Embed presentation
Download to read offline

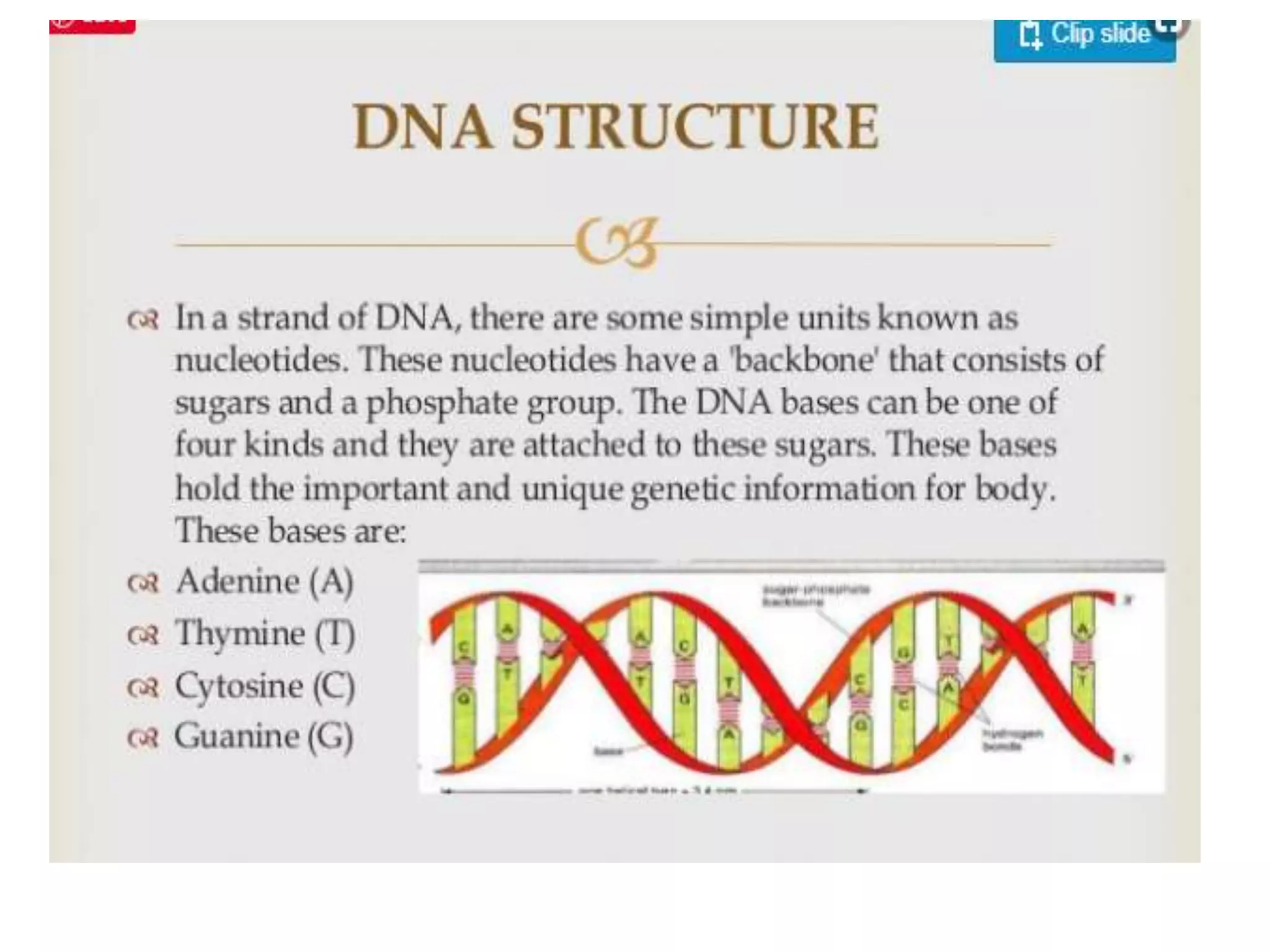









The document discusses DNA sequencing and cloning disease genes in the human genome. It describes two methods for cloning a disease gene: 1) cloning a gene of known function by first isolating and sequencing the associated protein to design a DNA probe to identify the gene in a cDNA library, with examples including phenylalanine hydroxylase for phenylketonuria. 2) positional cloning by mapping the disease locus to a chromosome region containing many DNA markers, then testing the markers for co-segregation with disease to narrow down the region containing the gene.










