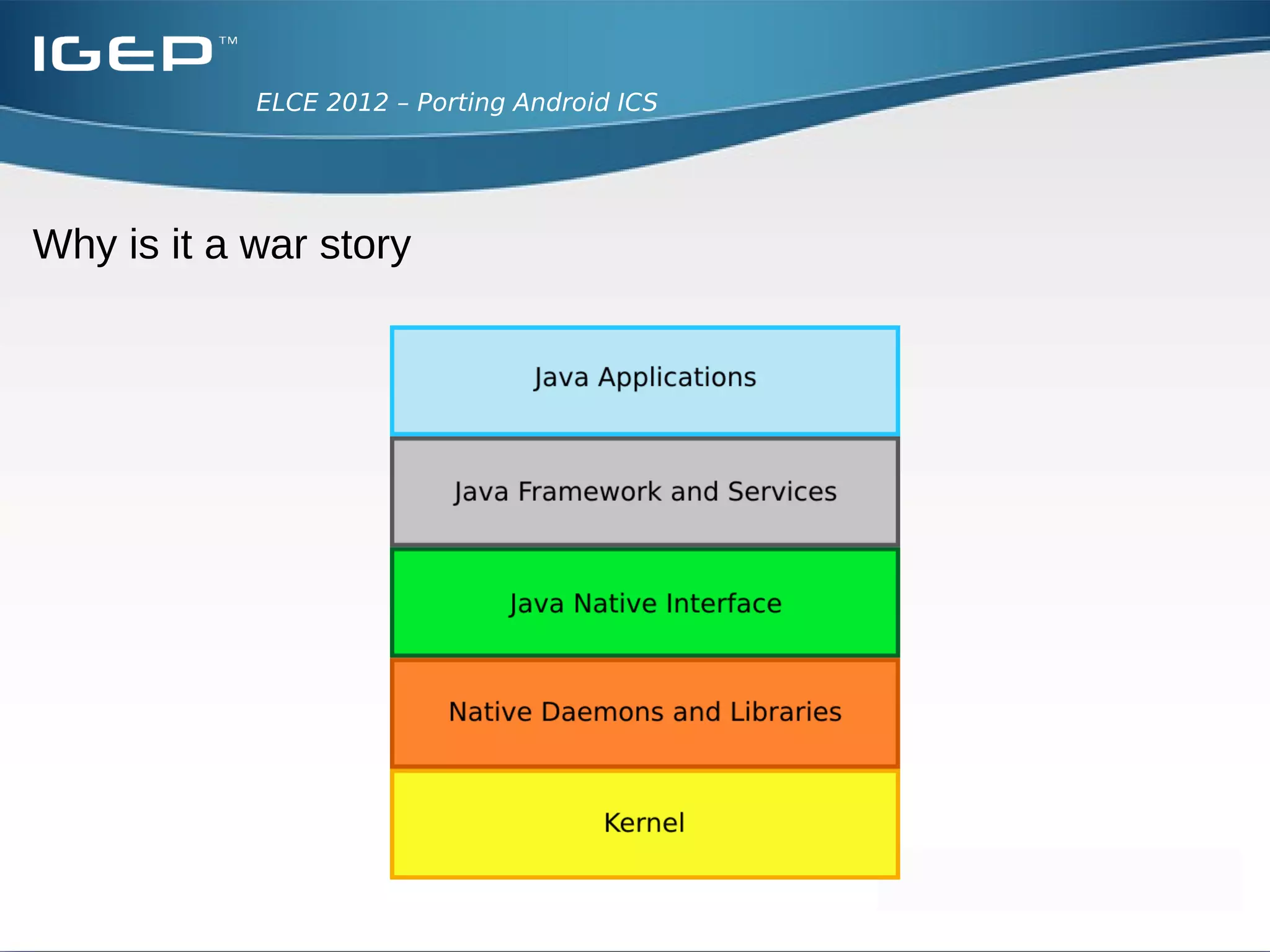
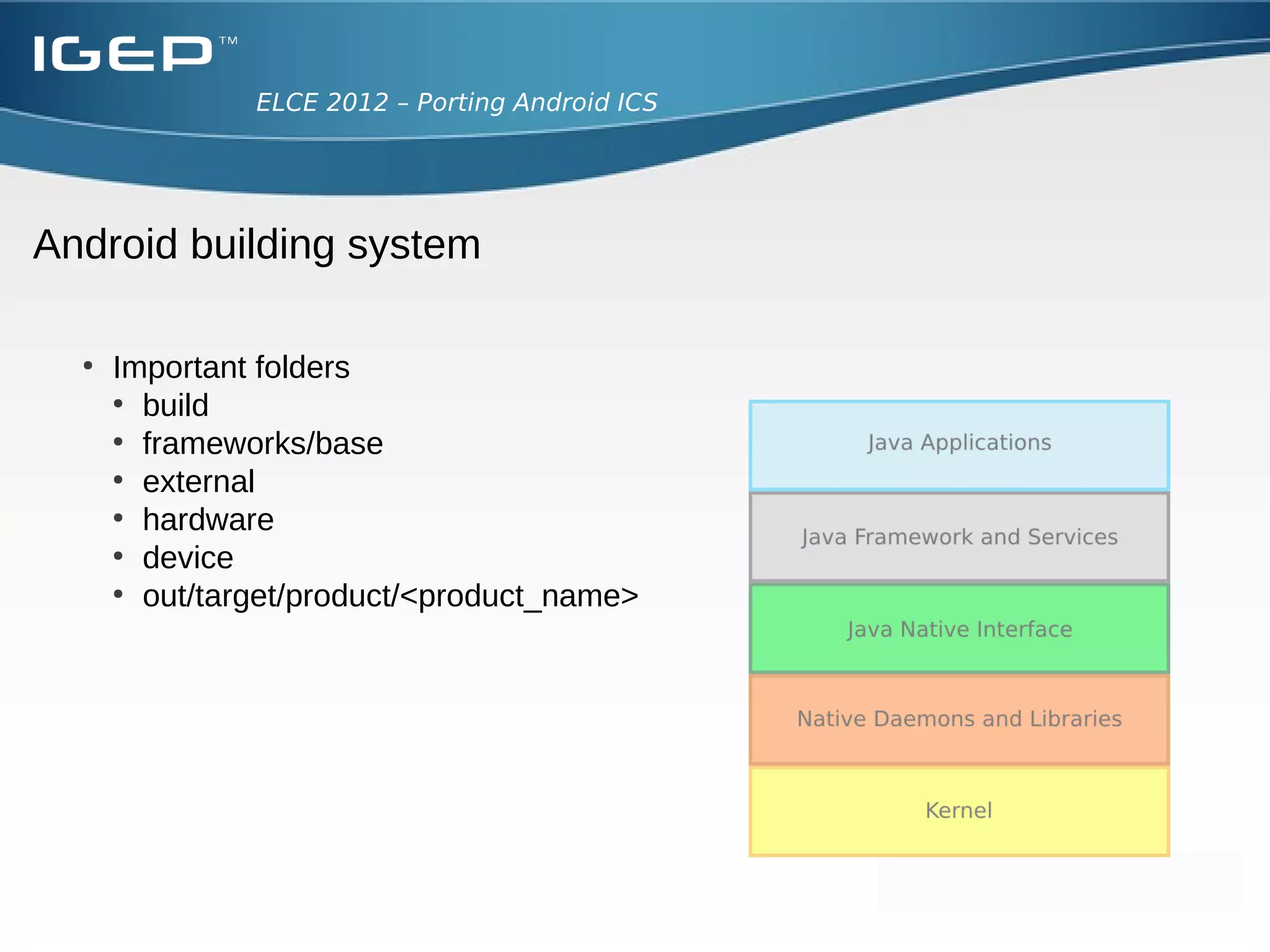
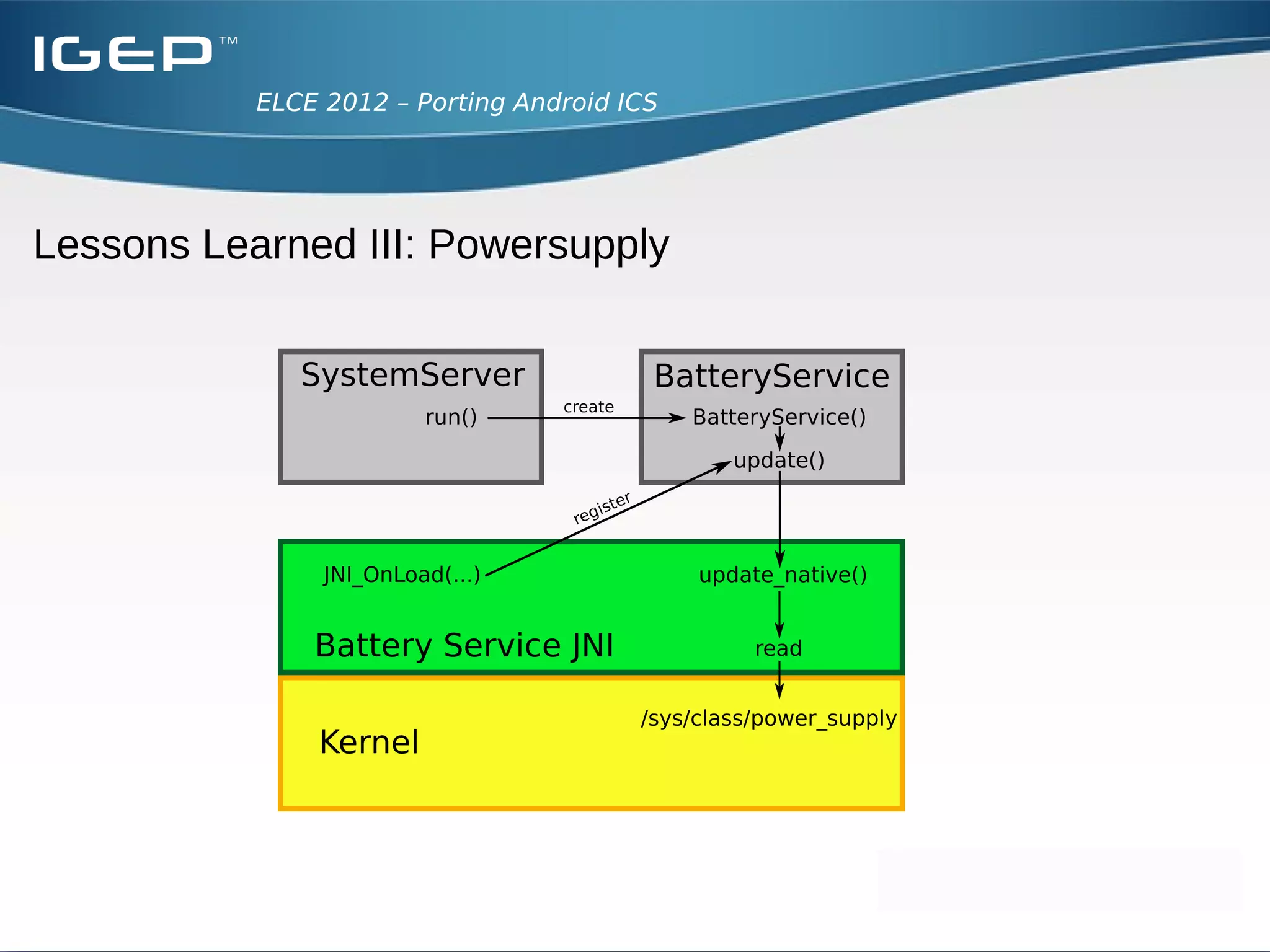
