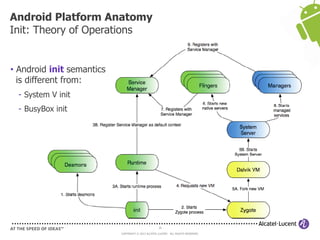
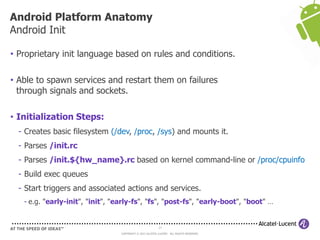
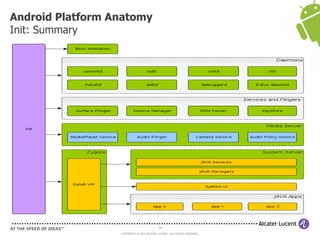
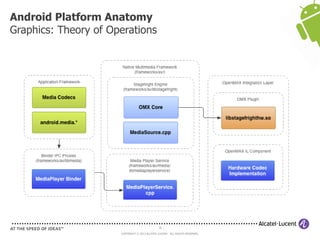
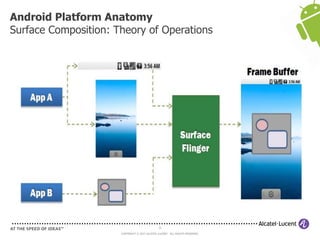
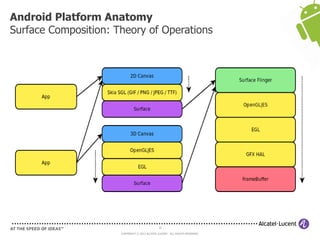
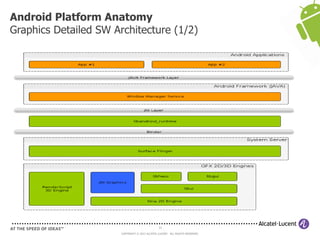
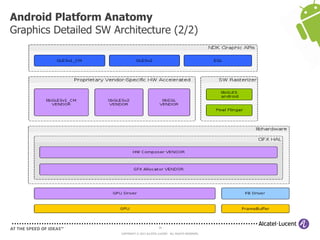
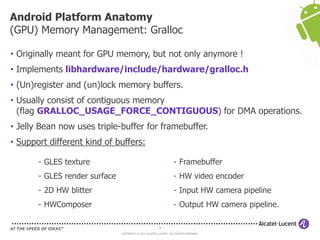
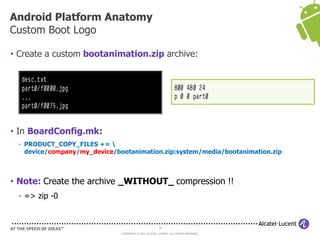
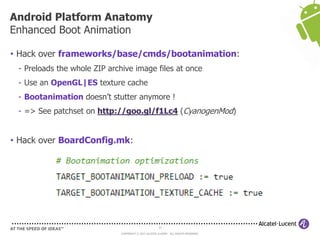
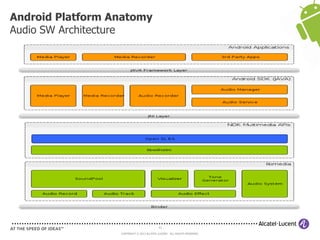
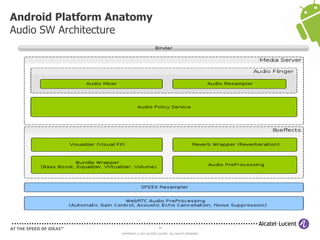
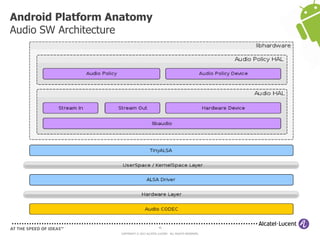
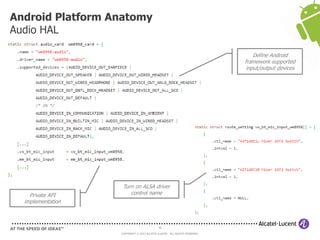
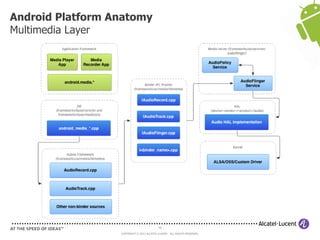
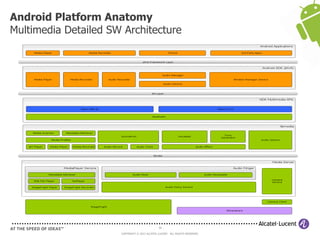
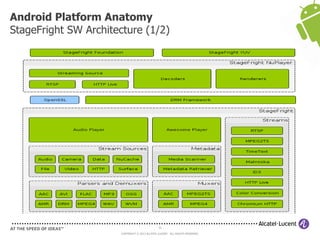
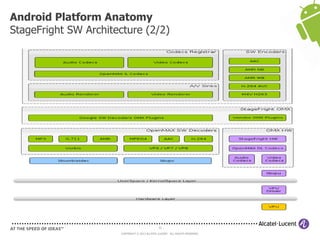
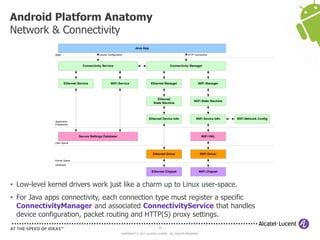
The document discusses Benjamin Zores' presentation on Android platform anatomy. It includes an overview of Zores' background and experience with Android and open source projects. It then covers topics like the history of Android releases, the Android system architecture, sources for Android development, the device porting process, hardware requirements, and components of the Android kernel and user-space.