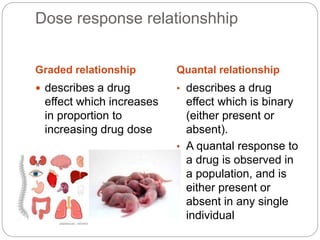
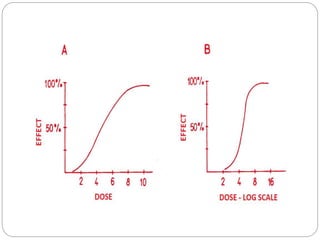
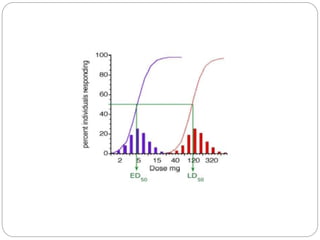
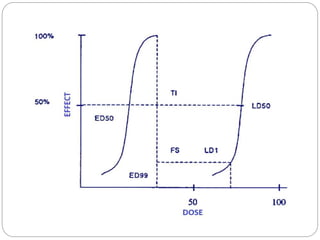
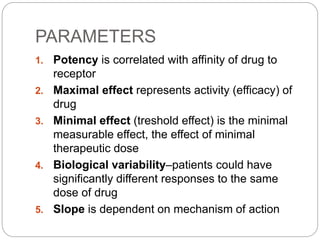
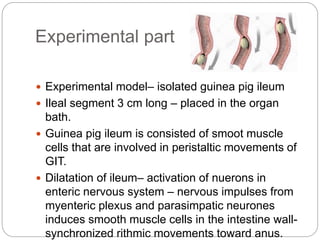
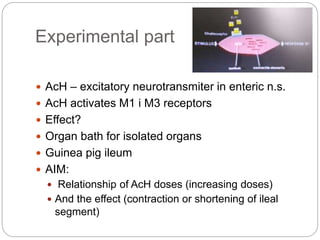
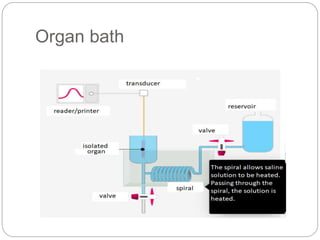
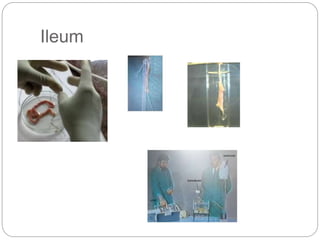
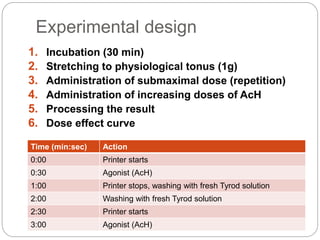
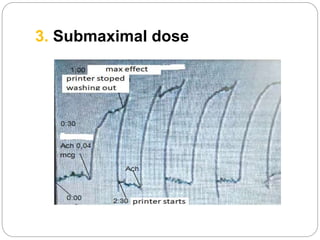
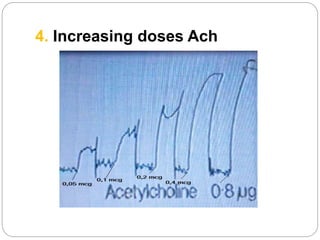
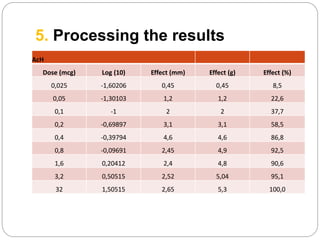
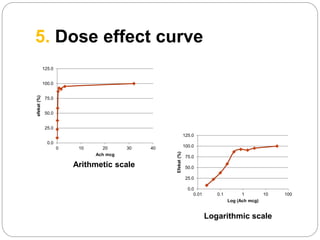
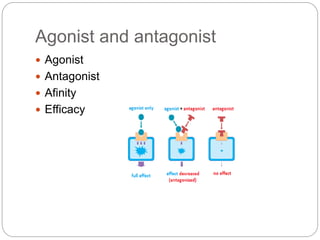
This document discusses dose-response relationships and key pharmacological concepts. It defines agonists and antagonists, and describes graded and quantal dose-response curves. Therapeutic index, safety factor, and therapeutic range are defined. Parameters that influence dose-response curves like potency, efficacy, and biological variability are covered. Different types of doses are outlined. The experimental method uses isolated guinea pig ileum to examine the dose-dependent contractions induced by acetylcholine. Results are processed to generate dose-response curves on both arithmetic and logarithmic scales.

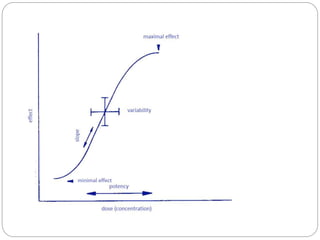
![Dose response relationship
Full description of drug effect in the function of dose
[E=f(D)]
Dose response line: dose is ploted on X-axe and the
effect is ploted on Y-axe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-240325130303-4ff57bff/85/Dose-response-relationship-ppt-pharmacology-3-320.jpg)