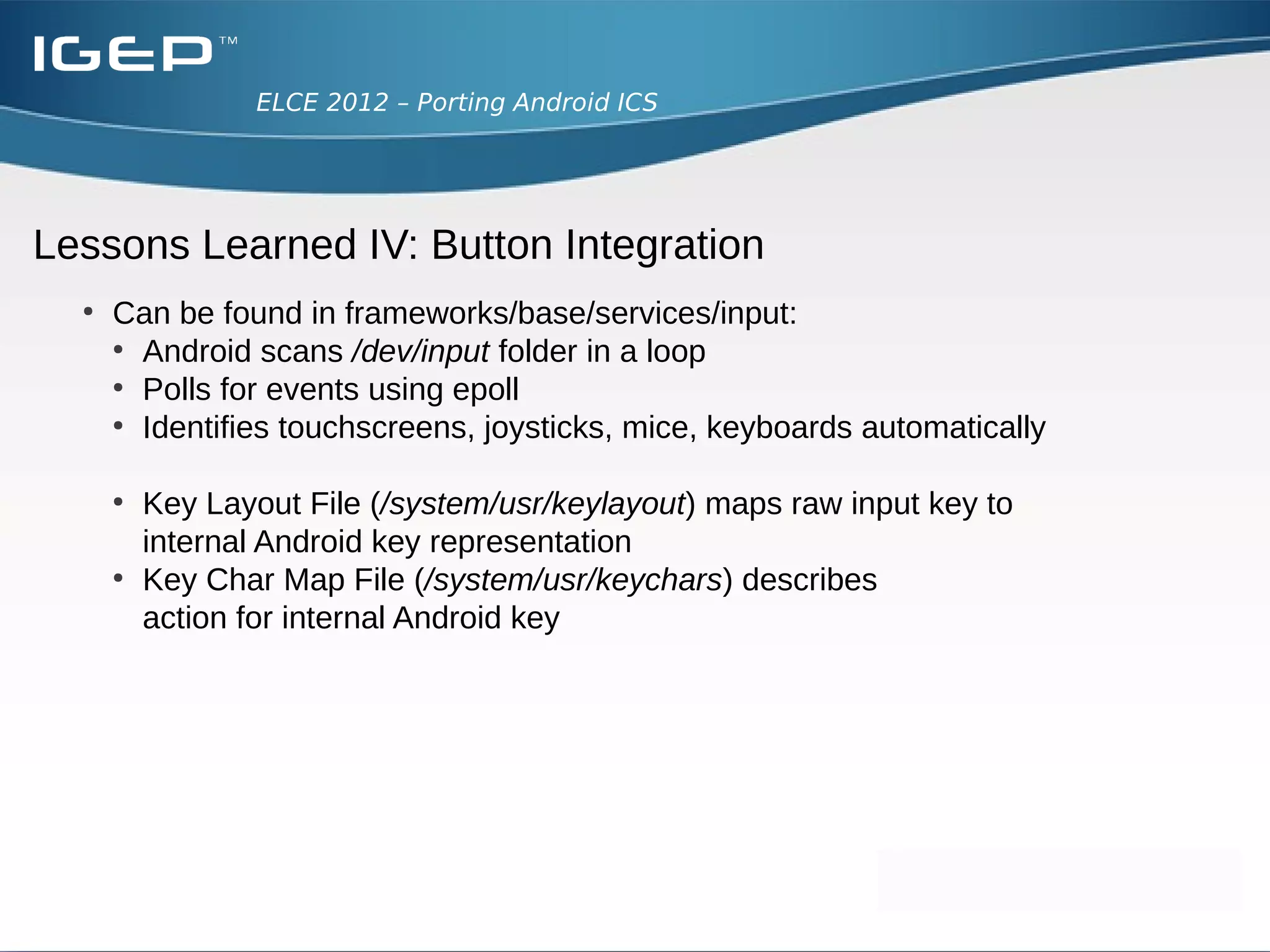
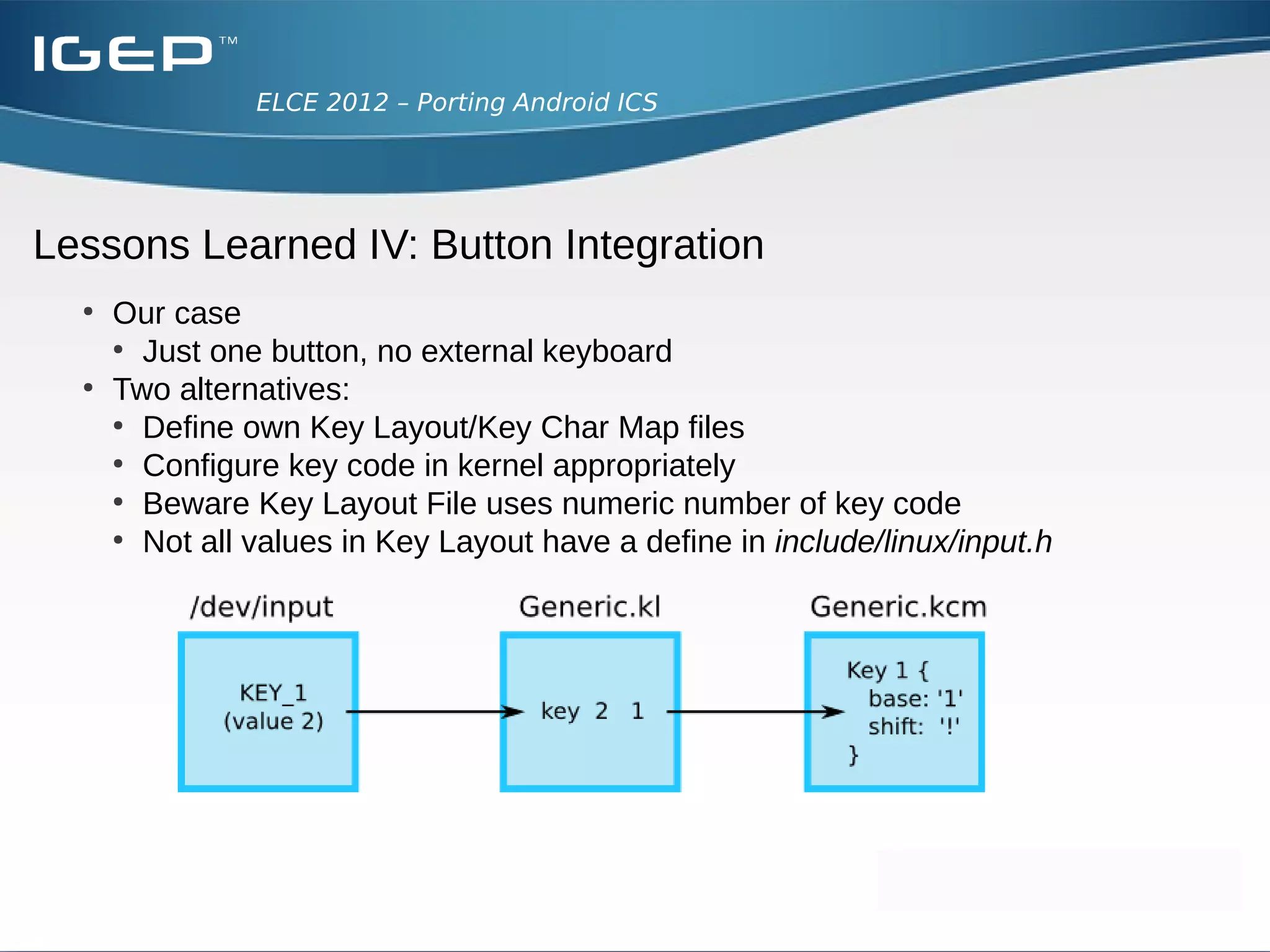
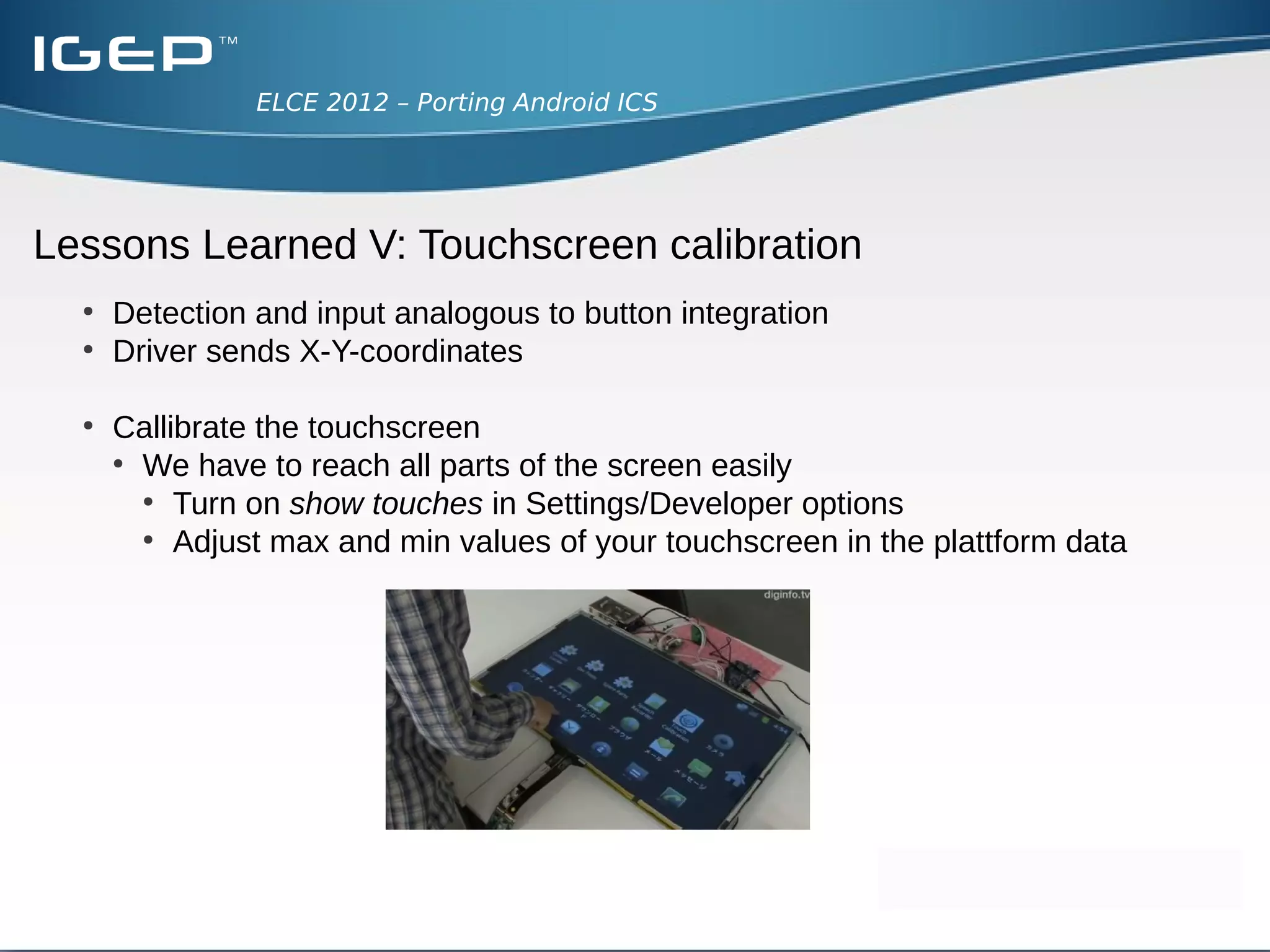
