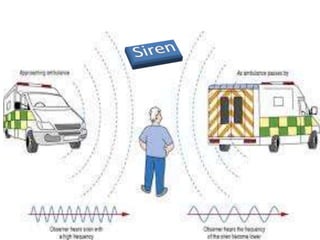
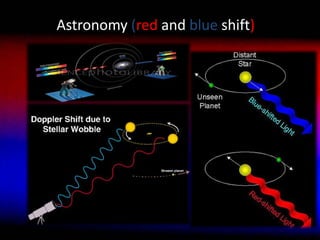
The document discusses Doppler's effect, which is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave for an observer moving relative to its source. It was first proposed by Austrian physicist Christian Doppler in 1842 and later tested and confirmed for sound waves. The key applications of Doppler's effect include satellite communication, astronomy through the observation of redshifts and blueshifts, and producing sonic booms. The effect may also have future uses in computer navigation.