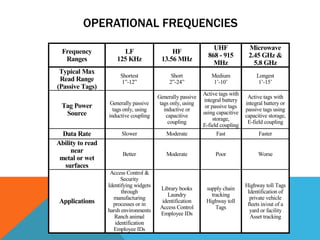
RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to identify objects wirelessly. It can identify, track, and categorize items tagged with RFID tags from a distance without needing direct line of sight. RFID tags come in both passive and active varieties. Passive tags have no power source and operate by harvesting power from reader signals, while active tags have an onboard power source. RFID readers wirelessly communicate with tags to read and sometimes write data to them. Common applications of RFID include tracking inventory, assets, livestock, and access control.