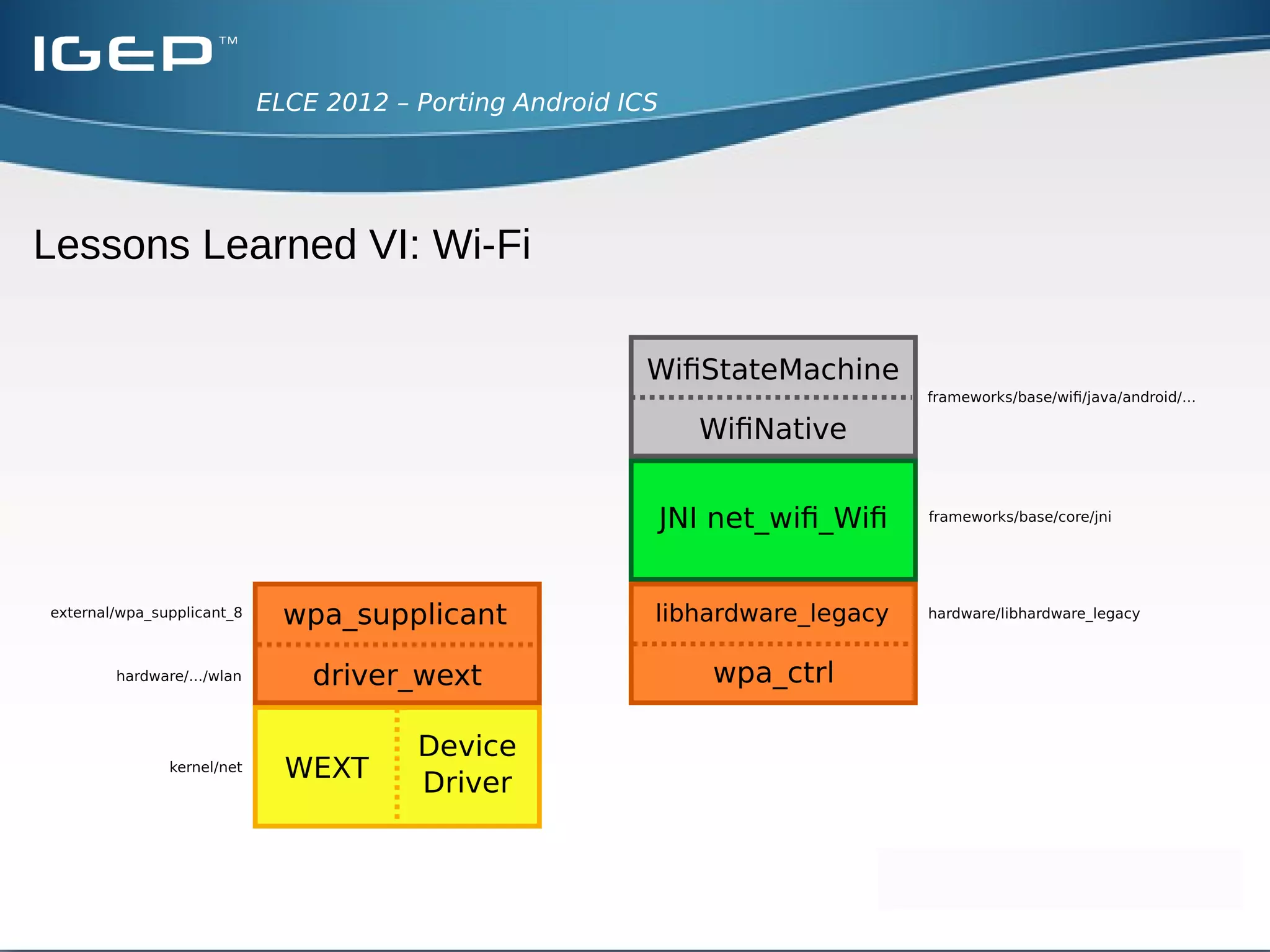
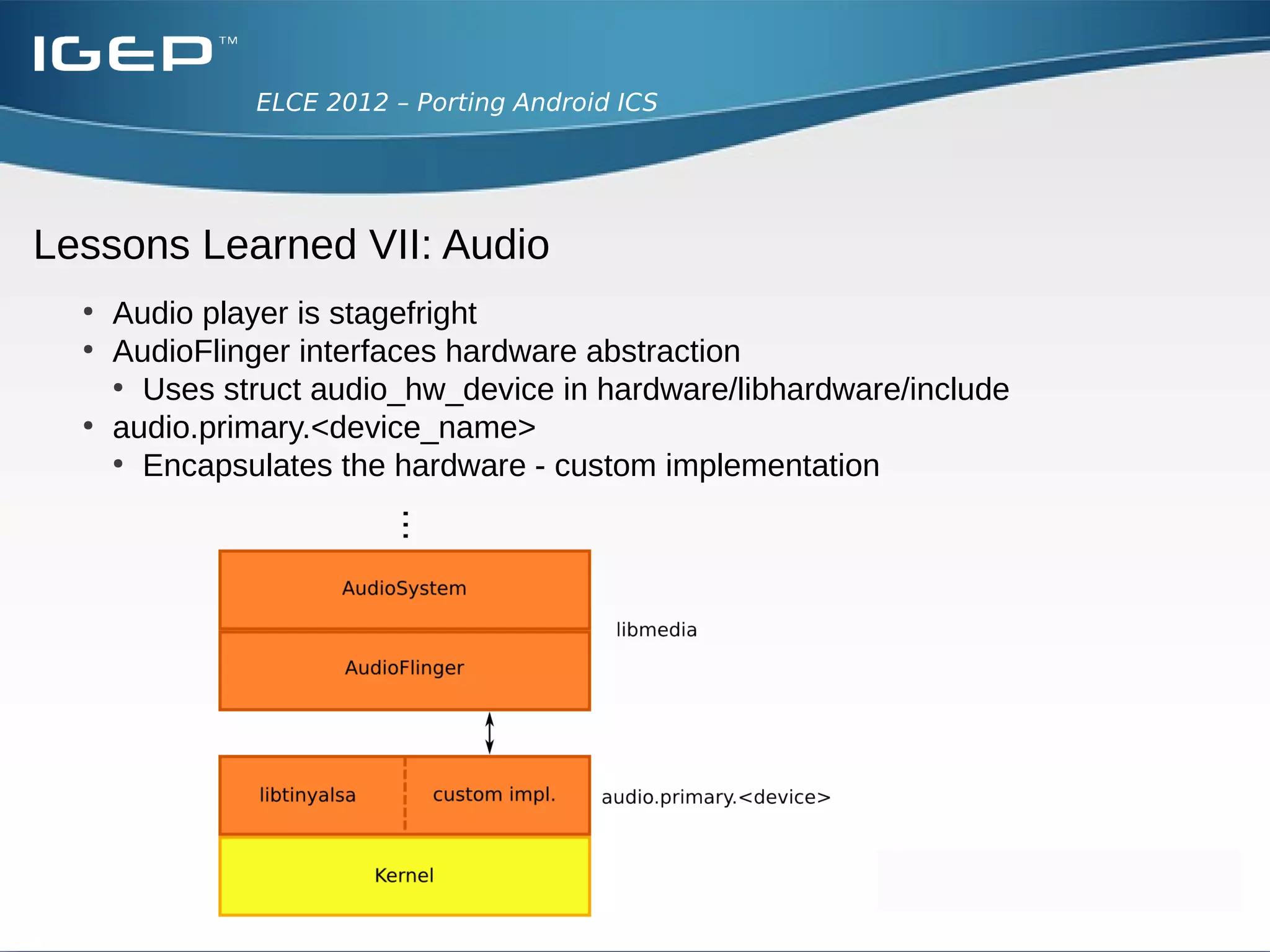
