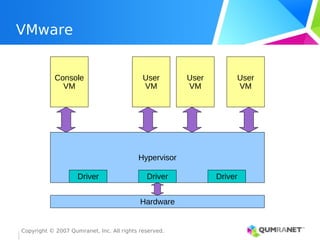
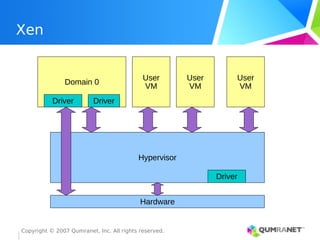
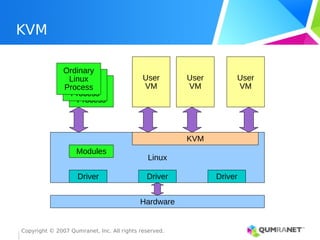
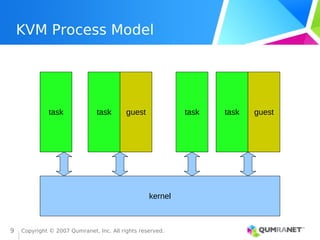
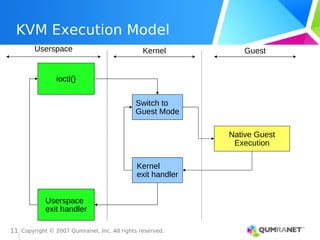
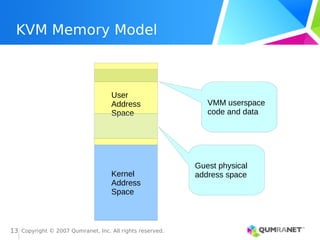
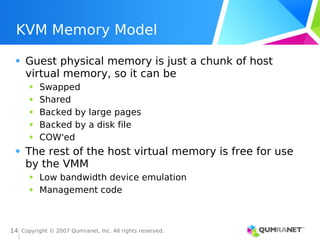
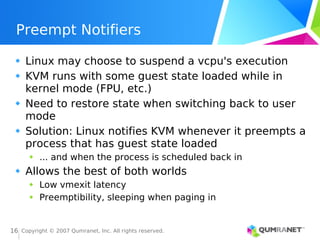
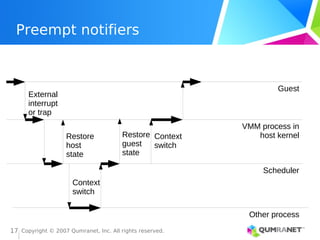
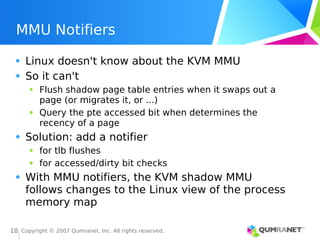
KVM, or Kernel-based Virtual Machine, is a Linux kernel module that enables the Linux operating system to function as a hypervisor, supporting various architectures and providing advanced memory management. It emphasizes integration with existing Linux infrastructure and features a unique execution model that allows for efficient virtual CPU scheduling. KVM's architecture facilitates competitive performance while also incorporating paravirtualization and power management features.