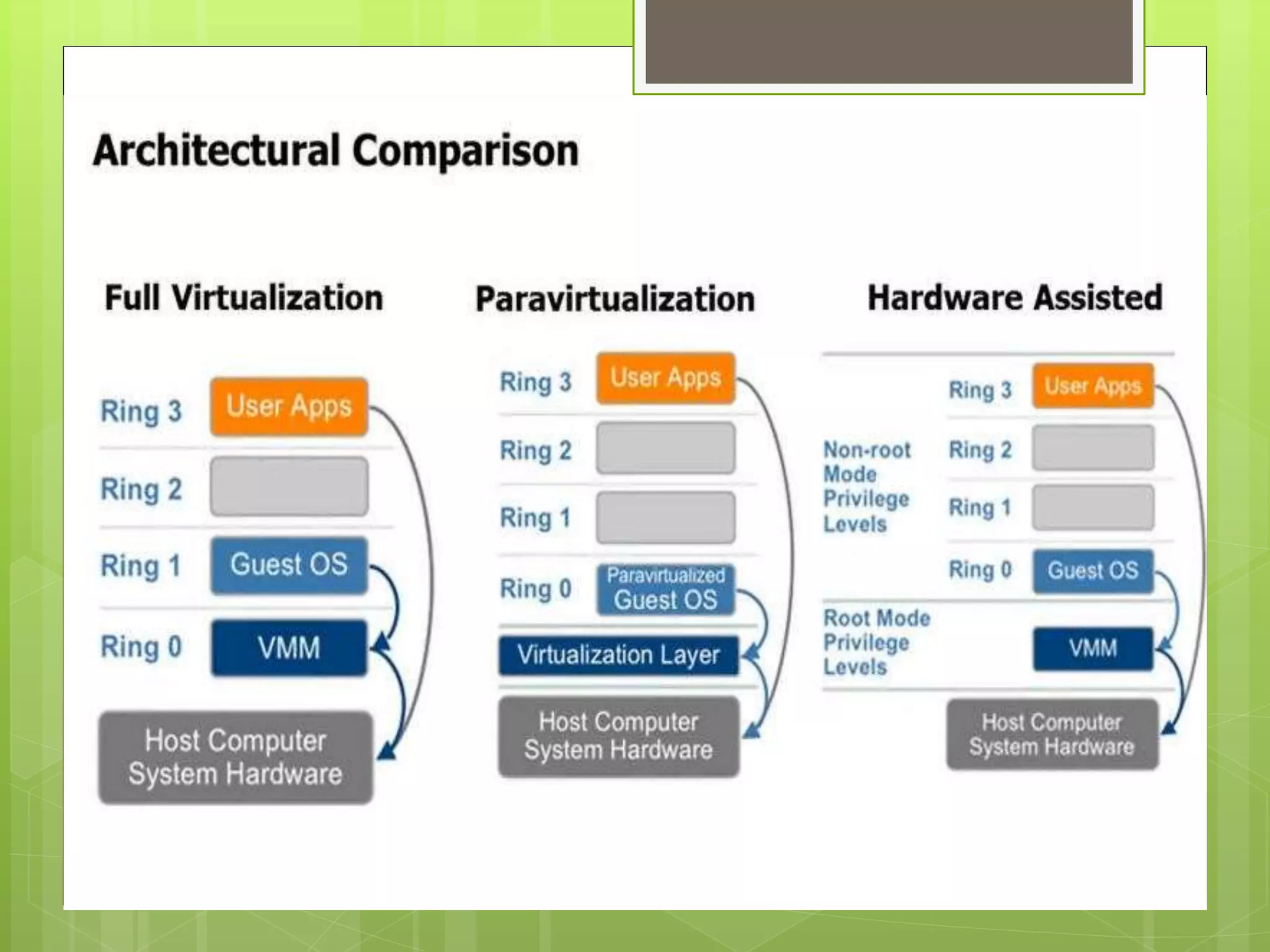
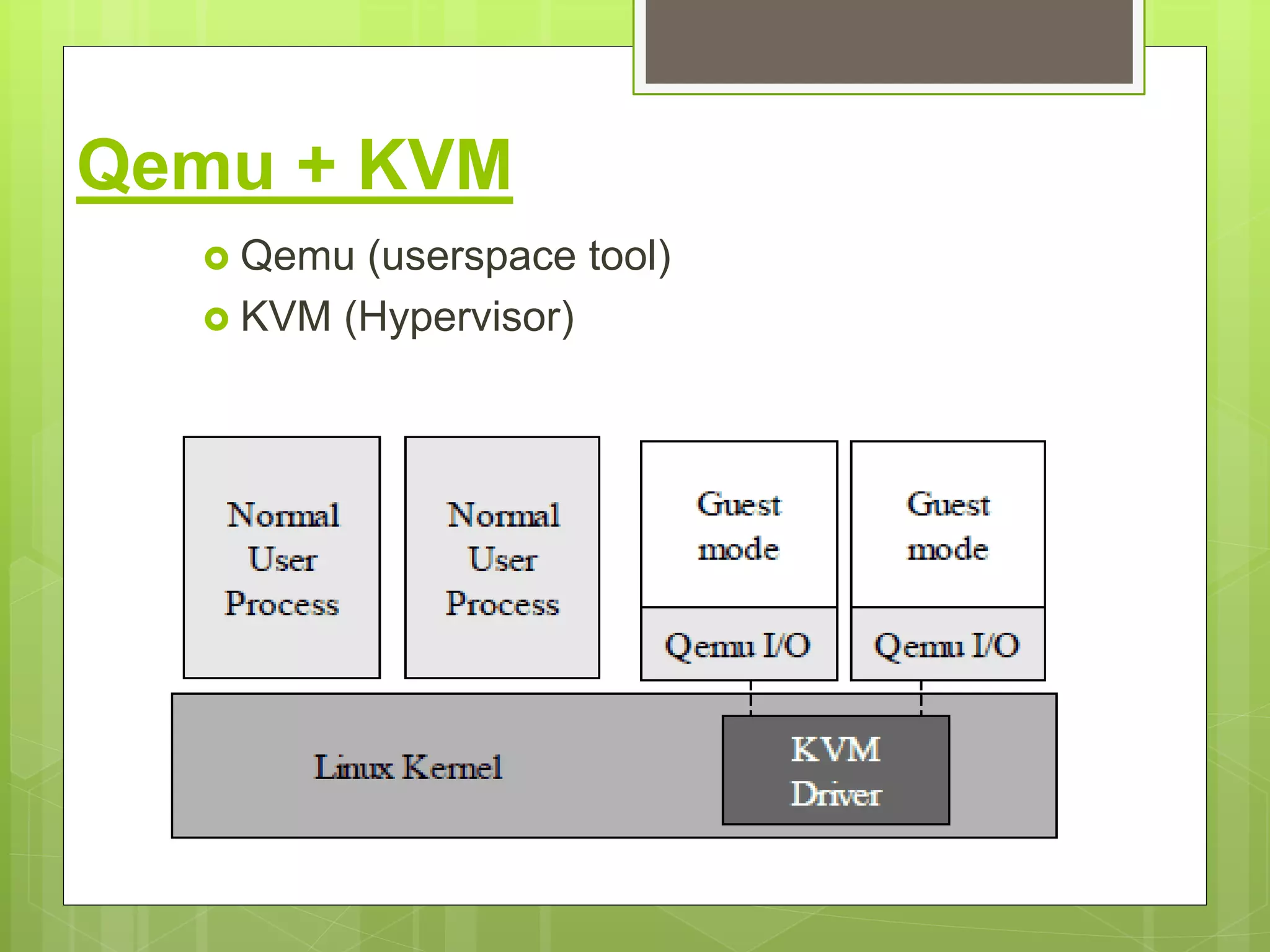
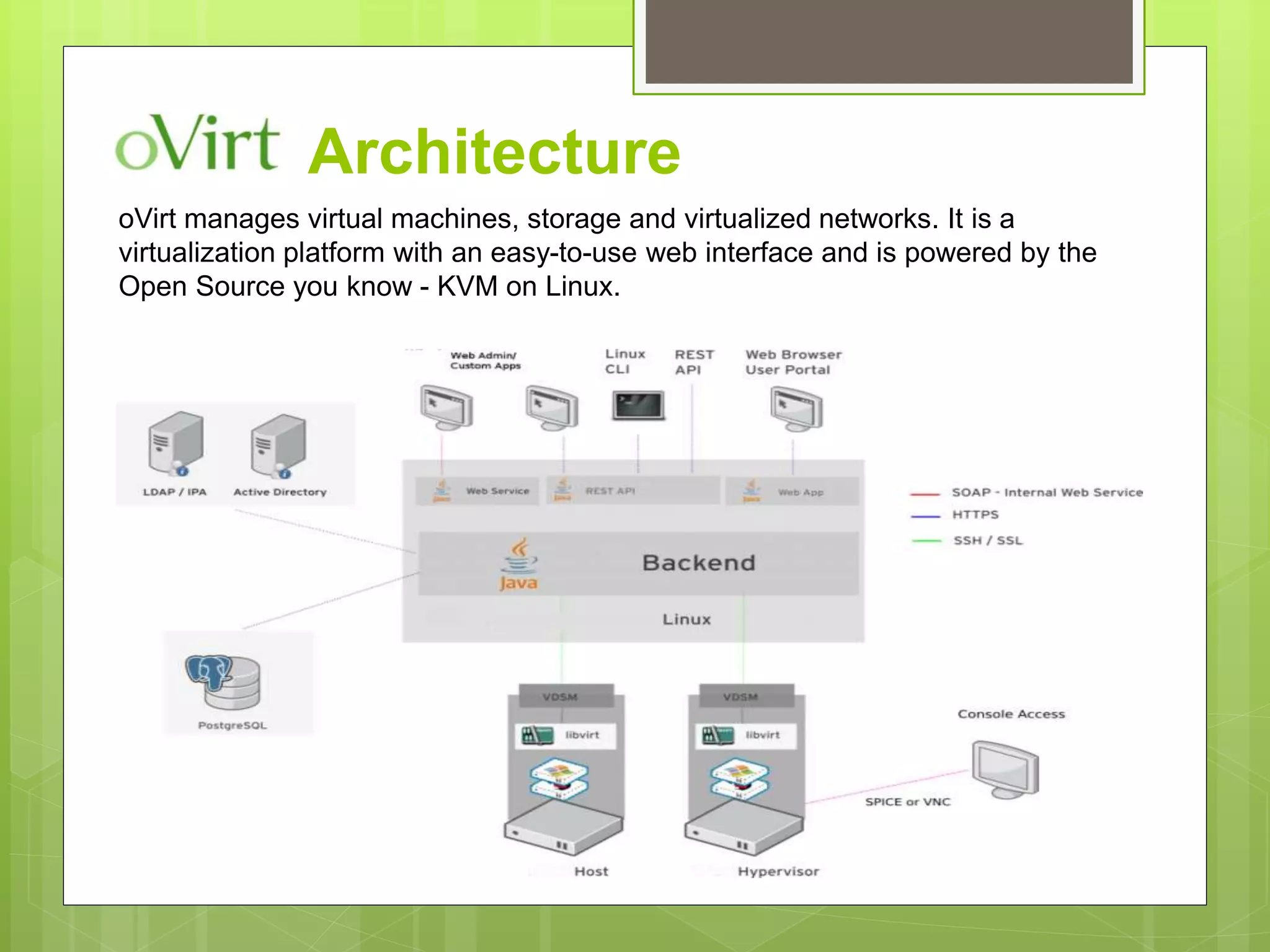
This document provides an overview of virtualization using KVM and oVirt. It discusses the architecture of KVM and Xen, how Qemu works with KVM, and the Libvirt architecture. It also covers installing KVM on CentOS, checking for hardware virtualization support, and installing required packages. Finally, it briefly introduces oVirt and provides some reference documentation links.