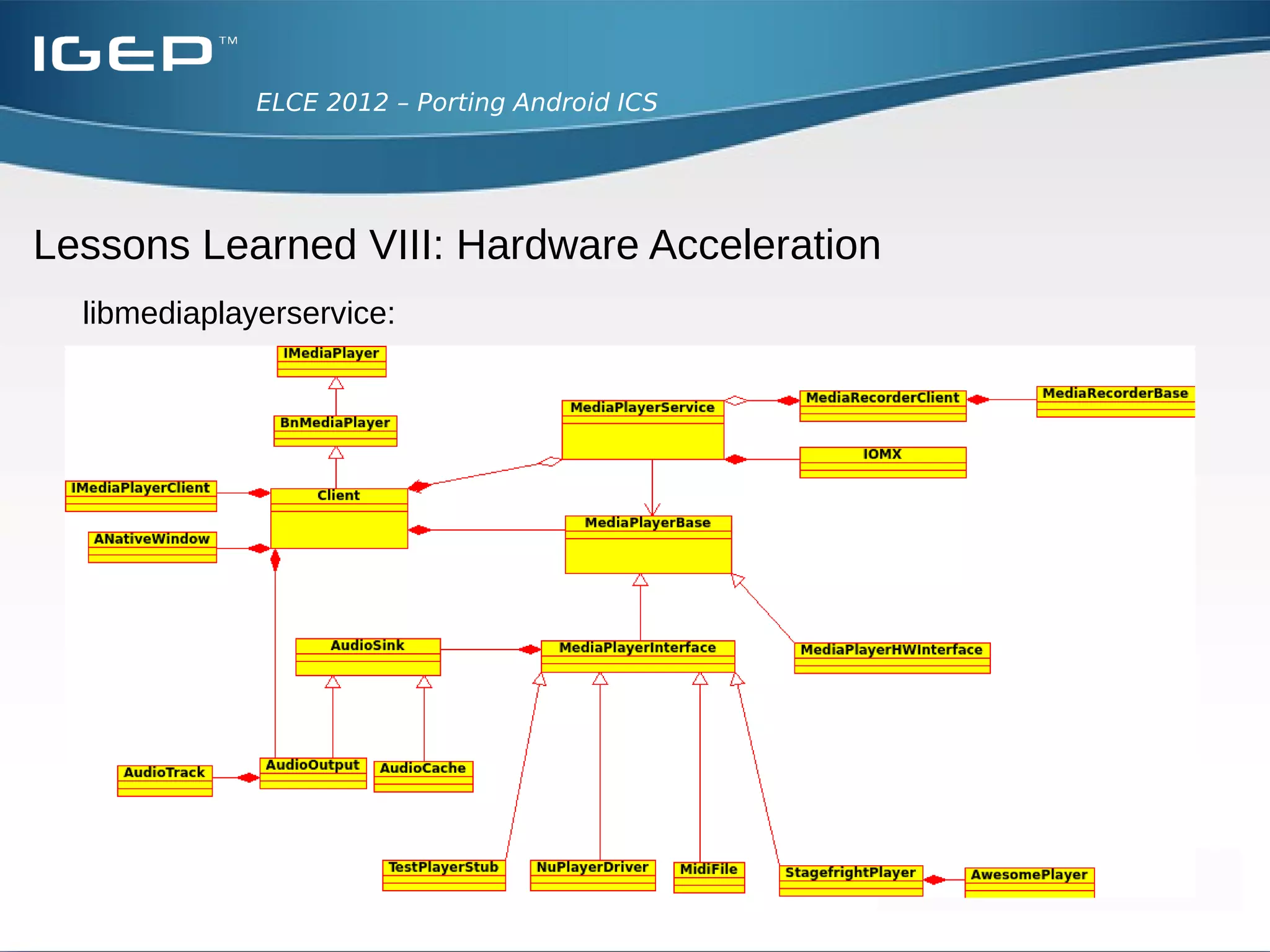
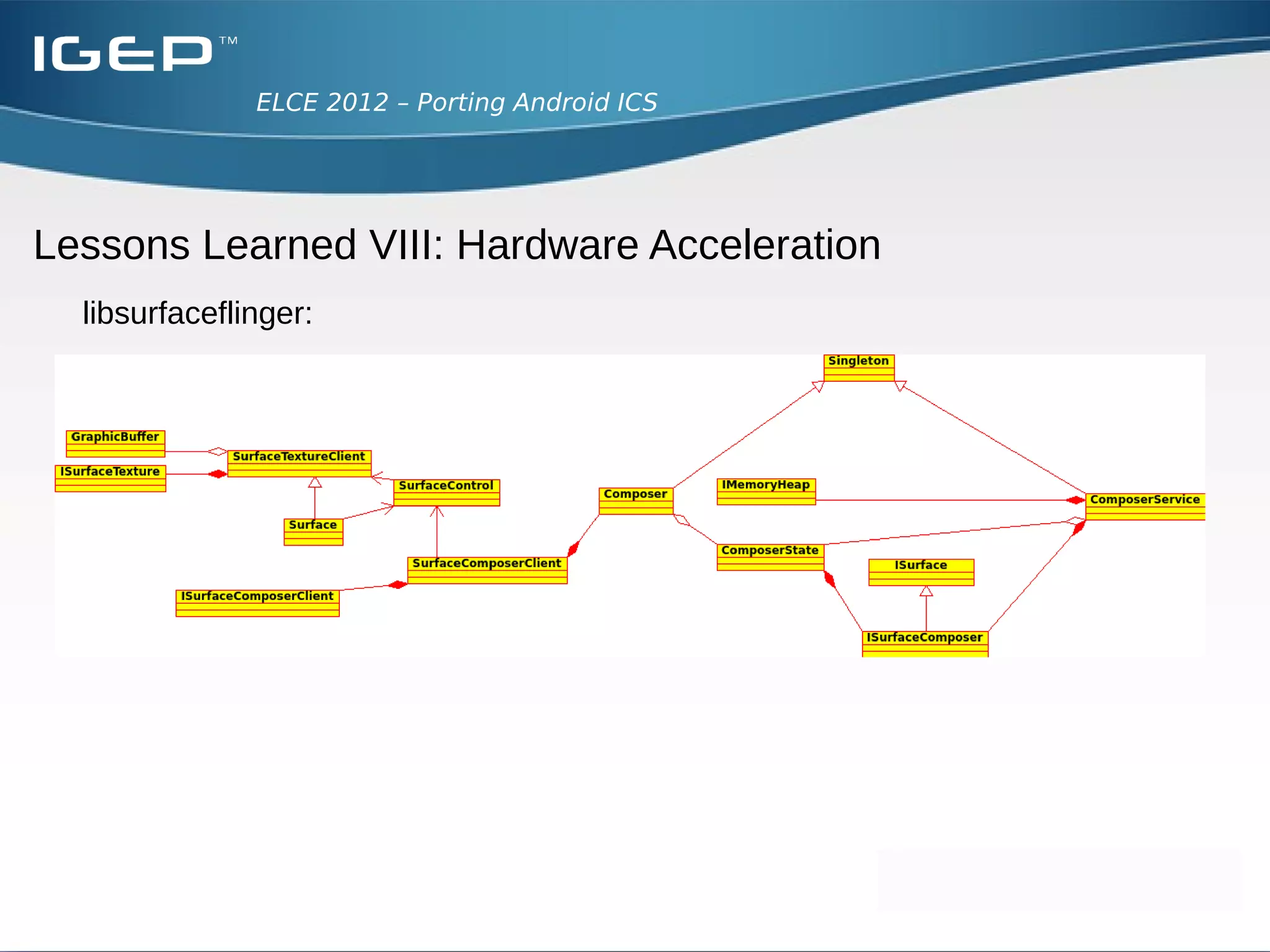
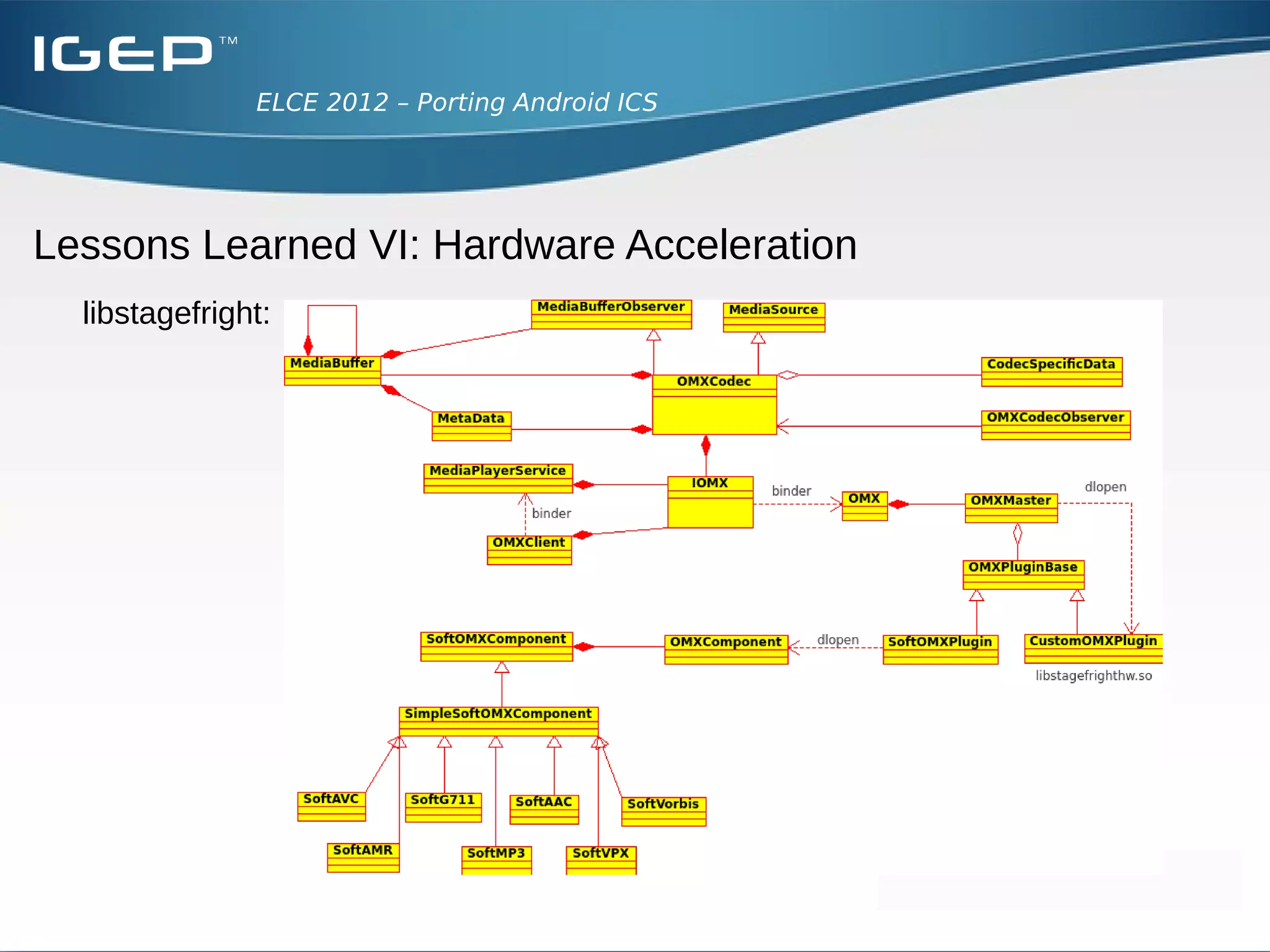
The document discusses the challenges of porting Android ICS to a custom board. It describes adding device-specific code, integrating the bootloader and kernel, addressing issues with battery monitoring and power supply detection, configuring button and touchscreen input, and integrating Wi-Fi. The author notes Android diverges from Linux in many areas, and porting requires addressing device drivers, firmware, and services across different parts of the Android source code.