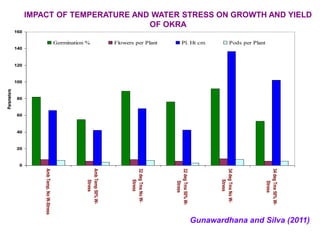
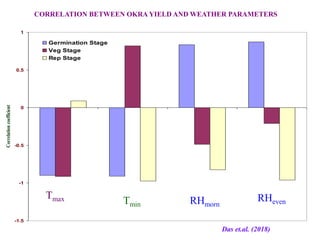
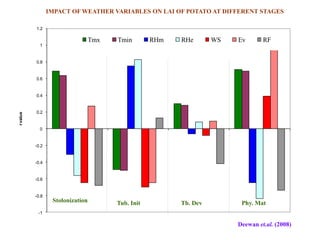
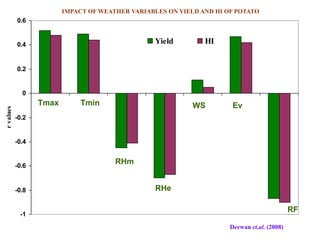
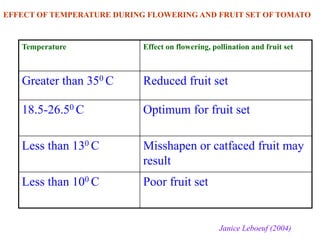
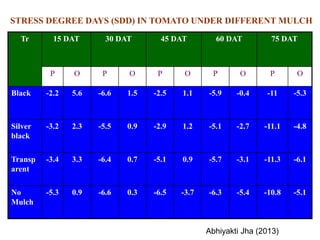
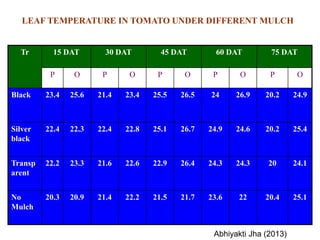
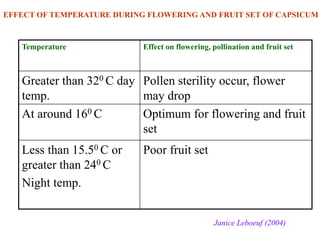
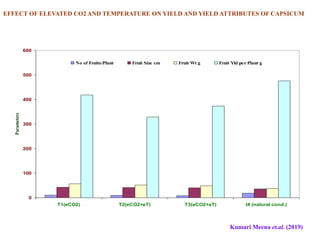
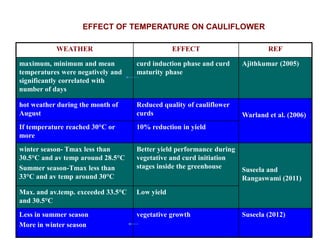
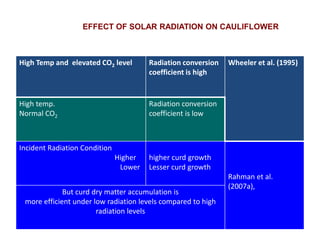
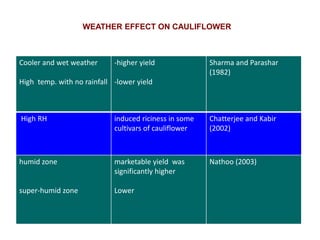
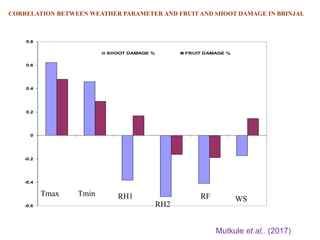
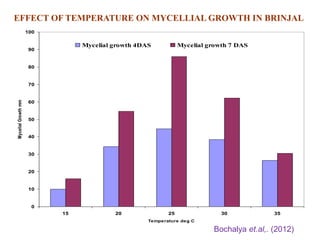
This document summarizes the impact of various weather parameters on vegetable cultivation based on the doctoral credit seminar of Abha Nutan Kujur. It discusses how climate variability and climate change can significantly impact crop production through changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events. Increased temperatures can negatively affect the growth, development, and quality of vegetables as well as increase pest and disease incidence. Other factors like light intensity, humidity, wind, solar radiation, and elevated carbon dioxide levels can physiological impact vegetables. The document reviews several studies showing effects of these parameters on specific vegetables like tomato, potato, capsicum, cauliflower, and okra.