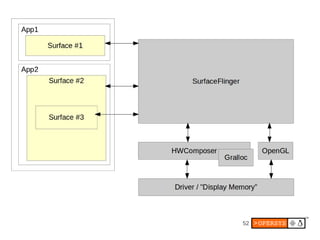
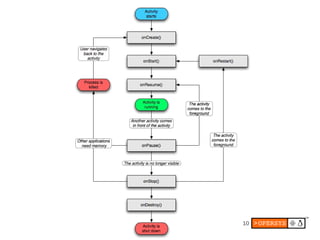
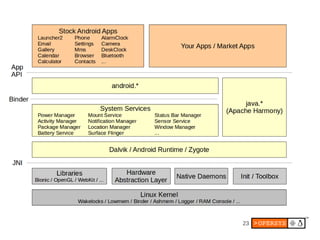
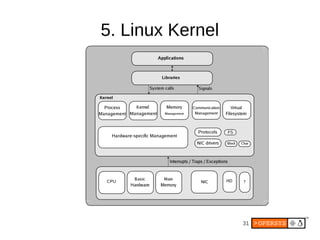
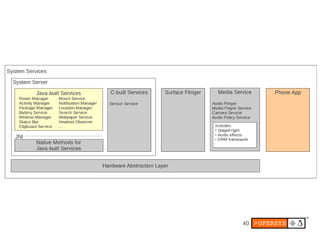
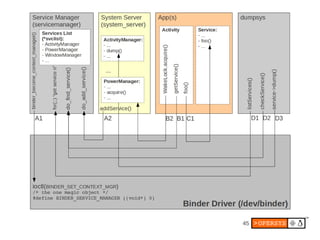
The document provides an overview of Android internals, covering aspects such as its architecture, system startup, and development components. It details Android concepts, including application components, intents, and the lifecycle of processes, as well as security permissions and native development. Additionally, it examines the Android framework, system services, and hardware support necessary for building applications on the Android platform.


































![14. Hardware Abstraction Layer
/frameworks/base/core/...
/frameworks/base/services/java/...
AOSP-provided
ASL
/frameworks/base/services/jni/
/hardware/libhardware/
/device/[MANUF.]/[DEVICE]
Manuf.-provided /sdk/emulator/
Manuf. license
Kernel or module
Manuf.-provided
GPL-license
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embedded-android-workshop-part1-130304-130305003324-phpapp02/85/Android-Internals-at-Linaro-Connect-Asia-2013-46-320.jpg)